
Concept explainers
For each of the following molecules or ions that contain sulfur, write the Lewis structure(s), predict the molecular structure (including bond angles), and give the expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur.
a. SO2
b. SO3
c. 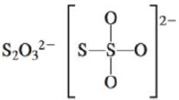
d. 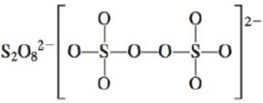
e. SO32−
f. SO42−
g. SF2
h. SF4
i. SF6
j. F3S—SF
k. SF5+
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on each sulfur and oxygen atom. Two oxygen atoms are bonded to sulfur atom. Therefore, the total valence electrons are
Therefore the geometry is bent. The bond angle is less than
The Lewis structure of
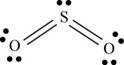
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Two oxygen atoms are attached to sulfur, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecule has trigonal planar geometry with bond angle
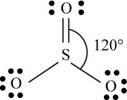
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom is attached to central sulfur atom and charge on the molecule is
By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is tetrahedral with bond angle approximately equal to
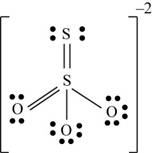
Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. There are eight oxygen atoms and two sulfur atoms are present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
The two oxygen atoms in the centre are bonded by single bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is tetrahedral with bond angle approximately equal to
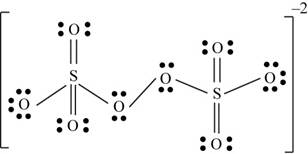
Figure 4
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Three oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
One oxygen atom is single bonded with sulfur and one is joined by pi bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is trigonal pyramidal with bond angle approximately equal to
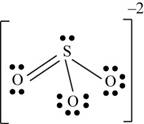
Figure 5
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and each oxygen atom. Four oxygen atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
Two oxygen atoms are single bonded with sulfur and two joined by pi bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is tetrahedral with bond angle approximately equal to
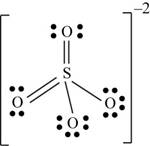
Figure 6
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Two fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The sulfur is bonded to two fluorine atoms by sigma bond. By bonding in this way, they complete their octet. The molecular structure is bent due to presence of lone pairs of electrons on sulfur. The bond angle is less than
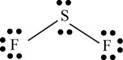
Figure 7
(h)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Four fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecular structure is see-saw due to presence of lone pair of electrons on sulfur. The equatorial bond angles are
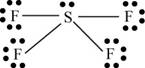
Figure 8
(i)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Six fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecular structure is octahedral with bond angle
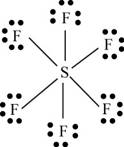
Figure 9
(j)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Four fluorine atoms and two sulfur atoms are present in the molecule, therefore, the total number of valence electrons is
The molecular structure is see-saw due to presence of lone pair of electrons on sulfur. The equatorial bond angles are
The Lewis structure of
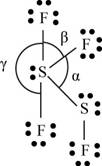
Figure 10
(k)
Interpretation: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles of the given molecules and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur is to be stated.
Concept introduction: When the atomic orbitals overlap with each other in the region where density of electrons is high, then molecular orbitals are formed. Overlap of the atomic orbitals determines the efficiency of the interaction between the atomic orbitals.
Energy of bonding molecular orbitals is less than the nonbonding molecular orbitals.
To determine: The Lewis dot structure, molecular geometry, bond angles and expected hybrid orbitals for sulfur in
Explanation of Solution
Explanation
There are six valence electrons on sulfur and seven valence electrons on each fluorine atom. Five fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom is present in the molecule and charge on the molecule is
The molecular structure is trigonal bipyramidal with equatorial bond angles
The Lewis structure of
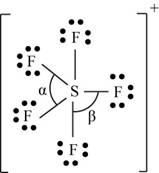
Figure 11
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
EBK CHEMISTRY: AN ATOMS FIRST APPROACH
- Reason whether it is possible to determine changes in the Galvani potential difference at the metal-solution interface.arrow_forwardObtain the standard potential at 25°C of the Cu* I Cu | Pt electrode from the standard potentials E° Cu²+/Cu = 0.341 V and E Cu²+ /Cu+ = 0.153 V.arrow_forwardIn electrochemistry, briefly describe the Galvani potential, the Volta potential, and the surface potential. Differentiate between them.arrow_forward
- What substances can neutralize, complex or adsorb and absorb both HF and CF carbonyl fluoride and hydrogen fluoride and intermediate formation of thermal decomposition of fluorinated inorganic compounds either due to hydrolysis and hygroscopic reactions. What is the known chemistry of these reactions and mechanisms.arrow_forwardBriefly differentiate between chemical potential and electrochemical potential.arrow_forwardAccording to open access forums ionic antimony Sb (111) can be reduced to elemental Sb (0) in solution and in macromolecules like condensation polymers polyethylene terephthalate (PET) causing greying of the polymer matrix. It has been connected to thermal degradation of the polymer during processing to the formation of thermally unstable EG ethyleen glycol that forms at various temperatures formic acid, formaldehyde, acetaldehyde and much more depending on temperature. I need to know what organics are more powerful reducing agents and at what concentration (relative) to each organic will initiate this reduction. Furthermore, is the pH dependant ? Are other trace elements in the plastic also a cause of concern e.g. aluminum from aluminum chloride (lewis acid). Therefore, the ultimate solution should include a means to inhibit reduction of ionic antimony and will the same solution comply with cobalt impurities from ionic cobalt? Some PET have combinations of catalyst and their residues…arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





