
1.
To prepare: The
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Prepare the journal entries for the transactions that occurred from January 1 to January 31:
|
Date |
Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January 1 |
Prepaid insurance (A+) |
5,700 |
||
| Cash (A-) | 5,700 | |||
| (To record the cash paid for the insurance expense) | ||||
| January 2 |
Prepaid rent |
4,200 |
||
| Cash (A-) | 4,200 | |||
| (To record the payment of prepaid rent) | ||||
| January 3 |
Cash (A+) |
30,000 |
||
| Notes payable (L+) | 30,000 | |||
| (To record the note payable) | ||||
| January 4 |
Equipment (A+) |
24,000 |
||
| Cash (A–) | 24,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of an equipment) | ||||
| January 5 |
Cash (A+) |
6,000 |
||
| Common stock (SE+) | 6,000 | |||
| (To record the cash invested in common stock) | ||||
| January 6 |
Supplies (A+) |
1,000 |
||
| Accounts payable (L+) | 1,000 | |||
| (To record the additional purchase of supplies) | ||||
| January 7 |
Cash (A+) |
600 |
||
| Accounts receivable (A-) | 600 | |||
| (To record the accounts receivable) | ||||
|
January 8 |
Accounts payable (L-) |
400 |
||
| Cash (A-) | 40 | |||
| (To record the accounts payable) | ||||
| January 9 |
Accounts receivable (A+) |
10,400 |
||
| Service revenue (R+) (SE+) | 10,400 | |||
| (To record the service provided to the customer on account) | ||||
| January 10 |
Cash (A+) |
7,600 |
||
| Service revenue (R+) (SE+) | 7,600 | |||
| (To record the cash received for the service performed) | ||||
| January 16 |
Salaries and wages expense (E+) (SE-) |
2,200 |
||
| Cash (A-) | 2,200 | |||
| (To record the payment of salaries and wages) | ||||
| January 20 |
Cash (A+) |
3,500 |
||
| Unearned revenue (L+) | 3,500 | |||
| (To record the unearned revenue) | ||||
| January 25 |
Cash (A+) |
4,500 |
||
| Accounts receivable (A-) | 4,500 | |||
| (To record the collection of cash from customer for service provided before) | ||||
Table (1)
2.
To prepare: the T-Accounts using the beginning balances that are given in the January 1
2.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability,
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- The title of the account
- The left or debit side
- The right or credit side
Prepare the T-Accounts:
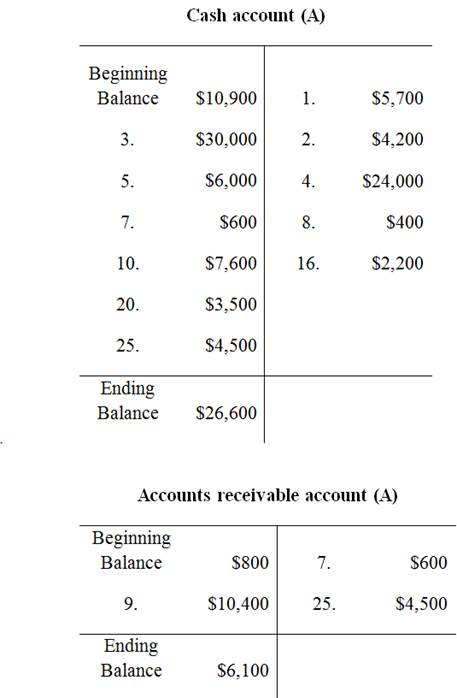
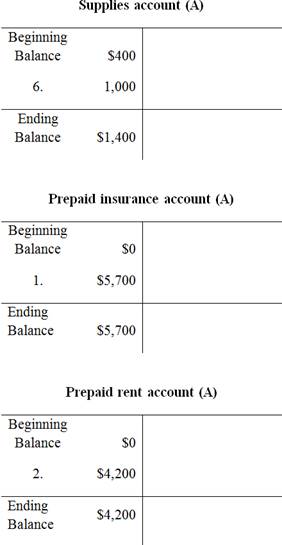
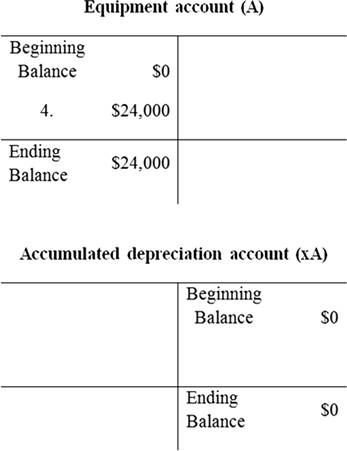

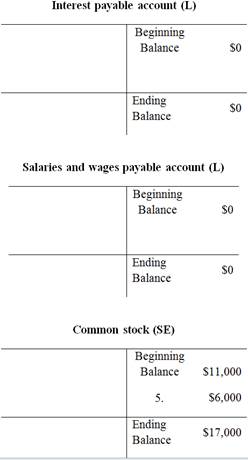
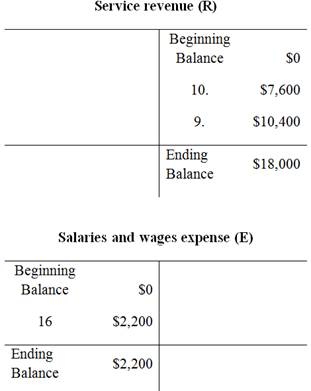
Unadjusted
Unadjusted trial balance is that statement which contains complete list of accounts with their unadjusted balances. This statement is prepared at the end of every financial period.
Prepare the unadjusted trial balance:
| Incorporation FD | ||
| Unadjusted trial balance | ||
| As on 31st January | ||
| Account titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 26,600 | |
| Accounts receivable | 6,100 | |
| Supplies | 1,400 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 5,700 | |
| Prepaid rent | 4,200 | |
| Equipment | 24,000 | |
| 0 | ||
| Accounts payable | 1,100 | |
| Unearned revenue | 3,500 | |
| Notes payable | 30,000 | |
| Salaries and wages payable | 0 | |
| Interest payable | 0 | |
| Commonstock | 17,000 | |
| 600 | ||
| Service revenue | 18,000 | |
| Salaries and wages expense | 2,200 | |
| Supplies expense | 0 | |
| Depreciation expense | 0 | |
| Interest expense | 0 | |
| Total | 70,200 | 70,200 |
Table (2)
The debit column and credit column of the unadjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $70,200.
3.
To record: The adjusting journal entries that are needed at 31st January.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries are those entries which are made at the end of the accounting period, to record the revenues in the period of which they have been earned and to record the expenses in the period of which have been incurred, as well as to update all the balances of assets and liabilities accounts on the balance sheet, and to ascertain accurate amount of net income (loss) on the income statement to maintain the records according to the accrual basis principle.
Record the adjusting journal entries:
|
Date |
Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| January 31 |
a. |
Utilities Expense (E+, SE-) |
1,200 |
|
| Accounts payable (L+) | 1,200 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for utilities expense)) | ||||
| January 31 |
b. |
Supplies expense (E+) (SE-) |
1,150 |
|
| Supplies (A-) | 1,150 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for supplies expense) | ||||
| January 31 |
c. |
Unearned revenue (L-) |
2,100 |
|
| Service revenue (R+) (SE+) | 2,100 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for unearned revenue) | ||||
| January 31 |
d. |
Interest expense (E+) (SE-) |
150 |
|
| Interest payable (L+) | 150 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for interest expense) | ||||
| January 31 |
e. |
|
500 |
|
| Accumulated depreciation- Equipment (xA+) (A-) |
500 |
|||
| (To record the adjusting entry for accumulated depreciation) | ||||
| January 31 |
f. |
Salaries and wages expense (E+) (SE-) |
2,200 |
|
| Salaries and wages payable (L+) | 2,200 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for salaries and wages expense) | ||||
| January 31 |
g. |
Insurance expense (E+) (SE-) |
475 |
|
| Prepaid insurance (A-) | 475 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for insurance expense) | ||||
| January 31 |
g. |
Rent expense (E+) (SE-) |
350 |
|
| Prepaid rent (A-) | 350 | |||
| (To record the adjusting entry for insurance expense) | ||||
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of supplies expense:
Calculate the amount of unearned revenue:
Calculate the amount of interest expense:
Calculate the amount of depreciation expense:
Calculate the amount of Insurance expense:
Calculate the amount of rent expense:
4.
To prepare: The T-Account from the requirement 3 for the adjusting journal entries.
4.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholders’ equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- The title of the account
- The left or debit side
- The right or credit side
Prepare the T-Accounts:

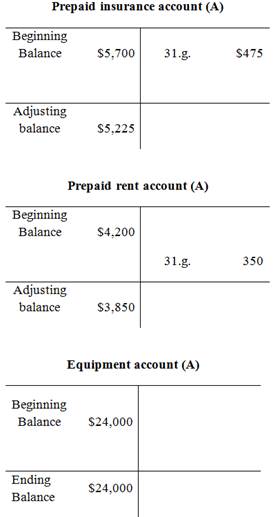
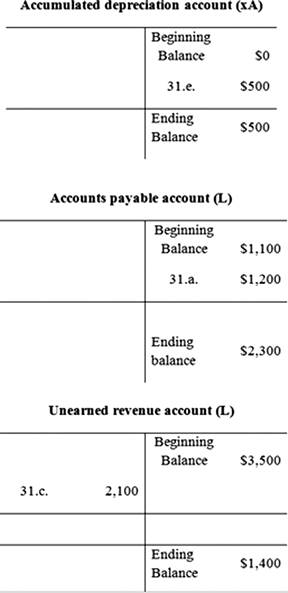
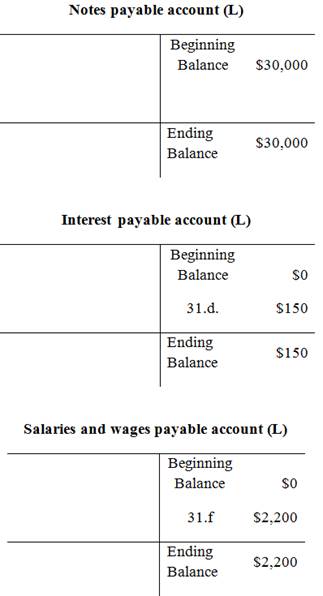
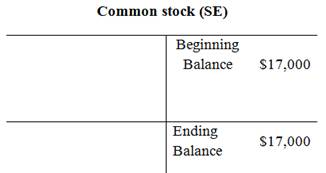
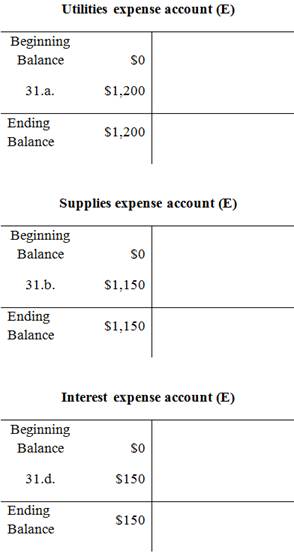
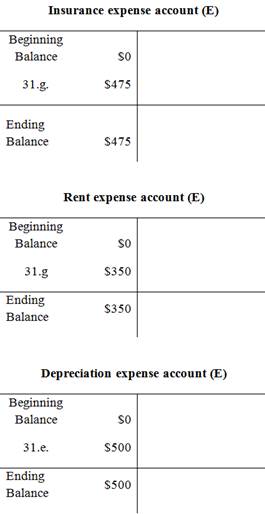
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is that statement which contains complete list of accounts with their adjusted balances, after all relevant adjustments have been made. This statement is prepared at the end of every financial period.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance:
| Incorporation FD | ||
| Adjusted trial balance | ||
| As on 31st January | ||
| Account titles | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 26,600 | |
| Accounts receivable | 6,100 | |
| Supplies | 250 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 3,850 | |
| Prepaid rent | 5,225 | |
| Equipment | 24,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | 500 | |
| Accounts payable | 2,300 | |
| Unearned revenue | 1,400 | |
| Notes payable | 2,200 | |
| Salaries and wages payable | 150 | |
| Interest payable | 30,000 | |
| Commonstock | 17,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 600 | |
| Service revenue | 20,100 | |
| Salaries and wages expense | 4,400 | |
| Utilities expense | 1,200 | |
| Supplies expense | 1,150 | |
| Depreciation expense | 500 | |
| Insurance expense | 475 | |
| Rent expense | 350 | |
| Interest expense | 150 | |
| Total | 74,250 | 74,250 |
Table (4)
The debit column and credit column of the adjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $74,250.
5.
To prepare: The income statement for the month ended 31st January.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement:
| Incorporation FD | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the month end 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount( $) | Amount ($) |
| Revenue | ||
| Service revenue | 20,100 | |
| Total revenue(A) | 20,100 | |
| Expense | ||
| Salaries and wages | 4,400 | |
| Utilities | 1,200 | |
| Supplies | 1,150 | |
| Depreciation | 500 | |
| Insurance | 475 | |
| Rent | 350 | |
| Interest expense | 150 | |
| Total expense (B) | 8,225 | |
| Net income
|
11,875 | |
Table (5)
Thus the income statement of Incorporation FD is prepared and it shows the net income of $11,875.
Statement of retained earnings:
This is an equity statement which shows the changes in the stockholders’ equity over a period of time.
Prepare the statement of retained earnings:
| Incorporation FD | ||
| Statement of Retained earnings | ||
| For the month end 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount( $) | Amount ($) |
| Retained earnings, beginning | 600 | |
| Add: Net income | 11,875 | |
| Less:Dividends | 0 | |
| Retained earnings, end | 12,475 | |
Table (6)
Hence, the statement of retained earnings is prepared and the ending retained earnings are $12,475.
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Prepare the classified balance sheet:
| Incorporation FD | ||
| Classified balance sheet | ||
| As on 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| current asset: | ||
| Cash | 26,600 | |
| Accounts receivable | 6,100 | |
| Supplies | 250 | |
| Prepaid rent | 3,850 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 5,225 | |
| Total current assets | 42,025 | |
| Non-current assets | ||
| Equipment | 24,000 | |
| Accumulated depreciation-equipment net | 500 | |
| Total non-current asset | 24,500 | |
| Total assets | 65,525 | |
| Liabilities and stock holders' equity: | ||
| Current liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | 2,300 | |
| Unearned revenue | 1,400 | |
| Salaries and wages payable | 2,200 | |
| Interest payable | 150 | |
| Total current liabilities | 6,050 | |
| Non-current liabilities: | ||
| Notes payable | 30,000 | |
| Total non-current liabilities | 30,000 | |
| Total liabilities | 36,050 | |
| Stock holders' equity | 17,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 12,475 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | 29,475 | |
| Total liabilities and stock holders' equity | 65,525 | |
Table (7)
Hence, the classified balance sheet is prepared and the total assets and total liabilities and stockholders’ equity is $65,525.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Connect 1 Semester Access Card for Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
- Don't use ai given answer accounting questionarrow_forwardLakeshore Technologies requires $900,000 in assets and will be 100% equity financed. If the Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) is $72,000 and the tax rate is 30%, what is the Return on Equity (ROE)?arrow_forwardAt Boston Industries, as of September 30, the company has net sales of $750,000 and a cost of goods available for sale of $620,000. Compute the estimated cost of the ending inventory, assuming the gross profit rate is 35%.arrow_forward
- I am looking for a step-by-step explanation of this financial accounting problem with correct standards.arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and accountingarrow_forwardTremont Manufacturing produced 3,500 units of finished goods requiring 15,400 actual hours at $18.75 per hour. The standard is 4.2 hours per unit of finished goods, at a standard rate of $19.00 per hour. Which of the following statements is true? a. The labor efficiency variance is $2,470 unfavorable. b. The total labor variance is $4,850 favorable. c. The labor rate variance is $3,850 favorable. d. The labor rate variance is $2,310 unfavorable. e. The labor efficiency variance is $4,940 favorable.arrow_forward
- Please show me the correct approach to solving this financial accounting question with proper techniques.arrow_forwardPlease explain this financial accounting problem by applying valid financial principles.arrow_forwardLatifah Industries incurs $12 in variable costs and $5 in allocated fixed costs to produce a product that sells for $28 per unit. A buyer in Mexico offers to purchase 2,400 units at $18 each. Latifah Industries has excess capacity and can handle the additional production. What effect will acceptance of the offer have on net income?arrow_forward
 Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning




