
(a)
The repeat unit structure for polychlorotrifluoroethylene polymer.
(a)
Answer to Problem 1QP
Explanation of Solution
Polychlorotrifluoroethylene polymer consists of one chlorine atom, three fluorine atoms and two carbon atoms.
The formula of ethylene is
Total electrons of outermost orbit in Chlorine and Fluorine is
Therefore, the structure of repeat unit is,
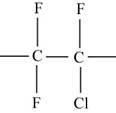
Figure I
Conclusion:
The repeat unit of polychlorotrifluoroethylene polymer is shown in Figure I.
(b)
The repeat unit structure for poly(vinyl alcohol) polymer.
(b)
Answer to Problem 1QP
Explanation of Solution
Poly(vinyl alcohol) polymer consists of one hydroxyl group; three hydrogen atoms and two carbon atoms.
The formula of ethylene is
Total electrons of outermost orbit in oxygen, hydrogen and carbon atoms are
Therefore, the structure of repeat unit is,
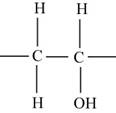
Figure II
Conclusion:
The repeat unit of poly(vinyl alcohol polymer is shown in Figure II
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK FUNDAMENTALS OF MATERIALS SCIENCE A
- CHAPTER 5 PC-BASED PARTITIONS 3. When an entry for a non-extended partition is processed, its starting sector and size are displayed. The ending sector address can be determined by adding the starting sector address and the size together and subtracting one. DATA STRUCTURES The previous section reviewed the DOS partition system. This section provides a detailed discussion of the structures that make the system work. If you are not interested in data structures, you can skip this; however, there is an interesting example of extended partitions. This section is organized into three subsections describing the MBR, extended partitions, and show tool output from an example image. MBR Data Structure DOS Partition tables exist in the MBR and in the first sector of each extended partition. Conveniently, they all use the same 512-byte structure. The first 446 bytes are reserved for assembly boot code. Code needs to exist in the MBR because it is used when the computer is started, but the…arrow_forwardQuestion 1: Consider the following hexdump of sample. bin and run of the dd command. $ xxd sample.bin 00000000: c7f2 24c0 a88e 559c 7f34 5bae 00al 7bld.....U..4[.... 00000010: b37d de 99 eelf 6b04 9761 5128 29bb f196 .....k..aQ().... 00000020: lee9 d578 7472 78d3 483a 3635 f6e0 bf45 ...xtrx.H: 65...E 00000030: 5644 4ceb c9ed 92be 70d8 6721 44b4 31cd VDL.....p.g!D.1. $ dd if=sample.bin of-output.bin bs-32 skip-1 count-1 status-none What is the output of running the following command dd if-output.bin bs-1 skip-14 count-4 status-none | xxd A: 00000000: a88e 559c B: 00000000: c7f2 24c0 C: 00000000: bf45 5644 D: 00000000: c9ed 92be E: 00000000: 7bld b37d Question 2: Here is a hexdump of a partition table. ..U. ..$. . EVD (..) 00000000: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 000001b0: 0000 0000 0000 0000 4d2c 7283 0000 0021 ...... 000001c0: 2400 0c13 615c 0008 0000 0000 0b00 0013 $...a\. 000001d0: 625c 0706 be17 0008 0b00 00e8 0500 0006 b\... 000001e0: bd17 8301 e310 00f0 1000 00e0 0700…arrow_forward(read image, answer given)arrow_forward
- 6/86 The connecting rod AB of a certain internal-combustion engine weighs 1.2 lb with mass center at G and has a radius of gyration about G of 1.12 in. The piston and piston pin A together weigh 1.80 lb. The engine is running at a constant speed of 3000 rev/min, so that the angular velocity of the crank is 3000(2)/60 = 100л rad/sec. Neglect the weights of the components and the force exerted by the gas in the cylinder compared with the dynamic forces generated and calculate the magnitude of the force on the piston pin A for the crank angle 0 = 90°. (Suggestion: Use the alternative moment relation, Eq. 6/3, with B as the moment center.) Answer A = 347 lb 3" 1.3" B 1.7" PROBLEM 6/86arrow_forwardDraw an ERD that will involve the entity types: Professor, Student, Department and Course. Be sure to add relationship types, key attributes, attributes and multiplicity on the ERD.arrow_forward6/85 In a study of head injury against the instrument panel of a car during sudden or crash stops where lap belts without shoulder straps or airbags are used, the segmented human model shown in the figure is analyzed. The hip joint O is assumed to remain fixed relative to the car, and the torso above the hip is treated as a rigid body of mass m freely pivoted at O. The center of mass of the torso is at G with the initial position of OG taken as vertical. The radius of gyration of the torso about O is ko. If the car is brought to a sudden stop with a constant deceleration a, determine the speed v relative to the car with which the model's head strikes the instrument panel. Substitute the values m = 50 kg, 7 = 450 mm, r = 800 mm, ko = 550 mm, 0 = 45°, and a = 10g and compute v. Answer v = 11.73 m/s PROBLEM 6/85arrow_forward
- Draw an ERD that represents a book in a library system. Be sure to add relationship types, key attributes, attributes and multiplicity on the ERD.arrow_forwardWhat is the shear and normal stresses of Point J and Point K?arrow_forwardWhat are the states of stress (magnitude and tension/compression of the normal stresses and shear stress) at Point J and Point K?arrow_forward
- Using AutoCADarrow_forwardA3 m long cantilever ABC is built-in at A, partially supported at B, 2 m from A, with a force of 10 kN and carries a vertical load of 20 kN at C. A uniformly distributed bad of 5 kN/m is also applied between A and B. Determine (a) the values of the vertical reaction and built-in moment at A and (b) the deflection of the free end C of the cantilever, Develop an expression for the slope of the beam at any position and hence plot a slope diagram. E = 208GN / (m ^ 2) and 1 = 24 * 10 ^ - 6 * m ^ 4arrow_forward7. Consider the following feedback system with a proportional controller. K G(s) The plant transfer function is given by G(s) = 10 (s + 2)(s + 10) You want the system to have a damping ratio of 0.3 for unit step response. What is the value of K you need to choose to achieve the desired damping ratio? For that value of K, find the steady-state error for ramp input and settling time for step input. Hint: Sketch the root locus and find the point in the root locus that intersects with z = 0.3 line.arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





