
Complex
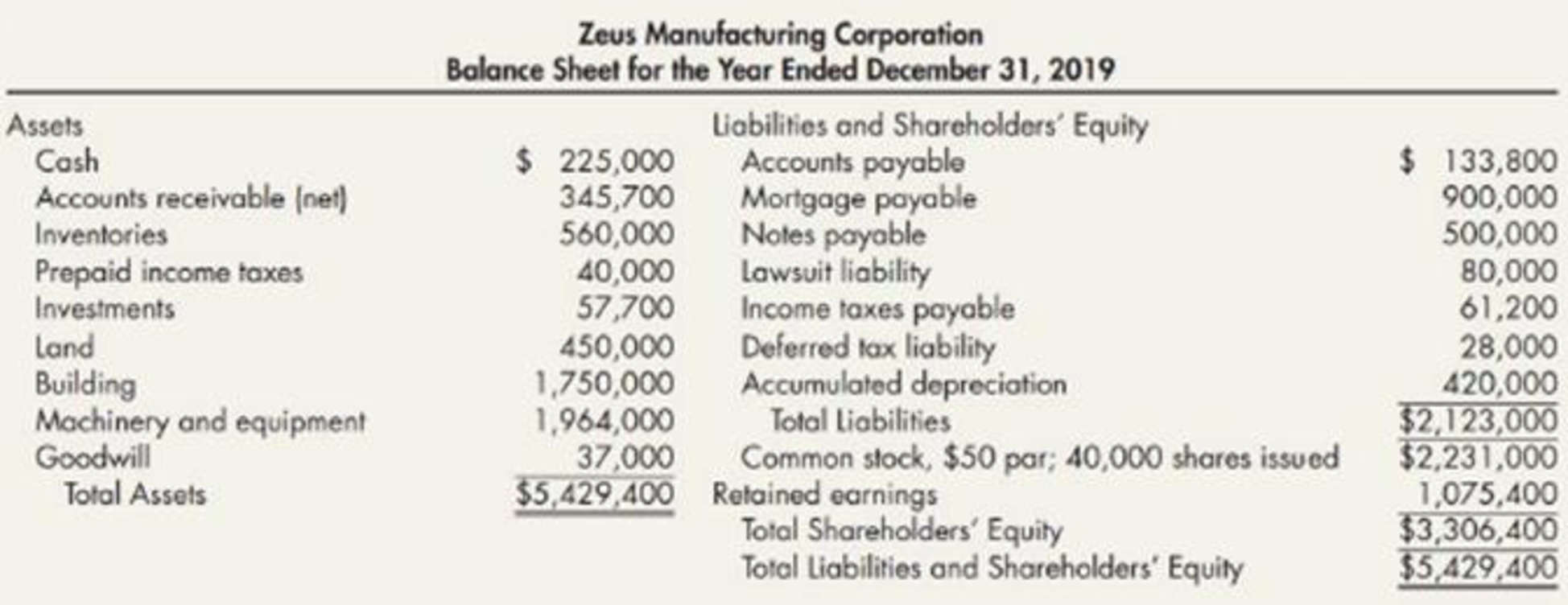
Your company has been engaged to perform an audit, during which you discover the following information:
- 1. Checks totaling $14,000 in payment of accounts payable were mailed on December 31, 2019, but were not recorded until 2020. Late in December 2019, the bank returned a customer’s $2,000 check marked “NSF,” but no entry was made. Cash includes $100,000 restricted for building purposes.
- 2. Included in
accounts receivable is a $30,000 note due on December 31, 2022, from Zeus’s president. - 3. During 2019, Zeus purchased 500 shares of common stock of a major corporation that supplies Zeus with raw materials. Total cost of this stock was $51,300, and fair value on December 31, 2019, was $51,300. Zeus plans to hold these shares indefinitely.
- 4.
Treasury stock was recorded at cost when Zeus purchased 200 of its own shares for $32 per share in May 2019. This amount is included in investments. - 5. On December 31, 2019, Zeus borrowed $500,000 from a bank in exchange for a 10% note payable, manning December 31, 2024. Equal principal payments are due December 31 of each year beginning in 2020. This note is collateralized by a $250,000 tract of land acquired as a potential future building site, which is included in land.
- 6. The mortgage payable requires $50,000 principal payments, plus interest, at the end of each month. Payments were made on January 31 and February 28, 2020. The balance of this mortgage was due June 30, 2020. On March 1, 2020, prior to issuance of the audited financial statements, Zeus consummated a non-cancelable agreement with the lender to refinance this mortgage. The new terms require $100,000 annual principal payments, plus interest, on February 28 of each year, beginning in 2021. The final payment is due February 28, 2028.
- 7. The lawsuit liability will be paid in 2020.
- 8. Of the total
deferred tax liability ; $5,000 is considered a current liability. - 9. The current income tax expense reported in Zeus’s 2019 income statement was $61,200.
- 10. The company was authorized to issue 100,000 shares of $50 par value common stock.
Prepare a corrected classified balance sheet as of December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Prepare a corrected classified balance sheet of Company Z:
| Company Z | |||
| Balance Sheet | |||
| December 31,2019 | |||
| Current Assets: | Amount ($) | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash (1) | 109,000 | ||
| Accounts receivable (net) (2) | 317,700 | ||
| Inventories | 560,000 | ||
| Total current assets | 986,700 | ||
| Long-Term Investment, at fair value (3) | 51,300 | ||
| Property, Plant, and Equipment (at cost): | |||
| Land (4) | 200,000 | ||
| Building | 1,750,000 | ||
| Machinery and equipment | 1,964,000 | ||
| Total | 3,714,000 | ||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (420,000) | 3,294,000 | |
| Total property, plant, and equipment | 3,494,000 | ||
| Intangible Asset: | |||
| Goodwill | 37,000 | ||
| Other Assets: | |||
| Cash restricted for building purposes [ Refer working note (1) ] | 100,000 | ||
| Officer’s note receivable [ Refer working note (2) ] | 30,000 | ||
| Land held for future building site [ Refer working note (4) ] | 250,000 | 380,000 | |
| Total Assets | 4,949,000 | ||
| Liabilities | |||
| Current Liabilities: | |||
| Accounts payable (5) | 119,800 | ||
| Current instalments of long-term debt[ Refer working notes (6) & (7) ] | 200,000 | ||
| Lawsuit liability | 80,000 | ||
| Income taxes payable (8) | 21,200 | ||
| Deferred tax liability | 5,000 | ||
| Total current liabilities | 426,000 | ||
| Long-Term Debt: | |||
| Mortgage payable (6) | 800,000 | ||
| Notes payable (7) | 400,000 | ||
| Deferred tax liability | 23,000 | ||
| Total long-term debt | 1,223,000 | ||
| Total Liabilities | 1,649,000 | ||
| Shareholders’ Equity: | |||
| Contributed Capital: | |||
| Common stock, authorized 100,000 shares of $50 par value; issued 40,000 shares; outstanding 39,800 shares (9) | 2,000,000 | ||
| Additional paid-in capital [ Refer working note (9) ] | 231,000 | ||
| Total paid-in capital | 2,231,000 | ||
| Retained earnings | 1,075,400 | ||
| Total | 3,306,400 | ||
| Less: Cost of treasury stock capital [ Refer working note (3) ] | (6,400) | ||
| Total Shareholders’ Equity | 3,300,000 | ||
| Total Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | 4,949,000 | ||
Table (1)
Therefore, the total of assets and total liabilities and shareholders’ equity equals to $4,949,000.
Working notes:
(1) Calculate corrected amount of cash balance:
| Cash, per unaudited balance sheet | $225,000 |
| Less: Unrecorded checks in payment of accounts payable | ($14,000) |
| NSF check not recorded | ($2,000) |
| Cash restricted for building purposes (reported in other assets) | ($100,000) |
| Corrected balance | 109,000 |
Table (2)
(2) Calculate the corrected amount of accounts receivable:
| Accounts receivable (net), per unaudited balance sheet | $345,700 |
| Add charge-back for NSF check [refer working note (1)] | $2,000 |
| Less: Officer’s note receivable (reported in other assets) | ($30,000) |
| Corrected balance | $317,700 |
Table (3)
(3) Calculate the corrected amount of investments:
| Investments, per unaudited balance sheet | $57,700 |
| Less: Long-term investment [reported separately as an asset] | ($51,300) |
| Treasury stock [reported in shareholders’ equity] | ($6,400) |
| Corrected balance | $0 |
Table (4)
(4) Calculate the corrected amount of land:
| Land, per unaudited balance sheet | $450,000 |
| Less: Land acquired for future building site (reported in other assets) | ($250,000) |
| Corrected balance | $200,000 |
Table (5)
(5) Calculate the corrected amount of accounts payable:
| Accounts payable, per unaudited balance sheet | $133,800 |
| Less: Unrecorded payments [refer working note (1)] | ($14,000) |
| Corrected balance | $119,800 |
Table (6)
(6) Calculate the corrected amount of mortgage payable:
| Mortgage payable, per unaudited balance sheet | $900,000 |
| Less: Current portion | (100,000) |
| Refinanced as long-term mortgage payable | $800,000 |
Table (7)
(7) Calculate the corrected amount of long-term note payable:
| Notes payable, per unaudited balance sheet | $500,000 |
| Less: Current portion | ($100,000) |
| Long-term note payable | $400,000 |
Table (8)
(8) Calculate the corrected amount of income taxes payable:
| Income taxes payable, per unaudited balance sheet | $61,200 |
| Less: Prepaid income taxes | ($40,000) |
| Corrected balance | $21,200 |
Table (9)
(9) Calculate the corrected amount of common stock:
| Common stock, per unaudited balance sheet | $2,231,000 |
| Less: Additional paid-in capital in excess of par value | ($231,000) |
| Corrected balance | $2,000,000 |
Table (10)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
INTERM.ACCT.:REPORTING...-CENGAGENOWV2
- Don't use ai given answer accounting questionsarrow_forwardRequirement 1. For a manufacturing company, identify the following as either a product cost or a period cost: Period cost Product cost a. Depreciation on plant equipment Depreciation on salespersons' automobiles Insurance on plant building Marketing manager's salary Direct materials used Manufacturing overhead g. Electricity bill for human resources office h. Production employee wagesarrow_forwardI want to correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forward
- Tungsten, Inc. manufactures both normal and premium tube lights. The company allocates manufacturing over machine hours as the allocation base. Estimated overhead costs for the year are $108,000. Additional estimated information is given below. Machine hours (MHr) Direct materials Normal 23,000 $60,000 Premium 31,000 $480,000 Calculate the predetermined overhead allocation rate. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) OA. $4.70 per direct labor hour OB. $3.48 per machine hour OC. $2.00 per machine hour OD. $0.20 per direct labor hourarrow_forward< Factory Utilities Indirect Materials Used $1,300 34,500 Direct Materials Used 301,000 Property Taxes on Factory Building 5,100 Sales Commissions 82,000 Indirect Labor Incurred 25,000 Direct Labor Incurred 150,000 Depreciation on Factory Equipment 6,300 What is the total manufacturing overhead?arrow_forwardDiscuss the financial reporting environment and financial statements. What is the purpose of accounting? What impact does the AICPA, FASB, and SEC play in accounting, particularly with regards to the financial statements?arrow_forward
- K Sunlight Design Corporation sells glass vases at a wholesale price of $3.50 per unit. The variable cost to manufacture is $1.75 per unit. The monthly fixed costs are $7,500. Its current sales are 27,000 units per month. If the company wants to increase its operating income by 30%, how many additional units must it sell? (Round any intermediate calculations to two decimal places and your final answer up to the nearest whole unit.) A. 7,500 glass vases OB. 33,815 glass vases OC. 6,815 glass vases D. 94,500 glass vasesarrow_forwardCan you help me with of this question general accountingarrow_forwardWhat is the correct option? General accounting questionarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Auditing: A Risk Based-Approach (MindTap Course L...AccountingISBN:9781337619455Author:Karla M Johnstone, Audrey A. Gramling, Larry E. RittenbergPublisher:Cengage Learning

