
Concept explainers
A ball is thrown with an initial speed υi at an angle θi with the horizontal. The horizontal range of the ball is R. and the ball reaches a maximum height R/6. In terms of R and g, find (a) the time interval during which the ball is in motion, (b) the ball’s speed at the peak of its path, (c) the initial vertical component of its velocity, (d) its initial speed, and (e) the angle θi, (f) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed found in (d) but at the angle appropriate for reaching the greatest height that it can. Find this height. (g) Suppose the ball is thrown at the same initial speed but at the angle for greatest possible range. Find this maximum horizontal range.
(a)
The time interval during which the ball is in motion.
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The time interval during which the ball is in motion is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
The motion of the ball follows the parabolic path and the ball is said to projectile, the motion of the ball is shown in the Figure below.
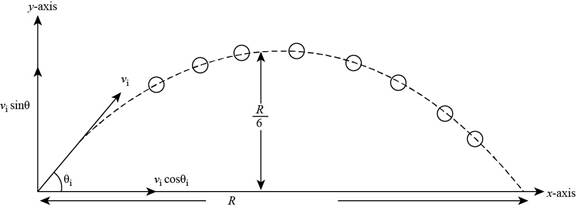
Figure (1)
The formula to calculate the maximum height reached by the projectile is,
Here,
Rearrange the above equation.
Substitute
Thus, the vertical component of the initial velocity is
The formula to calculate the time taken by the ball to reach the ground is,
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the time interval during which the ball is in motion is
(b)
The speed of the ball at the peak of its path.
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The speed of the ball at the peak of its path is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
From part (a) the time of flight is
From the Figure (1) the range of the ball and time of flight is,
Rearrange the above equation.
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the speed of the ball at the peak of its path is
(c)
The initial vertical component of the velocity.
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The initial vertical component of the velocity is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
From part (a) vertical component of the initial velocity is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the initial vertical component of the velocity is
(d)
The initial speed of the ball.
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The initial velocity of the ball is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
From part (a) vertical component of the initial velocity is,
Square both side of the above equation.
And from part (b) the horizontal component of the velocity is
Square both side of the above equation.
Add equation (1) and (2) to find the initial velocity.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the initial velocity of the ball is
(e)
The angle
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The angle
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
From part (a) vertical component of the initial velocity is,
And from part (b) the horizontal component of the velocity is
Take the ratio of the horizontal component and the vertical component of the initial velocity.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle
(f)
The maximum height that the ball can reach with the same initial velocity.
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The maximum height that the ball can reach with the same initial velocity is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
For the maximum height to be gained by the ball the angle made by the horizontal should be
The formula to calculate the maximum height reached by the projectile is,
Here,
Rearrange the above equation.
From part (d) the initial velocity of the ball is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum height that the ball can reach with the same initial velocity is
(g)
The maximum range of the ball with the same initial velocity.
Answer to Problem 4.56AP
The maximum range of the ball with the same initial velocity is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The initial speed of the ball is
For the maximum range to be gained by the ball the angle made by the horizontal should be
The formula to calculate the maximum height reached by the projectile is,
Here,
From part (d) the initial velocity of the ball is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the maximum range of the ball with the same initial velocity is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- ----- vertical diste Section 4.6 Newton's Third Law 31. What upward gravitational force does a 5600-kg elephant exert on Earth?arrow_forward64. Two springs have the same unstretched length but different spring constants, k₁ and k₂. (a) If they're connected side by side and stretched a distance x, as shown in Fig. 4.24a, show that the force exerted by the combination is (k₁ + k₂)x. (b) If they're con- nected end to end (Fig. 4.24b) and the combination is stretched a distance x, show that they exert a force k₁k2x/(k₁ + k₂). www (a) FIGURE 4.24 Problem 65 www (b)arrow_forward65. Although we usually write Newton's second law for one-dimensional motion in the form F =ma, which holds when mass is constant, d(mv) a more fundamental version is F = . Consider an object dt whose mass is changing, and use the product rule for derivatives to show that Newton's law then takes the form F dm = ma + v dtarrow_forward
- If a proton is located on the x-axis in some coordinate system at x0 = -3.2 x 10-5 meters, what is the x-component of the Electric Field due to this proton at a position x = +3.2 x 10-5 meters and on the x axis as the y-axis is 0 giving a number of Newtons/Coulomb?arrow_forwardConsider a single square loop of wire of area A carrying a current I in a uniform magnetic field of strength B. The field is pointing directly up the page in the plane of the page. The loop is oriented so that the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the plane of the page (this means that the normal vector for the loop is always in the plane of the page!). In the illustrations below the magnetic field is shown in red and the current through the current loop is shown in blue. The loop starts out in orientation (i) and rotates clockwise, through orientations (ii) through (viii) before returning to (i). (i) Ø I N - - I N - (iii) (iv) (v) (vii) (viii) a) [3 points] For each of the eight configurations, draw in the magnetic dipole moment vector μ of the current loop and indicate whether the torque on the dipole due to the magnetic field is clockwise (CW), counterclockwise (CCW), or zero. In which two orientations will the loop experience the maximum magnitude of torque? [Hint: Use the…arrow_forwardPlease help with calculating the impusle, thanks! Having calculated the impact and rebound velocities of the ping pong ball and the tennis ball calculate the rebounding impulse: 1.Measure the weight of the balls and determine their mass. Tennis ball: 0.57 kg Ping Pong Ball: 0.00246 kg The impulse, I, is equal to the change in momentum, Pf-Pi. Note the sign change, i.e., going down is negative and up is positive. The unit for momentum is kg-m/s. The change is momentum, impulse, is often givens the equivalent unit of N-S, Newton-Secondarrow_forward
- 5. Three blocks, each with mass m, are connected by strings and are pulled to the right along the surface of a frictionless table with a constant force of magnitude F. The tensions in the strings connecting the masses are T1 and T2 as shown. m T1 T2 F m m How does the magnitude of tension T₁ compare to F? A) T₁ = F B) T₁ = (1/2)F C) T₁ = (1/3)F D) T₁ = 2F E) T₁ = 3Farrow_forwardUsing Coulombs Law, what is the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons?arrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of the gravitational force between 2 protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons using Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation.arrow_forward
- If the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere if there is a distance 25 cm from the person to the sphere using Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force. Give your answer as the number of Coulombs (with no unit label, as usual).arrow_forwardA balloon is rubbed on a sweater, giving the balloon a negative charge by adding an extra 3.9 x 107 electrons compared to its neutral state. What is the magnitude of the net charge on the balloon, in Coulombs?arrow_forwardA ping pong ball and a tennis ball are dropped and there is a very small gap between them when the tennis ball hits the floor. Indicate the directions of the momentums of the ping pong ball and the tennis ball after the tennis ball collides with the floor, but before the balls collide with each other. (Drawing a diagram may be helpful.)arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





