
To discuss:
The inflammatory response and the part it plays in the generation of pain.
Concept Introduction:
Inflammation is the localized process initiated due to the injury or infection in the tissues. Tissue cells produce inflammatory cytokines such as (leukotrienes, bradykinin, histamine, and so on) that lead to the migration of macrophage immune cells to the injured tissue site and cause phagocytosis, which is an inflammatory-mediated response. Inflammation has a series of pathways involved. The common symptoms found in inflammation are pain and swelling.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
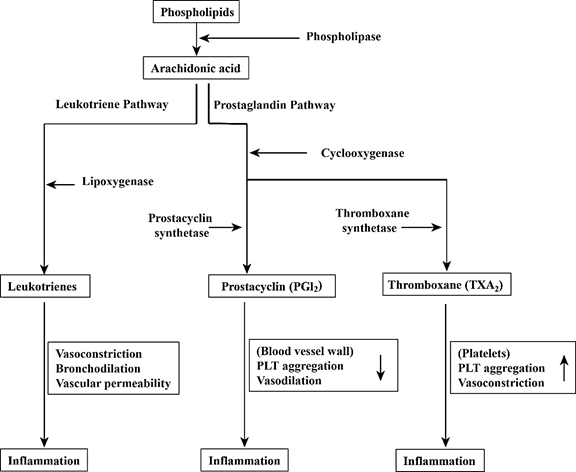
Figure: Inflammatory pathways
The first and foremost step in the inflammation is triggering the inflammatory pathway mediated by the endogenous compounds present inside the host such as histamine, leukotrienes, prostaglandins, serotonin, and histamines. These endogenous compounds are collectively called as inflammatory compounds. There are two different modes of inflammatory pathways. One is leukotriene pathway and the other is prostaglandin pathway.
The common precursor phospholipid in the cell membrane is transformed to arachidonic acid mediated by phospholipase enzyme as a trigger during tissue injury. Phospholipase is an important inflammatory mediatory enzyme. Arachidonic acid enters the inflammatory pathway either by leukotriene or prostaglandin pathway.
Leukotriene pathway:
Leukotrienes are the eicosanoid mediated inflammatory agents. Arachidonic acid is
Prostaglandin pathway:
In this pathway, arachidonic acid is converted into prostaglandins like prostacyclin (PGl2), and thromboxane (TXA2), by the cyclooxygenase enzyme. These prostaglandins, in turn, mediate the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as histamines, and bradykinin, which induces the pain and edema. The occurrence of fever during inflammation is mediated by Prostaglandin E2 synthesized in the hypothalamus region. Prostaglandin-mediated inflammatory pathway brings vasoconstriction, vasodilation, and platelet aggregation in the host.
The inflammatory response is a body natural defense mechanism by which the tissue injury caused by endogenous substances such as pathogens, inflammatory agents are eliminated by the phagocytes. Macrophage cells migrate toward the inflammation site and execute the phagocytosis process. Vasoconstriction, vasodilation, and platelet aggregation during inflammatory pathways cause pain and edema at the inflammatory site.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 44 Solutions
Pharmacology and the Nursing Process, 8e
- true or false dark skinned infants should be screened for vitamin D levelsarrow_forwardtrue or false any practice employee is authorized to and should communicate collection guidelines with practice?arrow_forwardrtrue or false equesting a listing of specific creditreferences during patient intake os an acceptable business practice?arrow_forward
- give an overview on the respiratory assessmentarrow_forwardexplain an abdominal exam?arrow_forwardDiscuss β -Lactam antibiotics under the following subheadings Classifications of penicillins Classification of Cephalosporins General Mechanism of Actions Clinical Indications of penicillins and cephalosporins Adverse effects of β-lactamsarrow_forward
- a. Define neoplasm b. Differentiate between benign and malignant tumours c. Describe the molecular basis of cancerarrow_forwarddifferentiate the extra heart sounds S3,S4, murmurs and gallopsarrow_forward• Define shock and list types of shock • Discuss pathogenesis of septic shock. • Enumerate the stages of shock. • Define oedema and describe the pathophysiologic mechanisms of oedema with examples.arrow_forward
- Discuss Hypertension under the following headings: Definition Diagnosis Non-pharmacological intervention Drugs Classification Management of a Hypertensive emergencyarrow_forwardExplain how the answer could be 2 or 1.8 WITHOUT changing the questionarrow_forwardoverview of the neurological system, cranial nerves and what part of the body it innervatesarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





