
(a)
Find the residual stress at
(a)
Answer to Problem 89P
The residual stress is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The yield stress for the beam is
The Young’s modulus of steel is
Calculation:
Show the cross-section of the beam as shown in Figure 1.
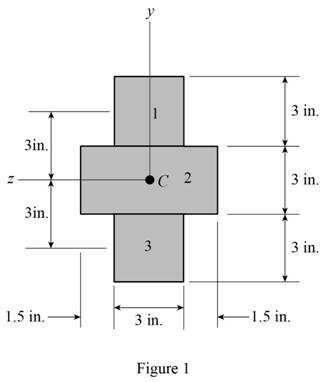
Refer Figure 1.
Refer to Figure 1.
Calculate the area of the cross section
Here, b is the width of the cross section and d is the depth of the cross section.
Calculate the area of the portion (1)
Substitute
Calculate the area of the portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the moment of inertia
Calculate the moment of inertia of portion (1)
Substitute
Hence,
Calculate the moment of inertia of portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the total moment of inertia
Substitute
Calculate the centroid (c) as shown below.
Substitute
Sketch the stress acting on the cross-section of the beam as shown in Figure 2.
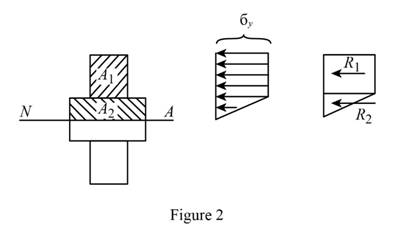
Refer Figure 1.
Calculate the area of the portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the reaction applied to portion (1)
Substitute
Calculate the reaction applied to portion (2)
Substitute
Calculate the moment
Substitute
Calculate the stress
Substitute
Calculate the stress
Substitute
Calculate the residual stress at
Substitute
Calculate the residual stress at
Substitute
Sketch the stress distribution as shown in Figure 3.
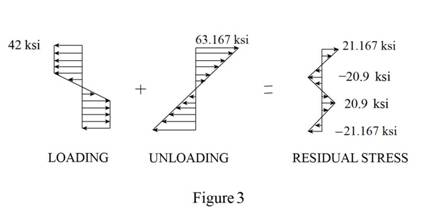
Hence, the residual stress is
(b)
Find the point where the residual stress is zero.
(b)
Answer to Problem 89P
The point where the residual stress is zero is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The yield stress for the beam is
The Young’s modulus of steel is
Calculation:
Consider that the residual stress
Calculate the yield stress
Calculate the point where the residual stress is zero as shown below.
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the point where the residual stress is zero is
(c)
Find the radius of curvature corresponding to the permanent deformation of the bar.
(c)
Answer to Problem 89P
The radius of curvature is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The yield stress for the beam is
The Young’s modulus of steel is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a).
The residual stress
Calculate the radius of curvature
Calculate the point where the residual stress is zero as shown below.
Substitute
Therefore, the radius of curvature is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
- using the theorem of three moments, find all the reactions and supportsarrow_forward(An ellipsoidal trapping region for the Lorenz equations) Show that there is a certain ellipsoidal region E of the form rx2 + σy2 + σ(z − 2r)2 ≤ C such that all trajectories of the Lorenz equations eventually enter E and stay in there forever. For a much stiffer challenge, try to obtain the smallest possible value of C with this property.arrow_forwardA) In a factory, an s-type pitot tube was used to calculate the velocity of dry air for a point inside a stack. Calculate the velocity at that point (ft/sec) using following conditions: ● • • Pressure = 30.23 ± 0.01 in Hg (ambient) Pitot tube coefficient = 0.847 ± 0.03 Temperature = 122 ± 0.1 F (stack) Temperature = 71.2 ± 0.1 F (ambient) AP = 0.324 ± 0.008 in H2O (pitot tube) • AP = 0.891 ± 0.002 in H2O (stack) B) Find the dominant error(s) when determining precision for the problem. C) For part A, what is the precision in ft/sec for the velocity?arrow_forward
- Q1/ For what value of x do the power series converge: 8 (-1)n-1. x2n-1 2n-1 x3 x5 = X n=1 3 Q2/ Find the Interval of convergence and Radius of convergence of the series: 8 n Σ 3+1 n=1 (x)"arrow_forwardExample-1: l D A uniform rotor of length 0.6 m and diameter 0.4 m is made of steel (density 7810 kg/m³) is supported by identical short bearings of stiffness 1 MN/m in the horizontal and vertical directions. If the distance between the bearings is 0.7 m, determine the natural frequencies and plot whirl speed map. Solution: Barrow_forwardfind the laplace transform for the flowing function 2(1-e) Ans. F(s)=- S 12) k 0 Ans. F(s)= k s(1+e) 0 a 2a 3a 4a 13) 2+ Ans. F(s)= 1 s(1+e") 3 14) f(t)=1, 0arrow_forwardFind the solution of the following Differential Equations Using Laplace Transforms 1) 4y+2y=0. y(0)=2. y'(0)=0. 2) y+w²y=0, (0)=A, y'(0)=B. 3) +2y-8y 0. y(0)=1. y'(0)-8. 4)-2-3y=0, y(0)=1. y'(0)=7. 5) y-ky'=0, y(0)=2, y'(0)=k. 6) y+ky'-2k²y=0, y(0)=2, y'(0) = 2k. 7) '+4y=0, y(0)=2.8 8) y+y=17 sin(21), y(0)=-1. 9) y-y-6y=0, y(0)=6, y'(0)=13. 10) y=0. y(0)=4, y' (0)=0. 11) -4y+4y-0, y(0)=2.1. y'(0)=3.9 12) y+2y'+2y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-3. 13) +7y+12y=21e". y(0)=3.5. y'(0)=-10. 14) "+9y=10e". y(0)=0, y'(0)=0. 15) +3y+2.25y=91' +64. y(0)=1. y'(0) = 31.5 16) -6y+5y-29 cos(2t). y(0)=3.2, y'(0)=6.2 17) y+2y+2y=0, y(0)=0. y'(0)=1. 18) y+2y+17y=0, y(0)=0. y'(0)=12. 19) y"-4y+5y=0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=2. 20) 9y-6y+y=0, (0)-3, y'(0)=1. 21) -2y+10y=0, y(0)=3, y'(0)=3. 22) 4y-4y+37y=0, y(0)=3. y'(0)=1.5 23) 4y-8y+5y=0, y(0)=0, y'(0)=1. 24) ++1.25y-0, y(0)=1, y'(0)=-0.5 25) y 2 cos(r). y(0)=2. y'(0) = 0. 26) -4y+3y-0, y(0)=3, y(0) 7. 27) y+2y+y=e y(0)=0. y'(0)=0. 28) y+2y-3y=10sinh(27), y(0)=0. y'(0)=4. 29)…arrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardThe 120 kg wheel has a radius of gyration of 0.7 m. A force P with a magnitude of 50 N is applied at the edge of the wheel as seen in the diagram. The coefficient of static friction is 0.3, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. Find the acceleration and angular acceleration of the wheel.arrow_forwardAuto Controls Using MATLAB , find the magnitude and phase plot of the compensators NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forward4-81 The corner shown in Figure P4-81 is initially uniform at 300°C and then suddenly exposed to a convection environment at 50°C with h 60 W/m². °C. Assume the = 2 solid has the properties of fireclay brick. Examine nodes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 and deter- mine the maximum time increment which may be used for a transient numerical calculation. Figure P4-81 1 2 3 4 1 cm 5 6 1 cm 2 cm h, T + 2 cmarrow_forwardAuto Controls A union feedback control system has the following open loop transfer function where k>0 is a variable proportional gain i. for K = 1 , derive the exact magnitude and phase expressions of G(jw). ii) for K = 1 , identify the gaincross-over frequency (Wgc) [where IG(jo))| 1] and phase cross-overfrequency [where <G(jw) = - 180]. You can use MATLAB command "margin" to obtain there quantities. iii) Calculate gain margin (in dB) and phase margin (in degrees) ·State whether the closed-loop is stable for K = 1 and briefly justify your answer based on the margin . (Gain marginPhase margin) iv. what happens to the gain margin and Phase margin when you increase the value of K?you You can use for loop in MATLAB to check that.Helpful matlab commands : if, bode, margin, rlocus NO COPIED SOLUTIONSarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





