
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The equilibrium constant for interconversion of given
Concept introduction:
The free energy diagram of a reaction is the plot of standard free energy versus reaction coordinate or reaction progress. The products and reactants are placed at their respective free energy. The difference in the free energy of products and reactants is the standard free energy of the reaction.
Answer to Problem 4.68AP
The equilibrium constant for interconversion of given alkenes is
The alkene that is more favorable is shown below.
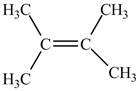
Explanation of Solution
The given alkenes undergoing interconversion along with their free energy of formation are shown below.
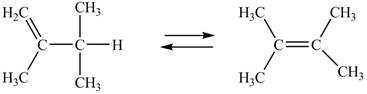
Figure 1
The free energy change for the interconversion of alkenes is equal to the free energy of formation of the product minus the free energy of formation of the reactant.
Substitute the free energy of formation of product alkene and reactant alkene in the equation (1) as shown below.
The Gibbs free energy of the reaction is related to its equilibrium constant by the relation shown below.
Where,
•
•
The value of
Substitute the value of
Rearrange above equation to calculate the
Take the antilog on both sides of the equation as shown below.
The equilibrium constant for the interconversion of alkenes is
The value of equilibrium constant is high, therefore, the alkene on the product is more favored. This can also be understood from the negative value of Gibbs free energy of the reaction which indicates that the reaction is spontaneous. Therefore, alkene on the product side is more favorable which is shown below.
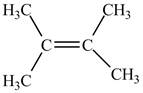
Figure 2
The equilibrium constant for interconversion of given alkenes is
The alkene that is more favorable is shown in Figure 2.
(b)
Interpretation:
The information of the rate at which the interconversion is taking place from the equilibrium constant value is to be stated.
Concept introduction:
The equilibrium constant of the reaction gives information about the
Answer to Problem 4.68AP
The rate of interconversion of alkene is moderate. The rate of forward reaction is
Explanation of Solution
The equilibrium constant in terms of the concentration of reactant alkene and product alkene is shown below.
The value of the equilibrium constant is
Substitute the value of the equilibrium constant in the above expression.
The concentration of product alkene at equilibrium is only
The equilibrium constant of the reaction is the ratio of rate constant of forward reaction and backward reaction.
The rate of interconversion of alkene is moderate from the value of the equilibrium constant.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY SAPLING ACCESS + ETEX
- Construct a molecular orbital energy-level diagram for BeH2. Sketch the MO pictures (schematic representation) for the HOMO and LUMO of BeH2 [Orbital Potential Energies, H (1s): -13.6 eV; Be (2s): -9.3 eV, Be (2p): -6.0 eV]arrow_forwardIndicate the isomers of the A(H2O)6Cl3 complex. State the type of isomerism they exhibit and explain it briefly.arrow_forwardState the formula of the compound potassium μ-dihydroxydicobaltate (III) tetraoxalate.arrow_forward
- Consider the reaction of the cyclopentanone derivative shown below. i) NaOCH2CH3 CH3CH2OH, 25°C ii) CH3!arrow_forwardWhat constitutes a 'reference material', and why does its utilization play a critical role in the chemical analysis of food products? Provide examples.arrow_forwardExplain what calibration is and why it is essential in relation to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forward
- The cobalt mu-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forwardThe cobalt mi-hydroxide complex cobaltate(III) of potassium is a dinuclear complex. Correct?arrow_forward3. Arrange the different acids in Exercise B # 2 from the strongest (1) to the weakest acid (10). 1. 2. (strongest) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10 10. (weakest)arrow_forward
- Name Section Score Date EXERCISE B pH, pOH, pка, AND PKD CALCULATIONS 1. Complete the following table. Solution [H+] [OH-] PH РОН Nature of Solution A 2 x 10-8 M B 1 x 10-7 M C D 12.3 6.8 2. The following table contains the names, formulas, ka or pka for some common acids. Fill in the blanks in the table. (17 Points) Acid Name Formula Dissociation reaction Ka pka Phosphoric acid H₂PO₁ H3PO4 H++ H₂PO 7.08 x 10-3 Dihydrogen H₂PO H₂PO H+ HPO 6.31 x 10-6 phosphate Hydrogen HPO₁ 12.4 phosphate Carbonic acid H2CO3 Hydrogen HCO 6.35 10.3 carbonate or bicarbonate Acetic acid CH,COOH 4.76 Lactic acid CH₂CHOH- COOH 1.38 x 10 Ammonium NH 5.63 x 10-10 Phenol CH₂OH 1 x 10-10 Protonated form CH3NH3* 3.16 x 10-11 of methylaminearrow_forwardIndicate whether it is true that Co(III) complexes are very stable.arrow_forwardMnO2 acts as an oxidant in the chlorine synthesis reaction.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





