
Concept explainers
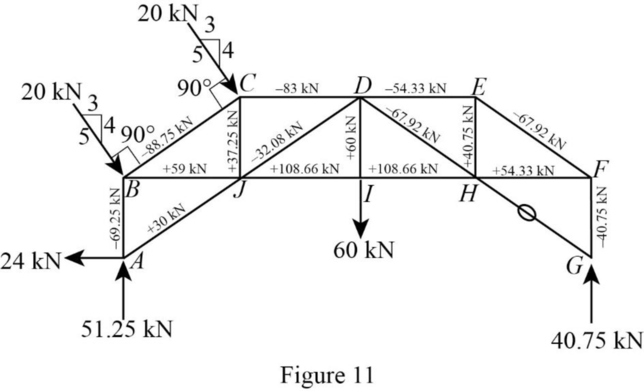
Find the force in each bar and mention the force is tension or compression of the bars in the truss.
Explanation of Solution
Assumptions:
- Consider the state of bars as tension (T) where the force is pulling the bar and as compression (C) where the force is pushing the bar.
- The sign of the force in the bar is positive when the force is in tension and negative when the force is in compression.
- Consider the force indicating right side as positive and left side as negative in horizontal components of forces.
- Consider the force indicating upward is taken as positive and downward as negative in vertical components of forces.
- Consider clockwise moment as negative and anti-clock wise moment as positive wherever applicable.
Show the free-body diagram of the entire truss as in Figure 1.
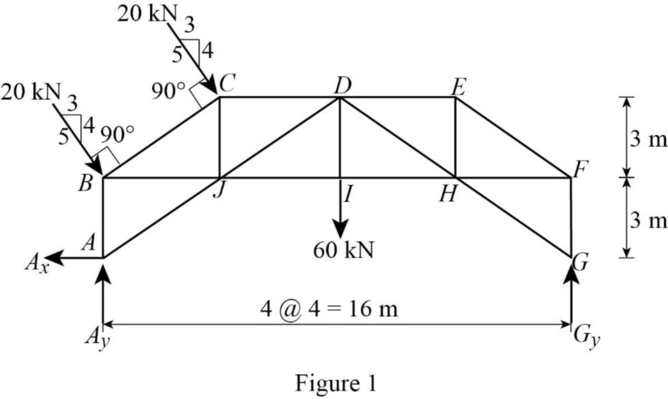
Find the horizontal reaction at point A by resolving the horizontal component of forces.
Find the vertical reaction at point G by taking moment about point A.
Find the vertical reaction at point A by resolving the vertical component of forces.
Consider the joint G;
Show the forces acting at the joint G as in Figure 2.
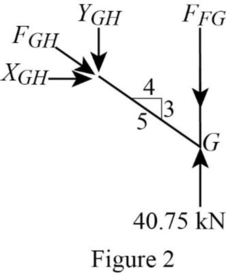
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Use the proportion:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Consider the joint F;
Show the forces acting at the joint F as in Figure 3.
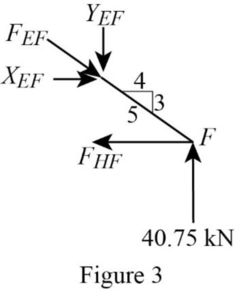
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Use the proportion:
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the joint E;
Show the forces acting at the joint E as in Figure 4.
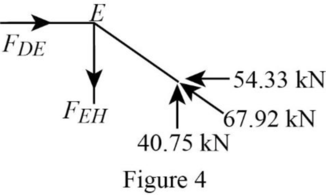
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the joint H;
Show the forces acting at the joint H as in Figure 5.
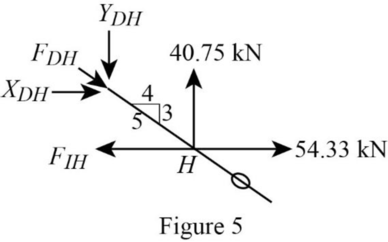
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Use the proportion:
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the joint I;
Show the forces acting at the joint I as in Figure 6.
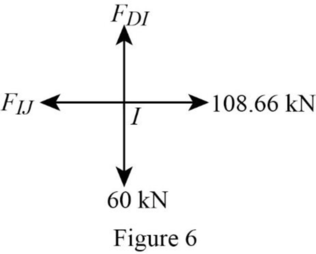
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the joint D;
Show the forces acting at the joint D as in Figure 7.
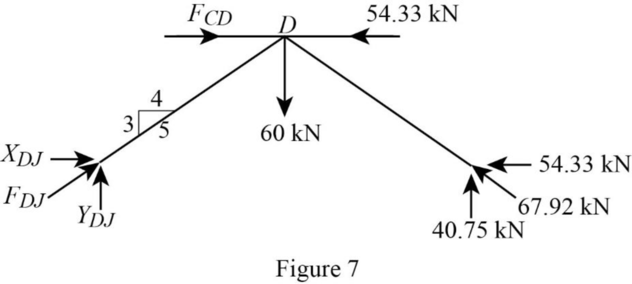
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Use the proportion:
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the joint C;
Show the forces acting at the joint C as in Figure 8.
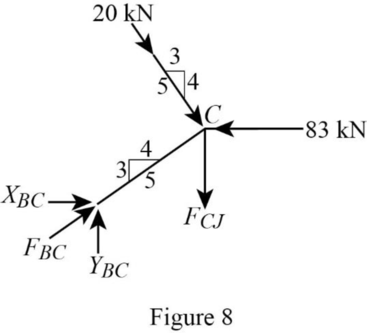
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Use the proportion:
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Consider the joint J;
Show the forces acting at the joint J as in Figure 9.
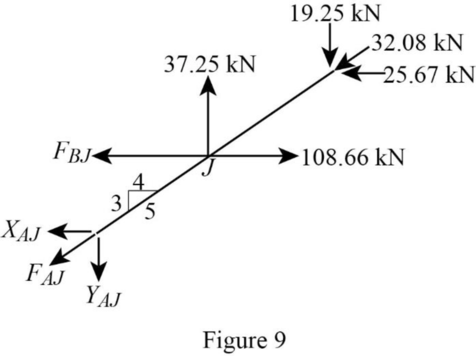
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Use the proportion:
Resolve the horizontal component of forces.
Consider the joint A;
Show the forces acting at the joint A as in Figure 10.
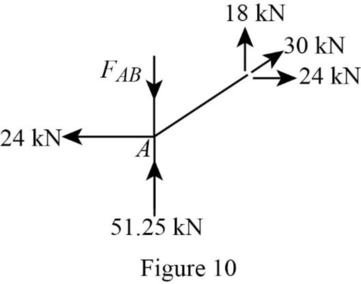
Resolve the vertical component of forces.
Show the forces in the bars of the truss as in Figure 11.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Structural Analysis:
- A national pricing service says the National price is $12.35 per unit. The adjusted price adjustment for Los Angeles is 1.15. The price adjustment for Tulsa is 0.94. What is the expected price difference between Tulsa and Los Angeles? c.$2.98 b.$2.59 d.$0.00 a.$0.21arrow_forwardPROBLEM: Design the transversely reinforced concrete deck slab shown in the cross-sectional detail below. 8" REINFORCED CONCRETE SLAB 1/4" PER FT. T 3-3% 8'-0" 8'-0" 4'-0" GIVEN: Bridge to carry two traffic lanes. Concrete strength =4.5 ksi. Grade 60 reinforcement f, = 60 ksi. Account for 25 psf future wearing surface. Assume stringers are W36 x 150. Deck has a 0.5 in integrated wearing surface.arrow_forwardPlease help me answer this questionarrow_forward
- I need help solving this problem, I'm not sure how to draw these diagrams.arrow_forwardI need help solving this problemarrow_forward88 L Solle ined sove in peaper 96252 Example 5.5 The turbine rotor of a ship has a mass of 30 tons, a radius of gyration of 600 mm and rotates at 2400 rpm in a clockwise direction when viewed from aft. The ship pitches through a total angle of 15%, 7.5° above and 7.5° below the horizontal, the motion being simple harmonic and having a period of 12 sec. Determine the maximum gyroscopic couple on the holding down bolts of the turbine and the direction of yaw as the bow rises. النص ملصقات -20125 750 31 الرسم X 7.0! 989 Carrow_forward
- Design the deep beam in a wall for a warehouse, as shown in the drawing below using the strength design method of TMS 402-22. The wall is to be constructed of fully grouted hollow concrete masonry units in running bond. Determine the width of the masonry units, and the flexural and shear reinforcement required. Use mf ′ = 2,000 psi and Grade 60 (60 ksi) steel, and Type S Portland cement mortar. In addition to its own weight, it carries a dead load of 1.5 kip/ft. and a live load of 0.2 kip/ft. from the roof. The walls on both sides of the opening are very long. Therefore, you may assume that the beam is fixed from rotation at both ends. Design using the following two methods. (a) Design it as a deep beam with the moment arm z given by the code. Show the layout of the flexural and shear reinforcements with diagrams. (b) Design a masonry lintel beam (not a deep beam) that will carry the weight of the masonry of above, and the dead and live loads from the roof. Determine whether you can…arrow_forwardCivil Engineering Questionarrow_forward6:31 mi Official International Websit maserati.com/global/en Maserati 66 Continue without Accepting Maserati By clicking "Accept All Cookies", you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. Accept All Cookies Cookies Settings INTRODUCING THE ALL-NEW MASERATI GranCabrio DISCOVER MORE > 1/5 Oarrow_forward
- JOB UPDATE QUALCOMM FULL STACK DEVELOPER ASSOCIATE INFOR (FRESHERS) IBM QUALITY ENGINEER DATAVAIL DATABASE ADMINISTRATOR INTOUCH CUST SERVICE (CHAT/EMAIL) ACCENTURE Vinkjobs.com #vinkjobs CUSTOMER SUPPORT Search "Vinkjobs.com" on Googlearrow_forwardHello, I would like to ask if the answer provided in this link is correct based on the floor plan shown in the attached pictures? Kindly verify if the solution matches the actual layout and measurements. Thank you! https://www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/i-need-help-estimating-the-required-materials-for-masonry-works-using-chb-in-a-2-storey-residential-/bdb70948-ded3-4461-9057-f63a7a1c5f8farrow_forwardStructural analysis question Cleary explain each step with appropriate solviarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





