
Subpart (a):
The consumer surplus , total surplus and deadweight loss .
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
Figure -1 illustrates the
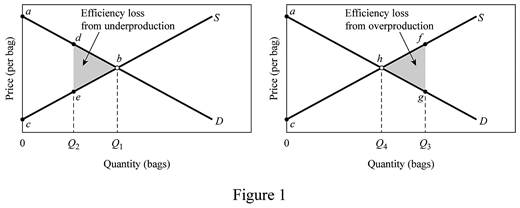
In figure -1 panel (a) and (b), the horizontal axis measures the quantity of bags and the vertical axis measures the
The inverse demand function can be derived as follows:
The inverse demand functions of
The inverse supply curve can be calculated as follows:
The inverse supply functions of
The inverse demand function and supply functions reveal that the producer willing price is $5 and the consumer willing price is $85. The equilibrium price is $45. The total surplus can be calculated as follows:
The total surplus is $800.
The consumer surplus can be calculated as follows:
The consumer surplus is $400.
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable charge of a product that the consumer intends to pay and the actual price that he has already paid.
Subpart (b):
The consumer surplus, total surplus and deadweight loss.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The consumer willing price at Q2 level of output (15 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q2 level of output to the inverse demand function.
The consumer new willing price is $55.
The producer willing price at Q2 level of output (15 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q2 level of output into the inverse supply function.
The producer’s new willing price is $35.
The deadweight loss can be calculated as follows:
The deadweight loss is $50.
The total surplus can be calculated as follows:
The total surplus is $750.
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable charge of a product that the consumer intends to pay and the actual price that he has already paid.
Producer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable price that the producer intends to sell and the actual price that he has already sold.
Subpart c):
The consumer surplus, total surplus and deadweight loss.
Subpart c):
Explanation of Solution
The consumer willing price at Q3 level of output (27 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q3 level of output to the inverse demand function.
The consumer new willing price is $31.
The producer willing price at Q3 level of output (127 units) can be calculated by substituting the Q3 level of output to the inverse supply function.
The producer new willing price is $59.
The deadweight loss can be calculated as follows:
The deadweight loss is $98.
The total surplus can be calculated as follows:
The total surplus is $702.
Concept Introduction:
Consumer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable charge of a product that the consumer intends to pay and the actual price that he has already paid.
Producer surplus: It refers to the variation in the probable price that the producer intends to sell and the actual price that he has already sold.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
MICROECONOMICS(LL)COMPANION
- how to solve the attachment?arrow_forwardProblem 3-ABC Challenges: Attrition, Balance and ComplianceCan television inform people about public affairs? Political scientists Bethany Albertson and Adria Lawrence (2009) conducted an experiment in which they randomly assigned people to treatment and control groups to evaluate the effect of watching TV on a person’s information level. Those assigned to the treatment group were told to watch a specific television broadcast and were later asked questions related to what they watched. Those in the controlgroup were not shown the TV broadcast but were asked questions related to the material in the TV broadcast. The dataset contains the following variables: : Dummy variable which =1 if a person reads news and 0 otherwise. : interest in political affairs (not interested=1 to very interested=4) : years of education : female dummy variable (female=1; male=0) : family income in thousands of dollars : information level (low information level=1 to high information level=4) =1 if the…arrow_forwardProblem 2-Experiments/Randomized Control Trial Suppose you are interested in studying the effect of academic counselling on the years it takes for a student to obtain an undergraduate degree. You conduct a randomized control trial to answer the question. You randomly assign 2500 individuals in a university in New York to receive academic counselling and 2500 students to not receive any academic counselling. a. Which people are a part of the treatment group and which people are a part of thecontrol group? b. What regression will you run? Define the variables where required. c. Suppose you estimate = -0.3. Interpret it. d. You test for balance using the variables mentioned in the table below. Based on the results do you think that the treatment and control group are balanced? If your answer is “yes” then explain why. If your answer is “no”, then explain why and mention how will you address the issue of imbalance. e. Suppose that some unmotivated students in the control group decided to…arrow_forward
- How to calculate total cost?arrow_forwardProblem 1-Experiments/Randomized Control TrialSuppose you are interested in studying the effect of being a part of the labor union on anindividual’s hourly wage.You collect data on 1000 people and run the following regression. where is a dummy variable which is equal t to 1 for people who are a part of labor union and0 for others. a. Suppose you estimate . Interpret b. Do you think is biased or unbiased? Explain. Now suppose you conduct a randomized control trial to answer the same question. Yourandomly assign some individuals to be a part of the labor union and others to not be a partof the labor union. The first step you take is to ensure that the randomization was donecorrectly. Then you estimate the following equation: =1 if the student is assigned to be a part of Labor Union=0 if the student is assigned to not be a part of Labor Union c. Why is it important to ensure that the randomization is done correctly? d. Name any two variables that you can use to test if Treatment and…arrow_forwardWhat is kiosk?arrow_forward
- If food is produced in the U.S., sold in the U.S. and consumed in the U.S., a reduction in its price will have which of the following effects ______? Two of the answers are correct. The consumer price index will decrease. None of the answers are correct. The GDP deflator will decrease.arrow_forwardhow to caculate verible cost?arrow_forwardWhat is the deficit?arrow_forward
- Identify the two curves shown on the graph, and explain their upward and downward slopes. Why does curve Aintersect the horizontal axis? What is the significance of quantity d? What does erepresent? How would the optimal quantity of information change if the marginal benefit of information increased—that is, if the marginal benefit curve shifted upward?arrow_forward6. Rent seeking The following graph shows the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves for a single-price monopolist that produces a drug that helps relieve arthritis pain. Place the grey point (star symbol) in the appropriate location on the graph to indicate the monopoly outcome such that the dashed lines reveal the profit-maximizing price and quantity of a single-price monopolist. Then, use the green rectangle (triangle symbols) to show the profits earned by the monopolist. 18 200 20 16 16 14 PRICE (Dollars per dose) 12 10 10 8 4 2 MC = ATC MR Demand 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Millions of doses per year) Monopoly Outcome Monopoly Profits Suppose that should the patent on this particular drug expire, the market would become perfectly competitive, with new firms immediately entering the market with essentially identical products. Further suppose that in this case the original firm will hire lobbyists and make donations to several key politicians to extend its…arrow_forwardConsider a call option on a stock that does not pay dividends. The stock price is $100 per share, and the risk-free interest rate is 10%. The call strike is $100 (at the money). The stock moves randomly with u=2 and d=0.5. 1. Write the system of equations to replicate the option using A shares and B bonds. 2. Solve the system of equations and determine the number of shares and the number of bonds needed to replicate the option. Show your answer with 4 decimal places (x.xxxx); do not round intermediate calculations. This is easy to do in Excel. A = B = 3. Use A shares and B bonds from the prior question to calculate the premium on the option. Again, do not round intermediate calculations and show your answer with 4 decimal places. Call premium =arrow_forward




 Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning





