
(a)
To test: Whether the area under the curve is 1 or not.
(a)
Answer to Problem 60E
Solution: Yes, the area under the curve is 1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: The area of a triangle is,
The height is 1 and the base is equal to 2. Thus, the area can be calculated as:
Hence, the area is 1. The provided curve is shown below:
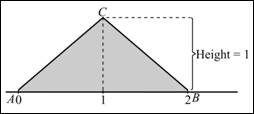
(b)
Section 1:
To find: The
(b)
Section 1:
Answer to Problem 60E
Solution: The probability is 0.5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: First, obtain the area in the interval of
In the graph, the total area is 1 and the dotted area which is also called the density of the curve. Thus, the area of
Now, the probability of Y is less than 1 can be calculated as:
Hence, the probability is 0.5.
Section 2:
To graph: The density curve and shade the area which represents the probability.
Section 2:
Explanation of Solution
Graph: In the provided triangle, draw a vertical line at 1. Construct a triangle on the left end of the triangle and shade the left area. Hence, the density curve is shown below:
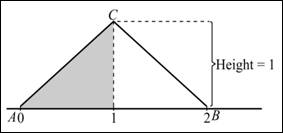
Section 3:
To find: The area.
Section 3:
Answer to Problem 60E
Solution: The area is 0.5.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: From the provided triangle, base is equal to 1 and height is equal to 1. Thus, the area can be calculated as:
Hence, the area is 0.5.
(c)
Section 1:
To find: The probability
(c)
Section 1:
Answer to Problem 60E
Solution: The probability is 0.875.
Explanation of Solution
First, obtain the area in the interval of
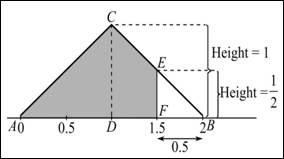
base is equal to 0.5 and height is equal to 0.5. Thus, the area can be calculated by the formula:
The area of
Now, the probability of Y is greater than 1.5 can be calculated as:
Hence, the probability is 0.875.
Section 2:
To graph: The density curve and shade the area which represents the probability.
Section 2:
Explanation of Solution
Graph: In the provided triangle, draw a vertical line at 1.5. Construct a triangle on the right end of the triangle and shade the left area. Hence, the density curve is shown below:
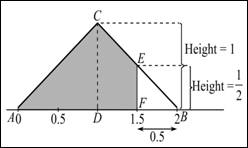
Section 3:
To find: The area.
Section 3:
Answer to Problem 60E
Solution: The area is 0.125.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: From the provided triangle, base is equal to 0.5 and height is equal to 0.5. Thus, the area can be calculated as:
Hence, the area is 0.125.
(d)
To find: The probability
(d)
Answer to Problem 60E
Solution: The probability is 0.875.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation: First, obtain the area in the interval of
The area of
Now, the probability of Y is greater than 0.5 can be calculated as:
Hence, the probability is 0.875.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTION TO THE PRACTICE OF STA
- Should you be confident in applying your regression equation to estimate the heart rate of a python at 35°C? Why or why not?arrow_forwardGiven your fitted regression line, what would be the residual for snake #5 (10 C)?arrow_forwardCalculate the 95% confidence interval around your estimate of r using Fisher’s z-transformation. In your final answer, make sure to back-transform to the original units.arrow_forward
- BUSINESS DISCUSSarrow_forwardA researcher wishes to estimate, with 90% confidence, the population proportion of adults who support labeling legislation for genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Her estimate must be accurate within 4% of the true proportion. (a) No preliminary estimate is available. Find the minimum sample size needed. (b) Find the minimum sample size needed, using a prior study that found that 65% of the respondents said they support labeling legislation for GMOs. (c) Compare the results from parts (a) and (b). ... (a) What is the minimum sample size needed assuming that no prior information is available? n = (Round up to the nearest whole number as needed.)arrow_forwardThe table available below shows the costs per mile (in cents) for a sample of automobiles. At a = 0.05, can you conclude that at least one mean cost per mile is different from the others? Click on the icon to view the data table. Let Hss, HMS, HLS, Hsuv and Hмy represent the mean costs per mile for small sedans, medium sedans, large sedans, SUV 4WDs, and minivans respectively. What are the hypotheses for this test? OA. Ho: Not all the means are equal. Ha Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV B. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV = μMV Ha: Hss *HMS *HLS*HSUV * HMV C. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV =μMV = = H: Not all the means are equal. D. Ho Hss HMS HLS HSUV HMV Ha Hss HMS HLS =HSUV = HMVarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





