
Biology
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781260487947
Author: BROOKER
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 40.1, Problem 1CS
Core Skill: Connections Look back to Figure 32.14 to see a more detailed illustration of the flowering plant life cycle. How can you recognize and where can you find the gametophyte generation of a flowering plant?
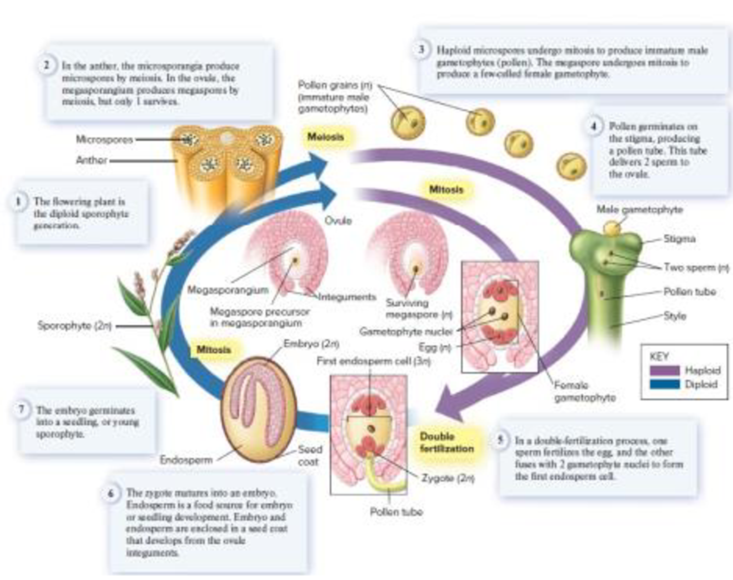
Figure 32.14 The life cycle of a flowering plant, illustrated by the genus Polygonum. Flowering plant life cycles differ in length and in the number of cells and nuclei occurring in the female gametophyte, with the seven cells and eight nuclei of Polygonum being common.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
what are the answer from the book
what is lung cancer why plants removes liquid water intead water vapours
*Example 2: Tracing the path of an autosomal dominant trait
Trait: Neurofibromatosis
Forms of the trait:
The dominant form is neurofibromatosis, caused by the production of an abnormal form of the protein
neurofibromin. Affected individuals show spots of abnormal skin pigmentation and non-cancerous
tumors that can interfere with the nervous system and cause blindness. Some tumors can convert to a
cancerous form. i
The recessive form is a normal protein - in other words, no neurofibromatosis.moovi
A typical pedigree for a family that carries neurofibromatosis is shown below. Note that carriers are not
indicated with half-colored shapes in this chart. Use the letter "N" to indicate the dominant neurofibromatosis
allele, and the letter "n" for the normal allele.
Nn
nn
nn
2
nn
Nn
A
3
N-
Chapter 40 Solutions
Biology
Ch. 40.1 - Core Skill: Connections Look back to Figure 32.14...Ch. 40.1 - Prob. 1CCCh. 40.1 - Prob. 2CCCh. 40.2 - What inference can you draw from the observation...Ch. 40.2 - List several ways in which the flowers at the rim...Ch. 40.2 - Why do you think Liang and Mahadevan used Lilium...Ch. 40.2 - How did time-lapse video improve data gathering in...Ch. 40.3 - Prob. 1CCCh. 40.3 - Prob. 2CCCh. 40.3 - Prob. 1CS
Ch. 40.4 - Prob. 1CCCh. 40.4 - Prob. 2CCCh. 40.4 - Prob. 1CSCh. 40 - Where do the pollen grains of flowering plants...Ch. 40 - Prob. 2TYCh. 40 - Where would you find female gametophytes of a...Ch. 40 - How does double fertilization occur in flowering...Ch. 40 - Prob. 5TYCh. 40 - Prob. 6TYCh. 40 - Prob. 7TYCh. 40 - If an ovary contains eight ovules, how many seeds...Ch. 40 - Prob. 9TYCh. 40 - Prob. 10TYCh. 40 - Prob. 1CQCh. 40 - Prob. 2CQCh. 40 - Prob. 3CQCh. 40 - Prob. 1COQCh. 40 - How do plants prevent the production of many...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
True or false? Some trails are considered vestigial because they existed long ago.
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Separate the list P,F,V,,T,a,m,L,t, and V into intensive properties, extensive properties, and nonproperties.
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Why do scientists think that all forms of life on earth have a common origin?
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Gregor Mendel never saw a gene, yet he concluded that some inherited factors were responsible for the patterns ...
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
To test your knowledge, discuss the following topics with a study partner or in writing ideally from memory. Th...
HUMAN ANATOMY
An obese 55-year-old woman consults her physician about minor chest pains during exercise. Explain the physicia...
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- I want to be a super nutrition guy what u guys like recommend mearrow_forwardPlease finish the chart at the bottom. Some of the answers have been filled in.arrow_forward9. Aerobic respiration of one lipid molecule. The lipid is composed of one glycerol molecule connected to two fatty acid tails. One fatty acid is 12 carbons long and the other fatty acid is 18 carbons long in the figure below. Use the information below to determine how much ATP will be produced from the glycerol part of the lipid. Then, in part B, determine how much ATP is produced from the 2 fatty acids of the lipid. Finally put the NADH and ATP yields together from the glycerol and fatty acids (part A and B) to determine your total number of ATP produced per lipid. Assume no other carbon source is available. 18 carbons fatty acids 12 carbons 9 glycerol A. Glycerol is broken down to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, a glycolysis intermediate via the following pathway shown in the figure below. Notice this process costs one ATP but generates one FADH2. Continue generating ATP with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate using the standard pathway and aerobic respiration. glycerol glycerol-3- phosphate…arrow_forward
- Normal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO2 level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO2 triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. How might the location and slope of the O₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardforaging/diet type teeth tongue stomach intestines cecum Insectivory numerous, spiky, incisors procumbentExample: moleExample: shrew -- simple short mostly lacking Myrmecophagy absent or reduced in numbers, peg-likeExample: tamandua anteater extremely long simple, often roughened short small or lacking Terrestrial carnivory sharp incisors; long, conical canines; often carnassial cheek teeth; may have crushing molarsExample: dog -- simple short small Aquatic carnivory homodont, spiky, numerousExample: common dolphin -- simple or multichambered (cetaceans only) variable small or absent Sanguinivory very sharp upper incisors; reduced cheek teethExample: vampire bat grooved tubular, highly extensible long small or lacking Herbivory (except nectivores) incisors robust or absent; canines reduced or absent; diastema; cheek teeth enlarged with complex occlusal surfacesExample: beaver -- simple (hindgut fermenters) or multichambered (ruminants) long large Filter feeding none…arrow_forward3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 པར『ན་ cm 30 Species B 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 cm 10 Species C 0/4, 0/0,3/3, 3/3 020arrow_forward
- 3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 cm 30 Species B 0/4, 0/0, 3/3, 3/3 cm 10 Species C 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 E 0 cm 20 AILarrow_forwardNormal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO₂ level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO₂ triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. • How might the location and slope of the O2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- If a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade one small protein molecule into 8 molecules of pyruvic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume there is no other carbon source. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in molecules of ATP.arrow_forwardIf a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade a 30 mM solution of citric acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume no other carbon source is available. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781305389892
Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...
Biology
ISBN:9781305073951
Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax


General Embryology Review in 20 minutes; Author: Medical Animations;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4YKvVeVMmEE;License: Standard youtube license