
Label the parts of the following diagrams, indicating which parts represent a water-soluble hormone and which a lipid-soluble hormone.
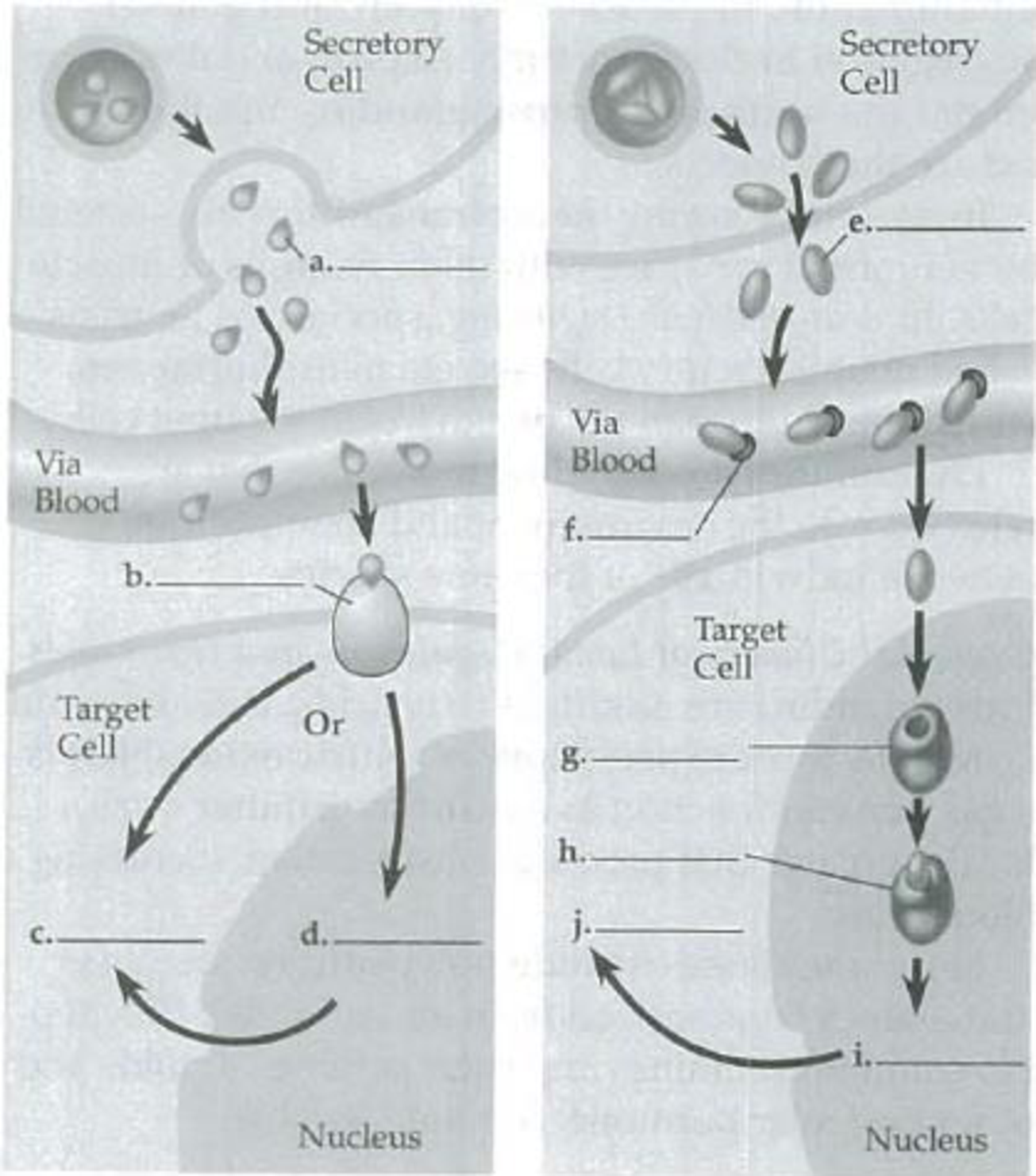
To label: The parts of the given diagram by indicating the parts that represent a water-soluble hormone and a lipid-soluble hormone.
Introduction: Hormones are small molecules that act as chemical messengers in the body. They regulate the body processes by binding to their specific receptors. For lipid-soluble hormones, the receptors are intracellular and for water-soluble hormones, the receptors are present on cell surface.
Answer to Problem 1IQ
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 represents the pathway of a water-soluble hormone and a lipid-soluble hormone.
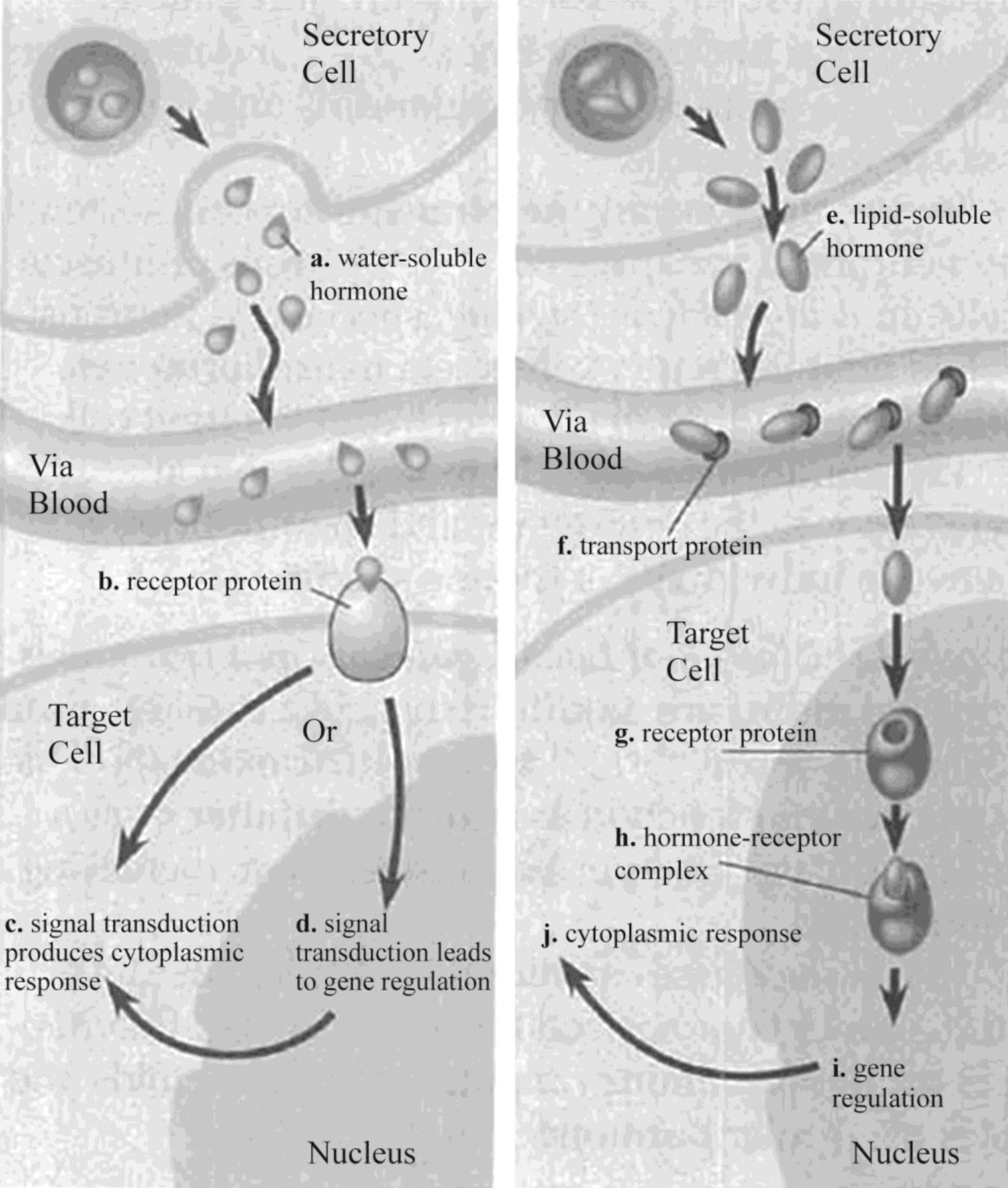
Fig. 1: Pathway of a water-soluble hormone and a lipid-soluble hormone
Explanation of Solution
Water-soluble hormones bind to cell surface receptors of their target cells, which stimulate gene expression and cause cytoplasmic changes. They cannot travel inside the cells through the plasma membrane because of its insoluble nature in the lipid. Transfer of the extracellular chemical signal to intracellular response is termed as signal transduction. Peptide hormones act through signal transduction pathways. Once water-soluble hormones bind to their receptors, they activate transfer of cytoplasmic protein to the nucleus, leading to alteration in gene expression.
Lipid-soluble hormones cross the barrier of the plasma membrane and interact with receptors, which are present in the cytoplasm or nucleus. It results in the formation of the hormone–receptor complex. The hormone receptors that bind to lipid-soluble hormone in their circulation are called as lipid-soluble hormone receptors. They are usually present in the cytoplasm or nucleus. The hormone–receptor complex is formed to initiate transcription by interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 45 Solutions
Study Guide for Campbell Biology
- Noggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- please helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forwardBiology grade 10 study guidearrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





