
1.
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions from January to March.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions from January to March.
| Date | Account title and explanation | PR | Amount | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 2016 | ||||
| 4-Jan | Wages Expense | 623 | $125 | |
| Wages Payable | 210 | $500 | ||
| Cash | 101 | $625 | ||
| (To record the Paid employee) | ||||
| 5-Jan | Cash | 101 | $25,000 | |
| Common Stock | 307 | $25,000 | ||
| (To record the Additional investment by owner for stock.) | ||||
| 7-Jan | Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $5,800 | |
| Accounts Payable - Corporation K | 201 | $5,800 | ||
| (To record the Purchase of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 9-Jan | Cash | 101 | $2,668 | |
| 106.6 | $2,668 | |||
| (To record the Collected accounts receivable) | $5,500 | |||
| 11-Jan | Accounts Receivable—Company AE | 106.1 | $5,500 | |
| Unearned Computer Services Revenue | 236 | $1,500 | ||
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $7,000 | ||
| ( To record the Completed work on project) | ||||
| 13-Jan | Accounts Receivable—Corporation L | 106.5 | $5,200 | |
| Sales | 413 | $5,200 | ||
| (To record the merchandise sold on credit.) | ||||
| 13-Jan | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $3,560 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $3,560 | ||
| ( To Record the cost of January 13 sale) | ||||
| 15-Jan | Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $600 | |
| Cash | 101 | $600 | ||
| ( To record the freight paid on incoming merchandise) | ||||
| 16-Jan | Cash | 101 | $4,000 | |
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $4,000 | ||
| (To record the cash collected revenue from customer) | ||||
| 17-Jan | Accounts Payable - Corporation K | 201 | $5,800 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $58 | ||
| Cash | 101 | $5,742 | ||
| (To record the payment of account payable within discount period) | ||||
| 20-Jan | Sales Returns and Allowances | 414 | $500 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation L | 106.5 | $500 | ||
| ( To record the defective goods returned from customers) | ||||
| 22-Jan | Cash | 101 | $4,653 | |
| Sales Discounts | 415 | $47 | ||
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation L | 106.5 | $4,700 | ||
| (To record the Collections from accounts receivable) | ||||
| 24-Jan | Accounts Payable | 201 | $496 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $496 | ||
| (To record the return of merchandise for credit) | ||||
| 26-Jan | Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $9,000 | |
| Accounts Payable - Corporation K | 201 | $9,000 | ||
| ( To record the purchase of merchandise for resale) | ||||
| 26-Jan | Accounts Receivable—Incorporation KC | 106.8 | $5,800 | |
| Sales | 413 | $5,800 | ||
| (To record the merchandise sold on credit) | ||||
| 26-Jan | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $4,640 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $4,640 | ||
| ( To record the cost of January 26 sales) | ||||
| 31-Jan | Wages Expense | 623 | $1,250 | |
| Cash | 101 | $1,250 | ||
| ( To record the payment of employee wages) | ||||
| 1-Feb | Prepaid Rent | 131 | $2,475 | |
| Cash | 101 | $2,475 | ||
| ( To record the payment of three months’ rent in advance) | ||||
| 3-Feb | Accounts Payable | 201 | $8,504 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $90 | ||
| Cash | 101 | $8,414 | ||
| (To record the payment of account payable within discount period) | ||||
| 5-Feb | Advertising Expense | 655 | $600 | |
| Cash | 101 | $600 | ||
| ( To record the payment for advertising expense) | ||||
| 11-Feb | Cash | 101 | $5,500 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Company AE | 106.1 | $5,500 | ||
| ( To record the collection of cash from customers) | ||||
| 15-Feb | Dividends | 319 | $4,800 | |
| Cash | 101 | $4,800 | ||
| (To record the payment of dividends) | ||||
| 23-Feb | Accounts Receivable—Corporation D | 106.7 | $3,220 | |
| Sales | 413 | $3,220 | ||
| ( To record the sale of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 23-Feb | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $2,660 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $2,660 | ||
| ( To record the cost of February 23 sales) | ||||
| 26-Feb | Wages Expense | 623 | $1,000 | |
| Cash | 101 | $1,000 | ||
| ( To record the payment of wages to employee) | ||||
| 27-Feb | Mileage Expense | 676 | $192 | |
| Cash | 101 | $192 | ||
| (To record the Reimbursement of business mileage) | ||||
| 8-Mar | Computer Supplies | 126 | $2,730 | |
| Accounts Payable-Company H | 201 | $2,730 | ||
| ( To record the purchase of supplies on credit) | ||||
| 9-Mar | Cash | 101 | $3,220 | |
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation D | 106.7 | $3,220 | ||
| ( To record the collection of accounts receivable) | ||||
| 11-Mar | Repairs Expense–Computer | 684 | $960 | |
| Cash | 101 | $960 | ||
| (To record the payment for computer repairs) | ||||
| 16-Mar | Cash | 101 | $5,260 | |
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $5,260 | ||
| ( To record the collection cash revenue from customer) | ||||
| 19-Mar | Accounts Payable | 201 | $3,830 | |
| Cash | 101 | $3,830 | ||
| ( To record the payment of accounts payable | ||||
| 24-Mar | Accounts Receivable—Company EL | 106.3 | $9,047 | |
| Computer Services Revenue | 403 | $9,047 | ||
| (To record the billed customer for services) | ||||
| 25-Mar | Accounts Receivable—Company WS | 106.2 | $2,800 | |
| Sales | 413 | $2,800 | ||
| ( To record the sale of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 25-Mar | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $2,002 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $2,002 | ||
| ( To record the cost of sales of March 25 ) | ||||
| 30-Mar | Accounts Receivable—Company IFM | 106.4 | $2,220 | |
| Sales | 413 | $2,220 | ||
| ( To record the sale of merchandise on credit) | ||||
| 30-Mar | Cost of Goods Sold | 502 | $1,048 | |
| Merchandise Inventory | 119 | $1,048 | ||
| ( To record the cost of sales of March 30 ) | ||||
| 31-Mar | Mileage Expense | 676 | $128 | |
| Cash | 101 | $128 | ||
| (To record the Reimbursement of business mileage) | ||||
Table (1)
2.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Account: A record, that documents or records the change in assets, liabilities, or equity for a particular period, is referred to as an account.
| Cash No. 101 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | $48,372 | ||||
| 4-Jan | $625 | $47,747 | |||
| 5-Jan | $25,000 | $72,747 | |||
| 9-Jan | $2,668 | $75,415 | |||
| 15-Jan | $600 | $74,815 | |||
| 16-Jan | $4,000 | $78,815 | |||
| 17-Jan | $5,742 | $73,073 | |||
| 22-Jan | $4,653 | $77,726 | |||
| 31-Jan | $1,250 | $76,476 | |||
| 1-Feb | $2,475 | $74,001 | |||
| 3-Feb | $8,414 | $65,587 | |||
| 5-Feb | $600 | $64,987 | |||
| 11-Jan | $5,500 | $70,487 | |||
| 15-Feb | $4,800 | $65,687 | |||
| 26-Feb | $1,000 | $64,687 | |||
| 27-Feb | $192 | $64,495 | |||
| 9-Mar | $3,220 | $67,715 | |||
| 11-Mar | $960 | $66,755 | |||
| 16-Mar | $5,260 | $72,015 | |||
| 19-Mar | $3,830 | $68,185 | |||
| 31-Mar | $128 | $68,057 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company AE No. 106.1 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 11-Jan | $5,500 | $5,500 | |||
| 11-Feb | $5,500 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company WS No. 106.2 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,800 | $2,800 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company EL No. 106.3 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 24-Mar | $9,047 | $9,047 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company IFM No. 106.4 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $3,000 | |||
| 30-Mar | $2,220 | $5,220 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Corporation L No. 106.5 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 13-Jan | $5,200 | $5,200 | |||
| 20-Jan | $500 | $4,700 | |||
| 22-Jan | $4,700 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company G 106.6 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $2,668 | |||
| 9-Jan | $2,668 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Company D No. 106.7 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 23-Feb | $3,220 | $3,220 | |||
| 9-Mar | $3,220 | $0 | |||
| Accounts Receivable—Incorporation KC No. 106.8 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 26-Jan | $5,800 | $0 | $5,800 | ||
| Accounts Receivable—Incorporation D No. 106.8 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| Merchandise inventory—Incorporation D No. 119 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $0 | |||
| 7-Jan | $5,800 | $5,800 | |||
| 13-Jan | $3,560 | $2,240 | |||
| 15-Jan | $600 | $2,840 | |||
| 17-Jan | $58 | $2,782 | |||
| 24-Jan | $496 | $2,286 | |||
| 26-Jan | $9,000 | $11,286 | |||
| 26-Jan | $4,640 | $6,646 | |||
| 3-Feb | $90 | $6,556 | |||
| 23-Feb | $2,660 | $3,896 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,002 | $1,894 | |||
| 30-Mar | $1,048 | $846 | |||
| Compute supplies No. 126 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $580 | |||
| 8-Mar | Balance | $2,730 | $3,310 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance No. 128 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,665 | |||
| Prepaid Rent No. 131 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $825 | |||
| 1-Feb | $2,475 | $3,300 | |||
| Office equipment No. 163 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $8,000 | |||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $400 | |||
| Computer equipment No. 167 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $20,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation- Computer equipment No. 168 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,250 | |||
| Accounts payable No. 201 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,100 | |||
| 7-Jan | Balance | $5,800 | $6,900 | ||
| 17-Jan | Balance | $5,800 | $1,100 | ||
| 24-Jan | Balance | $496 | $604 | ||
| 26-Jan | Balance | $9,000 | $9,604 | ||
| 3-Feb | Balance | $8,504 | $1,100 | ||
| 8-Mar | Balance | $2,730 | $3,830 | ||
| 9-Mar | Balance | $3,830 | $0 | ||
| Wages payable No. 210 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $500 | |||
| 4-Jan | $500 | $0 | |||
| Unearned computer services revenue No. 236 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $1,500 | |||
| 11-Jan | $1,500 | $0 | |||
| Common stock No. 307 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $73,000 | |||
| 5-Jan | $25,000 | $98,000 | |||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 31-Dec | Balance | $7,360 | |||
| Dividends No. 319 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 15-Feb | $4,800 | $4,800 | |||
| Computer services revenue No. 403 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 11-Jan | $7,000 | $7,000 | |||
| 16-Jan | $4,000 | $11,000 | |||
| 16-Mar | $5,260 | $16,260 | |||
| 24-Mar | $9,047 | $25,307 | |||
| Sales No. 413 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 13-Jan | $5,200 | $5,200 | |||
| 26-Jan | $5,800 | $11,000 | |||
| 23-Feb | $3,220 | $14,220 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,800 | $17,020 | |||
| 30-Mar | $2,220 | $19,240 | |||
| Sales returns and allowances No. 414 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 20-Jan | $500 | $500 | |||
| Sales discounts No. 415 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 20-Jan | $47 | $0 | $47 | ||
| Cost of goods sold No. 502 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 13-Jan | $3,560 | $3,560 | |||
| 26-Jan | $4,640 | $8,200 | |||
| 23-Feb | $2,660 | $10,860 | |||
| 25-Mar | $2,002 | $12,862 | |||
| 30-Mar | $1,048 | $13,910 | |||
| Depreciation expense - Office equipment No. 612 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Depreciation expense - Computer equipment No. 613 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Wages expense No. 623 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 4-Jan | $125 | $125 | |||
| 31-Jan | $1,250 | $1,375 | |||
| 26-Feb | $1,000 | $2,375 | |||
| Insurance expense No. 637 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Rent expense No. 640 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Computer supplies expense No. 652 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Advertising expense No. 655 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 5-Feb | $600 | $600 | |||
| Mileage expense No. 676 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 27-Feb | $192 | $192 | |||
| 31-Mar | $128 | $320 | |||
| Miscellaneous Expenses No. 677 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| Repairs Expense—Computer No. 684 | |||||
| Date | PR | Debit | Credit | Balance | |
| 11-Mar | $960 | $960 | |||
3.
Prepare a partial worksheet of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: A worksheet is the summarized form of accounting information which is made in order to ensure that the accounts are made properly.
Prepare a partial worksheet of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
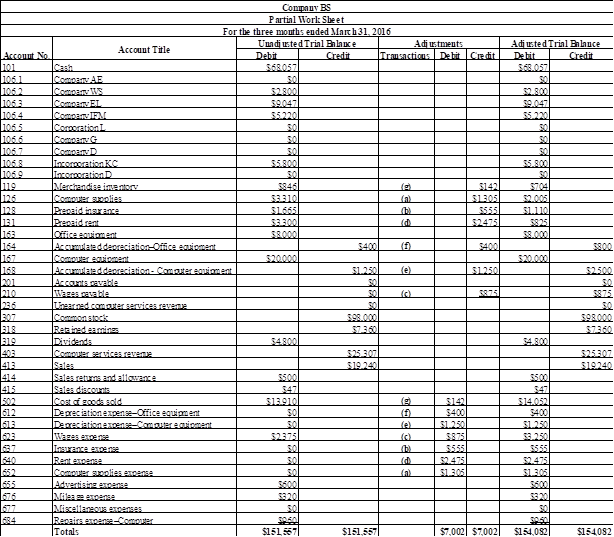
Table (2)
4.
Prepare a single step income statement of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare a statement of income of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
| Company BS | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the three months ended March 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenues | ||
| Computer services revenue | $25,307 | |
| Net sales (1) | $18,693 | |
| Total revenues | $44,000 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold | $14,052 | |
| $400 | ||
| Depreciation expense—Computer equipment | $1,250 | |
| Wages expense | $3,250 | |
| Insurance expense | $555 | |
| Rent expense | $2,475 | |
| Computer supplies expense | $1,305 | |
| Advertising expense | $600 | |
| Mileage expense | $320 | |
| Repairs expense—Computer | $960 | |
| Total expenses | ($25,167) | |
| Net income | $18,833 | |
Table (3)
The net income of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016 is $18,833.
Working note:
Calculate the amount of net sales:
5.
Prepare a statement of retained earnings of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of retained earnings: This is an equity statement which shows the changes in the
Prepare a statement of retained earnings of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
| Company BS | ||
| Statement of Retained earnings | ||
| For the three months ended March 31, 2016 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Retained earnings as on December 31, 2015 | $7,360 | |
| Add: Net income | $26,193 | |
| $33,553 | ||
| Less: Dividends | ($4,800) | |
| Retained earnings as on March 31, 2016 | $21,393 | |
Table (4)
The retained earnings of Company BS for the three months ended March 31, 2016 is $21,393.
6.
Prepare a classified
6.
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet: The main elements of balance sheet assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity are categorized or classified further into sections in a classified balance sheet. Assets are further classified as current assets, long-term investments, property, plant, and equipment (PPE), and intangible assets. Liabilities are classified into two sections current and long-term. Stockholders’ equity comprises of common stock and retained earnings. Thus, the classified balance sheet includes all the elements under different sections.
Prepare a classified balance sheet as of March 31, 2016.
| Company BS | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As of March 31, 2016 | ||
| Assets | Amount | Amount |
| Current assets | ||
| Cash | $68,057 | |
| Accounts receivable (2) | $22,867 | |
| Merchandise inventory | $704 | |
| Computer supplies | $2,005 | |
| Prepaid insurance | $1,110 | |
| Prepaid rent | $825 | |
| Total current assets | $95,568 | |
| Plant assets | ||
| Office equipment | $8,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation—Office equipment | ($800) | $7,200 |
| Computer equipment | $20,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation—Computer equipment | ($2,500) | $17,500 |
| Total plant assets | $24,700 | |
| Total assets | $120,268 | |
| Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Current liabilities | ||
| Wages payable | $875 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common stock | $98,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $21,393 | |
| Total equity | $119,393 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $120,268 | |
Table (5)
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ACCT 2301 >IC<
- I need help with this general accounting question using the proper accounting approach.arrow_forwardDuring 2018, the band Maroon 5 is touring across the U.S. on its "Red Pill Blues Tour 2018." Two of those concerts, on October 14 and 15, will be held at Madison Square Garden in New York City. Madison Square Garden has a seating capacity for concerts of approximately 19,000. According to a Business Insider article in December 2016, Maroon 5 had an average concert ticket price of $165.Assume that these two Madison Square Garden concerts were sold out on the first day the tickets were available for sale to the public, November 4, 2017. Also assume, for the sake of simplicity, that all tickets are sold directly by Maroon 5.Question:How will Maroon 5's balance sheet and income statement be impacted by the sale of the Madison Square Garden tickets on November 4, 2017 and what specific accounts will be impacted and will it increase ir decrease.arrow_forwardAccounting problem with helparrow_forward
- What are rangoons profit margin and debt ratio?arrow_forwardQuestion: When will Maroon 5 recognize revenue from its 2018 concerts at Madison Square Garden in New York City?During 2018, the band Maroon 5 is touring across the U.S. on its "Red Pill Blues Tour 2018." Two of those concerts, on October 14 and 15, will be held at Madison Square Garden in New York City. Madison Square Garden has a seating capacity for concerts of approximately 19,000. According to a Business Insider article in December 2016, Maroon 5 had an average concert ticket price of $165.Assume that these two Madison Square Garden concerts were sold out on the first day the tickets were available for sale to the public, November 4, 2017. Also assume, for the sake of simplicity, that all tickets are sold directly by Maroon 5.arrow_forwardI want to this question answer for General accounting question not need ai solutionarrow_forward
- Greenfield Company has current liabilities of $60,000 and long-term liabilities of $90,000. It also has $80,000 in common stock and $40,000 in retained earnings. Calculate Greenfield's debt-to-equity ratio.arrow_forwardCan you explain the correct methodology to solve this general accounting problem?arrow_forwardNot use ai solution for accounting questionarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





