
Concept explainers
Income: $27,350
accounts,
The unadjusted
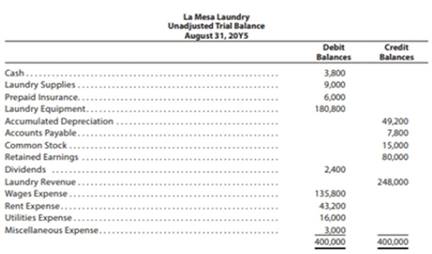
The data needed to determine >ear-end adjustments are as follows:
(a) Wages accrued but not paid at August 31 are $2,200.
(b)
(c) Laundry supplies on hand at August 31 are $2,000.
(d) Insurance premiums expired during the year are $5,300.
Instructions
1. For each account listed in the unadjusted trial balance, enter the balance in a T account. Identify the balance as “Aug. 51 Bal.” In addition, add T accounts for Wages Payable. Depreciation Expense, Laundry Supplies Expense, and Insurance Expense.
2. (Optional) Enter the unadjusted trial balance on an end-of-period spreadsheet and complete the spreadsheet. Add the accounts listed in part (1) as needed.
3. Journalize and post the adjusting entries. Identify the adjustments by “Adj.” and the new balances as “Adj. Bal.”
4. Prepare an adjusted trial balance.
5. Prepare an income statement, a statement of stockholders’ equity, and a
6. Journalize and
7. Prepare a post-closing trial balance.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 4 Solutions
Corporate Financial Accounting
- Can you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardIn 2019, Philip Industries sold 3,800 units at $275 each. Variable costs were $195 per unit, and fixed costs were $120,000. What was Philip Industries' 2019 net income?arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forward
- A machine costs $50,000 with a salvage value of $5,000 and a useful life of 5 years. Calculate the annual depreciation expense using straight-line, double-declining balance, and sum-of-years-digits methods.arrow_forwardNirvana Technologies has $85,000 in assets. They also have $32,000 in liabilities and $8,500 in expenses, and they paid out $10,000 in dividends this year. The extended accounting equation is assets = liabilities + (revenue - (expenses + dividends)). What would their revenue need to be for their accounts to be in balance?arrow_forwardI need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardAbigail Industries uses a perpetual inventory system. Beginning inventory consisted of 600 units at $24 each. During the month, the following transactions occurred: Purchase #1: 800 units at $25; Sale #1: 900 units at $40; Purchase #2: 700 units at $26; Sale #2: 850 units at $42. Using the FIFO method, what is the gross profit for the month?arrow_forward4 MARKSarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub  College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





