
To Explain:
The meaning of
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus is the measure of benefit of the consumer from the purchase of a good or service.
Explanation of Solution
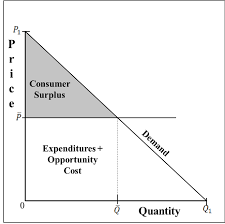
Consumer surplus is the difference between the maximum amount the consumer is willing to pay for a good and the amount the consumer actually pays. Suppose a moviegoer is willing to pay $15 for a blockbuster movie ticket but pays $12. Then $3 is her consumer surplus. When the consumer surpluses of all consumers buying a product are added, a measure of aggregate consumer surplus is obtained. Thus, consumer surplus is the total benefit from the consumption of a product, net of the total cost of purchasing it. The situation is depicted in the figure below.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Loose-leaf Version for Microeconomics in Modules
- Published in 1980, the book Free to Choose discusses how economists Milton Friedman and Rose Friedman proposed a one-sided view of the benefits of a voucher system. However, there are other economists who disagree about the potential effects of a voucher system.arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand and marginal revenue curves facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. a. Calculate the values of profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss, and illustrate these on the graph. b. Repeat the calculations in part a, but now assume the monopoly is able to practice perfect price discrimination.arrow_forwardThe projects under the 'Build, Build, Build' program: how these projects improve connectivity and ease of doing business in the Philippines?arrow_forward
- Critically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardOutline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





