
Concept explainers
a.
Prepare the adjusting entry as at December 31, 2015.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the adjusting entries:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31 | 1,500 | ||
| Studio revenue earned | 1,500 | ||
| (To record the accrued studio revenue earned) | |||
| December 31 | Unearned Retainer fees | 2,500 | |
| Client fees earned | 2,500 | ||
| (To record the collection of advance) | |||
| December 31 | Office supplies expense | 95 | |
| Office supplies | 95 | ||
| (To record the insurance expense) | |||
| December 31 | 750 | ||
| 750 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) | |||
| December 31 | Rent expense (2) | 300 | |
| Prepaid rent | 300 | ||
| (To record the rent expense) | |||
| December 31 | Insurance expense (3) | 90 | |
| Unexpired insurance | 90 | ||
| (To record the insurance expense) | |||
| December 31 | Salaries expense | 1,900 | |
| Salaries payable | 1,900 | ||
| (To record the salaries expense) | |||
| December 31 | Interest expense (4) | 60 | |
| Interest payable | 60 | ||
| (To record the interest expense) | |||
| December 31 | Income taxes expense | 600 | |
| Income taxes payable | 600 | ||
| (To record the income tax expense) |
Table (1)
1. To record the accrued revenue earned:
- Accounts receivable is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore, debit accounts receivable with $1,500.
- Client fees earned is a revenue account and it increases the stockholders’ equity account. Therefore, credit client fees earned with $1,500.
2. To record the collections made in advance:
- Unearned retainer fees are a liability account and it is decreased. Therefore, debit unearned retained fees with $2,500.
- Client fees earned is a revenue account and it increases the stockholders’ equity account. Therefore, credit client fees earned with $2,500.
3. To record the office supplies expense:
- Office supplies expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity account. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $95.
- Office supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $95.
4. To record the depreciation expense, Office Equipment:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity account. Therefore, debit depreciation expense with $750.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-account and it decreases the value of asset. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation with $750.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of depreciation expense:
(1)
5. To record the rent expense:
- Rent expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit rent expenses with $300.
- Prepaid rent is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid rent with $300.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of rent expense:
(2)
6. To record the insurance expense:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit insurance expenses with $90.
- Unexpired insurance is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit unexpired insurance with $90.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of insurance expense:
(3)
7. To record the salaries expense:
- Salaries expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit salaries expenses with $1,900.
- Salaries payable is a liability account and it is increased. Therefore, credit salaries payable with $1,900.
8. To record the interest expense:
- Interest expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit interest expenses with $60.
- Interest payable is a liability account and it is increased. Therefore, credit interest payable with $60.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of interest expense:
(4)
9. To record the income tax expense:
- Income tax expense is an expense account and it decreases the stockholders’ equity. Therefore, debit income tax expenses with $600.
- Income tax payable is a liability account and it is increased. Therefore, credit salaries payable with $600.
b.
Prepare the adjusted
b.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance dated December 31, 2015:
| Agency SI | ||
| Adjusted trial balance | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| Cash | $40,585 | |
| Accounts receivable | $3,500 | |
| Office supplies | $110 | |
| Prepaid rent | $900 | |
| Unexpired insurance | $180 | |
| Office Equipment | $54,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation: Office equipment | $36,000 | |
| Accounts payable | $1,400 | |
| Interest payable | $420 | |
| Income taxes payable | $2,350 | |
| Note payable | $9,000 | |
| Unearned retainer fees | $1,000 | |
| Salaries payable | $1,900 | |
| Capital stock | $30,000 | |
| | $8,000 | |
| Dividends | $1,000 | |
| Client fees earned | $64,000 | |
| Office supplies expense | $700 | |
| Depreciation expense: Office equipment | $9,000 | |
| Rent expense | $6,075 | |
| Insurance expense | $1,100 | |
| Salaries expense | $29,000 | |
| Interest expense | $420 | |
| Income tax expense | $7,500 | |
| Totals | $154,070 | $154,070 |
Table (2)
c.
Compute the net income for the year ended December 31, 2015.
c.
Explanation of Solution
| Agency SI | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue | ||
| Client fees earned | $64,000 | |
| Total Revenue | $64,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Office supplies expense | $700 | |
| Depreciation expense: office equipment | $9,000 | |
| Rent expense | $6,075 | |
| Insurance expense | $1,100 | |
| Salaries expense | $29,000 | |
| Interest expense | $420 | |
| Income taxes expense | $7,500 | |
| Total Expenses | $53,795 | |
| Net Income | $10,205 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income for the year ended December 31, 2015 is $10,205.
d.
Identify the company’s average monthly rent expense in January through September for the Year 2015.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the average monthly rent expense from January through September for the Year 2015.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Rent expense for 12 months ended December 31, 2015 | $6,075 |
| Less: Rent expense in October through December | $900 |
| Rent expense for January through September | $5,175 |
| Average monthly rent expense for January to September | $575 |
Table (4)
Thus the average monthly rent expense from January through September is $575 for the year 2015.
e.
Identify the average company’s monthly insurance expense in January and February for the year 2015.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the average monthly insurance expense for January to July:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Insurance expense for 12 months ended | $1,100 |
| Less: Insurance expense from March through December | $900 |
| Insurance expense for January through February | $200 |
| Average monthly insurance expense for January to February | $100 |
Table (5)
Thus, the average monthly insurance expense from January through February is $100 for the 2015.
f.
Determine the life of the office equipment from the beginning of company’s operation.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the life of the office equipment from the beginning of company’s operation.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Accumulated depreciation per trial balance | $35,250 |
| Add: December depreciation expense (adjusting entry 4) | $750 |
| Accumulated depreciation at December 31, 2015 | $36,000 |
| Age of equipment at December 31, 2015 | 48 months |
Table (6)
Thus, the age of the equipment is 48months or 4 years.
g.
Indicate the effect of the adjusting entry on the income statement and balance sheet.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Indicate the effect of the adjusting entry on the income statement and balance sheet.
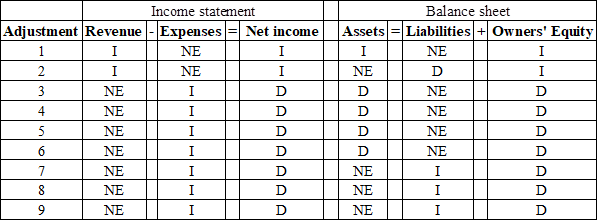
Table (7)
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Note:
“I” represents Increase
“D” represents Decrease
“NE” represents No effect
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
- What would be the effect on income from operations if absorption costing is used rather than variable costing ?arrow_forwardAlexander's Auto Accessories started the year with total assets of $320,000 and total liabilities of $190,000. During the year, the business recorded $425,000 in revenues, $235,000 in expenses, and dividends of $75,000. What was the net income reported by Alexander's Auto Accessories for the year? Provide answerarrow_forwardSamantha Sullivan's monthly pay stub indicates that her monthly gross income is $5,800. However, $1,250 is withheld for income and Social Security taxes, $320 is withheld for her health and dental insurance, and another $350 is contributed to her retirement plan. How much is Samantha's disposable income?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





