
Concept explainers
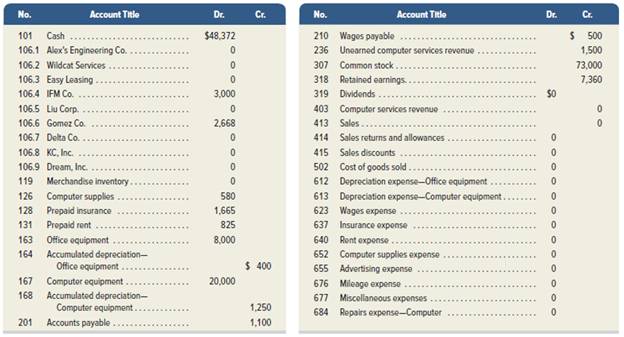
Santana Rey created Business Solutions on October 1, 2019. The company has been successful, and its list of customers has grown. To accommodate the growth, the accounting system is modified to set up separate accounts for each customer. The following chart of accounts includes the account number used for each account and any balance as of December 31, 2019. Santana Rey decided to add a fourth digit with a decimal point to the 106 account number that had been used for the single

(c)Alexander Image/Shutterstock
An response to requests from customers, S. Rey will begin selling computer software. The company will extend credit terms of
Jan. 4 The company paid cash to Lyn Addie for five days’ work at the rate of $125 per day. Four of the five days relate to wages payable that were accrued in the prior year.
5. Santana Rey invested an additional $25,000 cash in the company in exchange for more common stock.
7 The company purchased $5,800 of merchandise from Kansas Corp. with terms of
9 The company received $2,668 cash from Gomez Co. as full payment on its account.
11 The company completed a five-day project for Alex’s Engineering Co. and billed it $5,500, which is the total price of $7,000 less the advance payment of $1,500. The company debited Unearned Computer Services Revenue for $1,500.
13 The company sold merchandise with a retail value of $5,200 and a cost of $3,560 to Liu Corp., invoice dated January 13.
15 The company paid $600 cash for freight charges on the merchandise purchased on January 7.
16 The company received $4,000 cash from Delta Co. for computer services provided.
17 The company paid Kansas Corp. for the invoice dated January 7, net of the discount.
20 The company gave a price reduction (allowance) of $500to Liu Corp. and credited Liu's accounts receivable for that amount.
22 The company received the balance due from Liu Corp., net of the discount and the allowance.
24 The company returned defective merchandise to Kansas Corp. and accepted a credit against future purchases (debited accounts payable). The defective merchandise invoice cost, net of the discount, was $496.
26 The company purchased $9,000 of merchandise from Kansas Corp. with terms of
26 The company sold merchandise with a $4,640 cost for $5,800 on credit to KC, Inc., invoice dated January 26.
31 The company paid cash to Lyn Addie for 10 days' work at $125 per day.
Feb. 1 The company paid $2,475 cash to Hillside Mall for another three months' rent in advance.
3 The company paid Kansas Corp. for the balance due, net of the cash discount, less the $496 credit from merchandise returned on January 24.
5 The company paid $600 cash to Facebook for an advertisement to appear on February 5 only.
11 The company received the balance due from Alex's Engineering Co. for fees billed on January 11.
15 The company paid a $4,800 cash dividend.
23 The company sold merchandise with a $2,660 cost for $3,220 on credit to Delta Co., invoice dated February 23.
26 The company paid cash to Lyn Addie for eight days' work at $125 per day.
27 The company reimbursed Santana Rey $192 cash for business automobile mileage. The company recorded the reimbursement as "Mileage Expense."
Mar. 8 The company purchased $2,730 of computer supplies from Harris Office Products on credit with terms of
9 The company received the balance due from Delta Co. for merchandise sold on February 23.
11 The company paid $960 cash for minor repairs to the company's computer.
16 The company received $5,260 cash from Dream, Inc., for computing services provided.
19 The company paid the full amount due of $3,830 to Harris Office Products, consisting of amounts created on December 15 (of $1,100) and March 8.
24 The company billed Easy Leasing for $9,047 of computing services provided.
25 The company sold merchandise with a $2,002 cost for $2,800 on credit to Wildcat Services, invoice dated March 25.
30 The company sold merchandise with a $1,048 cost for $2,220 on credit to IFM Company, invoice dated March 30.
31 The company reimbursed Santana Rey $128 cash for business automobile mileage. The company recorded the reimbursement as "Mileage Expense."
The following additional facts are available for preparing adjustments on March 31 prior to financial statement preparation.
a. The March 31 amount of computer supplies still available totals $2,005.
b. Prepaid insurance coverage of $555 expired during this three-month period.
C. Lyn Addie has not been paid for seven days of work at the rate of $125 per day.
d. Prepaid rent of $2,475 expired during this three-month period.
e.
f. Depreciation on the office equipment for January 1 through March 31 is $400.
g. The March 31 amount of merchandise inventory still available totals $704.
Required
1. Prepare
2. Post the journal entries in part 1 to the accounts in the company's general ledger. Note: Begin with the
Check (2) Ending balances at March 31: Cash, $68,057; Sales, $19,240
3. Prepare a 6-column work sheet (similar to the one shown in Exhibit 3.13) that includes the unadjusted
(3) Unadj. TB totals, $151,557; Adj. TB totals, $154,082
4. Prepare an income statement (from the adjusted trial balance in part 3) for the three months ended March 31, 2020. (a) Use a single-step format. List all expenses without differentiating between selling expenses and general and administrative expenses. (b) Use a multiple-step format that begins with gross sales (service revenues plus gross product sales) and includes separate categories for net sales, cost of goods sold, selling expenses, and general and administrative expenses. Categorize the following accounts as selling expenses: wages expense, mileage expense, and advertising expense. Categorize the remaining expenses as general and administrative.
(4) Net income, $18,833
5. Prepare a statement of
(5) S. Rey, Capital (at March 31), $119,393
6. Prepare a classified
(6) Total assets, $120,268
Journal Entries:
Journal entries are the basic entries recoded as per the transactions being entered into by the business in its day to day operations in a chronological order.
Accounting rules regarding journal entries:
- Balance increases when: assets, losses and expenses are debited and liabilities, gains and incomes get credited.
- Balance decreases when: assets, losses and expenses get credited and liabilities, gains and incomes are debited.
To prepare: Journal entry
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 1, 2018 | Wages | 725 | ||
| Cash | 145 | |||
| Accrued wages | 580 | |||
| (Being wages paid through cash and accrued wages account) |
Table (1)
- Wages are expenses for the company which decrease the assets of the company hence debit wages account.
- Cash is an asset which is decreased after payment of wages.
- Accrued wages are provisions or gains are utilized in order to pay the wages.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 1, 2018 | Cash | 25,000 | ||
| Common stock | 25,000 | |||
| ( Being amount invested in exchange of common stock ) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on being invested in exchange for common stock.
- Common stock is sold out for cash hence asset is decreased hence credit common stock account.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 7, 2018 | Merchandise purchase | 5,800 | ||
| Cash | 5,800 | |||
| ( Being merchandise purchased ) |
Table (3)
- Purchase of merchandise increases the assets hence debit merchandise purchase account.
- Cash is an asset which is decreased by purchasing merchandise hence credit cash account.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 9, 2018 | Cash | 2,668 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 2,668 | |||
| ( Being cash received on account of fulfillment of accounts receivable) |
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on account of receiving full payment of accounts receivable hence debit cash account.
- Accounts receivable is an asset which is decreased as and when the payment is made hence accounts receivable account is credited.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 11, 2018 | Cash | 5,500 | ||
| Project fees | 5,500 | |||
| ( Being cash received on account of project being delivered ) |
Table (5)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on account of project being delivered to the client.
- Project fees is an income which is increases the asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 13, 2108 | Cash | 3,560 | ||
| Loss on sale | 1,640 | |||
| Sales | 5,200 | |||
| ( Being sales recorded ) |
Table (6)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on account of sales being made.
- Loss on sale is an expense which decreases the asset hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Sales generate incomes hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 15, 2018 | Freight | 600 | ||
| Cash | 600 | |||
| ( Being freight paid in cash ) |
Table (7)
- Freight is an expense which decreases the asset of the company hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Cash is an asset which is decreased on account of freight being paid.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 16,2018 | Cash | 4,000 | ||
| Computer Services delivered | 4,000 | |||
| (Being cash received on account of computer services being provided.) |
Table (8)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on account of computer services being delivered and fees received against it.
- Computer services provided is an income which increases the asset of the company hence credit all income and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 17,2018 | Accounts receivable | 500 | ||
| Purchase return | 500 | |||
| (Being purchase return of merchandise being recorded) |
Table (9)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on account of cash received after purchases being returned.
- Purchase return is credited as it decreases the inventory.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan. 20, 2018 | Sales R& A | 320 | ||
| Accounts Receivable | 320 | |||
| (Being Solutions to leave cost of defective products in costs of goods sold) |
Table (10)
- Sales R& A is an expense which decreases the asset hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Accounts Receivable is on being earned increases the asset hence, credit accounts receivable.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan. 22, 2018 | Cash | 500 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 500 | |||
| (Being amount received from customers) |
Table (11)
- Cash is an asset which is increased on account of amount received which increases the asset hence debit cash account.
- Accounts receivable is decreased as an asset hence credit accounts receivable.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 24, 2018 | Credit future purchases | 496 | ||
| Merchandise | 496 | |||
| (Being defective merchandise returned) |
Table (12)
- Credit future purchases will increase the asset hence debit credit future purchases.
- The return of defective merchandise will decrease the asset hence credit defective merchandise.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 26, 2018 | Cash | 5,800 | ||
| Profit on sales | 1,160 | |||
| Sales | 4,640 | |||
| (Being sales made and profit on sales earned) |
Table (13)
- Cash is earned on account of sales being made which increases the assets.
- Profit on sale increases the asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
- Sales generate revenue which adds to the value of asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Jan 31 2018 | Wages | 1,250 | ||
| Cash | 1,250 | |||
| (Being wages paid) |
Table (14)
- Wages are expense which decreases the assets hence debit all expenses and losses.
- Cash is paid to reimburse the wages which decreases the assets hence credit what goes out.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb 1, 2018 | Advance Rent | 2,475 | ||
| Cash | 2,475 | |||
| (Being advance rent paid) |
Table (15)
- Advance rent payment increases the asset hence debit advance rent account.
- Cash is paid to pay for advance rent hence cash as an asset is reduced hence credit what goes out.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb. 3, 2018 | Accounts payable | 5,800 | ||
| Cash | 5,304 | |||
| Credit Memorandum | 496 | |||
| ( Being payment of accounts payable made and credit memorandum benefit availed) |
Table (16)
- Accounts payable is a liability which is being paid off hence debit accounts payable.
- Cash is an asset which is decreased on account of payment of accounts payable hence credits all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb.5, 2018 | Advertisement expenses | 600 | ||
| Cash | 600 | |||
| ( Being advertisement expenses paid) |
Table (17)
- Advertisement expense is an expense which decreases the asset of the company hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Cash as an asset is reduced on account of such expenses being paid hence credit what goes out.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb.11,2018 | Cash | 5,000 | ||
| Bills Receivable | 5,000 | |||
| (Being bills receivable received) |
Table (18)
- Cash is increased on account of payment being received out bills receivable.
- Bills receivable as an asset is decreased on receiving the due payment over it hence credit bills receivable account.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb.15,2018 | Dividends | 4,800 | ||
| Cash | 4,800 | |||
| (Being dividends paid) |
Table (19)
- Dividends are expense for the company which reduces the assets of the company hence debit dividends account.
- Cash is an asset which is decreased on account of dividends being paid.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb 23, 2018 | Cash | 3,220 | ||
| Profit on sales | 560 | |||
| Sales | 2,660 | |||
| (Being sales made and profit on sales earned) |
Table (20)
- Cash is earned on account of sales being made which increases the assets.
- Profit on sale increases the asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
- Sales generate revenue which adds to the value of asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb.26,2018 | Wages | 1,000 | ||
| To cash | 1,000 | |||
| (Being dividends paid) |
Table (21)
- Wages are expense which decreases the assets hence debit all expenses and losses.
- Cash is paid to reimburse the wages which decreases the assets hence credit what goes out.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Feb.27,2018 | Reimbursement expenses | 192 | ||
| To cash | 192 | |||
| (Being dividends paid) |
Table (22)
- Reimbursement expense is an expense which decreases the asset of the company hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Cash as an asset is reduced on account of such expenses being paid hence credit what goes out.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| March8,2018 | Computer supplies | 2,370 | ||
| To cash | 2,370 | |||
| (Being dividends paid) |
Table (23)
- Computer supplies being purchased increases the asset of the company hence debit computer supplies account.
- Cash as an asset is decreased on purchase of computer supplies hence credit cash account.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| March9,2018 | Cash | 3,220 | ||
| Bills receivable | 3,220 | |||
| (Being cash received on bills receivable) |
Table (24)
- Cash is increased on account of payment being received out bills receivable.
- Bills receivable as an asset is decreased on receiving the due payment over it hence credit bills receivable account.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| March11,2018 | Minor Repairs | 960 | ||
| Cash | 960 | |||
| (Being cash paid for minor repairs) |
Table (25)
- Minor repairs expense is an expense which decreases the asset of the company hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Cash as an asset is reduced on account of such expenses being paid hence credit what goes out.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| March16,2018 | Cash | 5,260 | ||
| Services Revenue | 5,260 | |||
| (Being cash received on account of computing services provided) |
Table (25)
- Cash is increased as an asset on account of earning revenue hence debit cash account.
- Services revenue is an income hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| March17,2018 | Accounts Payable | 1,100 | ||
| Cash | 1,100 | |||
| (Being accounts payable cleared) |
Table (26)
- Accounts payable is an expense which decreases the asset hence debit accounts payable.
- Cash is decreased as an asset on accounts of payment of accounts payable being made.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Mar 24,2018 | Bills receivable | 9,047 | ||
| Services revenue earned | 9,047 | |||
| (Being bills receivable received on account of service revenue earned) |
Table (27)
- Bills receivable creates a future income which increases the assets hence debit bills receivable account.
- Services revenue earned is incomes hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Mar.25, 2018 | Cash | 2,800 | ||
| Profit on sales | 798 | |||
| Sales | 2,002 | |||
| (Being sales made and profit on sales earned) |
Table (28)
- Cash is earned on account of sales being made which increases the assets.
- Profit on sale increases the asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
- Sales generate revenue which adds to the value of asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Mar.25, 2018 | Cash | 2,200 | ||
| Profit on sales | 1,152 | |||
| Sales | 1,048 | |||
| (Being sales made and profit on sales earned) |
Table (29)
- Cash is earned on account of sales being made which increases the assets.
- Profit on sale increases the asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
- Sales generate revenue which adds to the value of asset hence credit all incomes and gains.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| March31,2018 | Reimbursement expenses | 128 | ||
| Cash | 128 | |||
| (Being bills receivable received on account of service revenue earned) |
Table (30)
- Reimbursement expense is an expense which decreases the asset of the company hence debits all expenses and losses.
- Cash as an asset is reduced on account of such expenses being paid hence credit what goes out.
2.
To prepare: General ledger of the journal entries in part (1).
Explanation of Solution
| Cash Acct. No. 101 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan1 | Common Stock | 25,000 | 25,000 | ||
| Jan1 | Wages | 145 | 24,855 | ||
| Jan7 | Purchase | 5,800 | 19,055 | ||
| Jan7 | Accounts payable | 5,800 | 24,855 | ||
| Jan9 | Accounts Receivable | 2,668 | 22,187 | ||
| Jan11 | Service Revenue | 5,500 | 27,687 | ||
| Jan13 | Loss on sale | 1,640 | 26,047 | ||
| Jan13 | Sales | 5,200 | 31,427 | ||
| Jan15 | Freight | 600 | 30,647 | ||
| Jan16 | Service Revenue | 4,000 | 34,647 | ||
| Jan26 | Sales | 5,800 | 40,447 | ||
| Jan31 | Wages | 5,800 | 34,647 | ||
| Jan17 | Accounts receivable | 500 | 34,147 | ||
| Feb.1 | Advance rent paid | 2,475 | 31,672 | ||
| Feb.3 | Cash memorandum | 496 | 31,176 | ||
| Feb.5 | Advertisement expenses | 600 | 30,576 | ||
| Feb.11 | Bills Receivable | 5,000 | 35,576 | ||
| Feb.15 | Dividends | 4,800 | 30,776 | ||
| Feb.26 | Wages | 1,000 | 29,776 | ||
| Feb.27, | Reimbursement expenses | 192 | 29,584 | ||
| March8 | Computer Supplies | 2,370 | 27,214 | ||
| March11 | Minor repairs | 960 | 26,254 | ||
| March16 | Service revenue earned | 5,260 | 31,514 | ||
| March17 | Accounts payable | 1,100 | 30,414 | ||
| March25 | Sales | 2,800 | 33,214 | ||
| March30 | Sales | 2,200 | 35,414 | ||
| March31 | Reimbursement expenses | 128 | 35,286 | ||
Table (31)
| Purchases Acct. No. 302 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan7 | Cash | 5,800 | 5,800 | ||
Table (32)
| Wages Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan1 | Cash | 145 | |||
| Jan31 | Cash | 1,250 | |||
| Feb.26 | Cash | 1,000 | 2,395 | ||
Table (33)
| Common Stock Acct. No. 302 | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan7 | Cash | 25,000 | 25,000 | ||
Table (34)
| Accounts Receivable Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan9 | Cash | 2,668 | |||
| Feb 11 | Cash | 5,000 | |||
| March9 | Cash | 3,220 | 10,888 | ||
Table (35)
| Service Revenue Earned Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan11 | Cash | 5,500 | |||
| Jan16 | Cash | 4,000 | |||
| March16 | Cash | 5,260 | 10,888 | ||
Table (36)
| Sales Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan13,2018 | Cash | 5,200 | |||
| Jan7,2018 | Cash | 5,800 | |||
| Feb 23,2018 | Cash | 3,220 | |||
| March25,2018 | Cash | 2,800 | |||
| March30,2018 | Cash | 2,200 | 19,220 | ||
Table (37)
| Cash Memorandum | |||||
| Date | Account Title | Debit(Dr.) ($) | Date | Account Title | Credit(Cr.) ($) |
| Feb 3,2018 | Balance b/d | 496 | Feb 3,2018 | Cash | 496 |
| 496 | 496 | ||||
Table (38)
| Loss on Sale Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan13 | Cash | 1,640 | |||
Table (39)
| Freight Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan15 | Cash | 600 | 600 | ||
Table (40)
| Advance Rent Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Feb 1 | Cash | 2,475 | 2,475 | ||
Table (41)
| Accounts Payable Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Jan7 | Cash | 5,800 | |||
| March17 | Cash | 1,100 | 6,900 | ||
Table (42)
| Advertisement Expenses Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Feb 5 | Cash | 600 | 600 | ||
Table (43)
| Dividends Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Feb 15 | Cash | 4,800 | 4,800 | ||
Table (44)
| Reimbursement Expenses Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| Feb 27 | Cash | 128 | 128 | ||
Table (45)
| Computer supplies Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| March8 | Cash | 2,370 | 2,370 | ||
Table (46)
| Minor Repairs Acct. No. | |||||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post ref | Debit($) | Credit($) | Balance($) |
| March11 | Cash | 960 | 960 | ||
Table (47)
3.
To prepare: A partial worksheet of 6 columns
Explanation of Solution
| Accounts | Unadjusted Trial balance | Adjustments | Adjusted Trial balance | Income Statement | Balance Sheet and statement of enquiry | |||||
| Dr. | Cr. | Dr. | Cr. | Dr. | Cr. | Dr. | Cr. | Dr. | Cr. | |
| Cash | 8,200 | 8,200 | 8,200 | |||||||
| Accounts Receivable | 11,250 | 11,250 | 11,250 | |||||||
| Allowance for sales discounts | 50 | 50 | 50 | |||||||
| Inventory | 21,250 | 250 | 21,000 | 21,000 | ||||||
| Inventory Returns estimated | 200 | 300 | 500 | 500 | ||||||
| Supplies | 3,800 | 3,000 | 800 | 800 | ||||||
| Prepaid insurance | 900 | 600 | 300 | 300 | ||||||
| Equipment | 34,200 | 34,200 | 34,200 | |||||||
| Accumulated depr.-Equipment | 3,700 | 3,700 | 7,400 | 7,400 | ||||||
| Accounts payable | 16,000 | 16,000 | 16,000 | |||||||
| Salaries payable | 800 | 800 | 800 | |||||||
| Sales refund payable | 300 | 900 | 1,200 | 1,200 | ||||||
| Capital Investments | 41,900 | 41,900 | 41,900 | |||||||
| Withdrawals | 4,000 | 4,000 | 4,000 | |||||||
| Sales | 321,000 | 321,000 | 321,000 | |||||||
| Sales returns and allowances | 1,100 | 900 | 2,000 | 2,000 | ||||||
| Sales discounts | 4,250 | 50 | 4,300 | 4,300 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 230,450 | 250 | 300 | 230,400 | 230,400 | |||||
| Depreciation expense-Equipment | 3,700 | 3,700 | 3,700 | |||||||
| Salaries expense | 43,000 | 800 | 43,800 | 43,800 | ||||||
| Insurance expense | 600 | 600 | 600 | |||||||
| Rent expense | 9,000 | 9,000 | 9,000 | |||||||
| Supplies expense | 3,000 | 3,000 | 3,000 | |||||||
| Advertising expense | 11,300 | 11,300 | 11,300 | |||||||
| Totals | 382,900 | 382,900 | 9,600 | 9,600 | 388,350 | 388,350 | 308,100 | 80,250 | 67,350 | |
| Net income | 12,900 | 12,900 | ||||||||
| Totals | 321,000 | 321,000 | 80,250 | 80,250 | ||||||
Table (48)
4.
To prepare: Income statement.
Explanation of Solution
| Company | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Month of March 31, 2018 | ||
| Amount ($) | Amount ($) | |
| Services Revenue | 25,307 | |
| Net sales | 18,693 | |
| Total Revenue | 44,000 | |
| :Cost of goods sold | 14,052 | |
| Depreciation expense office equipment | 400 | |
| Depreciation expense computer equipment | 1,250 | |
| Wages | 3,250 | |
| Insurance expense | 555 | |
| Rent expense | 2,475 | |
| Computer Supplies expense | 1,305 | |
| Advertising expense | 600 | |
| Reimbursement expense | 320 | |
| Repairs expense | 960 | |
| Total expenses | 25,167 | |
| Net Income | 18,833 | |
Table (49)
5.
To prepare: Statement of retained earnings.
Explanation of Solution
6.
To prepare: Classified balance sheet from unadjusted balance sheet.
Explanation of Solution
| Assets | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Cash | 68,057 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 22,867 | |
| Inventory | 704 | |
| Computer Supplies | 2,005 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,110 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 825 | |
| Office Equipment: | 8000 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | (800) | |
| Computer Equipment | 20,000 | |
| : Less: Accumulated Depreciation | (2500) | |
| Total Assets | 120,268 | |
| Liabilities and Owners' Equity | ||
| Accounts Payable | 0 | |
| Wages Payable | 875 | |
| Unearned computer service revenue | 0 | |
| Common Stock | 98,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 21,393 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners' Equity | 120,268 |
Table (50)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT.FUND.(LOOSELEAF)
- Answerarrow_forwardReliable Production company has a beginning finished goods inventory of $24,500, raw material purchases of $31,200, cost of goods manufactured of $42,800, and an ending finished goods inventory of $27,300. The cost of goods sold for this company is?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardI need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning




