
Concept explainers
(a)
Introduction:
Journal entries of P related to its investment in S
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Journal entries
| S. no | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| 1 | Investment in S | $ 203,000 | |
| Cash | $ 203,000 | ||
| (To record investment made in subsidiary company) | |||
| 2 | Cash | $ 20,000 | |
| Investment in S | $ 20,000 | ||
| (To record dividend declared by S) | |||
| 3 | Investment in S | $ 60,000 | |
| Income from S | $ 60,000 | ||
| (To record income generated from S) | |||
| 4 | Income from S | $ 3,000 | |
| Investment in S | $ 3,000 | ||
| (To record amortization expense) |
- Recording the initial investment in S
- Recording P’s share in S co.’s dividend
- Recording P’s share in S co.’s income
- Recording the amortization expense
| Particulars | Amount |
| Acquisition Price(a) | $ 203,000 |
| Net book value of acquisition(b) | $ 150,000 |
| $ 20,000 | |
| Fair value adjustment in Building and equipments (a-b-c) | $ 33,000 |
| Amortization of excess assigned to building and equipment =$33,000/11 | $ 3,000 |
| Calculation of Income of S | ||
| Sales | $ 400,000 | |
| Less: | ||
| COGS | $ 250,000 | |
| $ 15,000 | ||
| Other expenses | $ 75,000 | $ 340,000 |
| $ 60,000 |
(b)
Introduction: Journal entries is a systematic method of recording transactions as and when they occur. It is a summary of transactions divided into the debit and credit items that are recorded chronologically. It is an act of keeping and recording all the transactions occurring in the business.
Consolidation entries to prepare consolidation financial statements
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Consolidation entries
| S.no | Particulars | Debit (in $) | Credit (in$) |
| 1 | Income from subsidiary | 57,000 | |
| Dividends declared | 20,000 | ||
| Investment in S | 37,000 | ||
| (Eliminating entry for rejecting the income from subsidiary) | |||
| 2 | Common stock- S | 50,000 | |
| 100,000 | |||
Differential 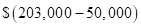 | 53,000 | ||
| Investment in S | 203,000 | ||
| (Eliminating entry for rejecting the investment balance) | |||
| 3 | Building and equipment | 33,000 | |
| Goodwill | 20,000 | ||
| Differential | 53,000 | ||
| (Eliminating entry for assigning the differential) | |||
| 4 | Depreciation expense 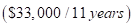 | 3,000 | |
| | 3,000 | ||
| (To record depreciation reclassification) | |||
| 5 | Accounts payable | 16,000 | |
| | 16,000 | ||
| (To record elimination entry of inter-company transactions) |
- Recording the eliminating entry for rejecting the income from subsidiary
- Recording the eliminating entry for rejecting the investment balance
- Recording the eliminating entry for assigning the differential
- Recording the eliminating entry for amortizing the differential
- Recording the eliminating entry for inter corporate receivables and payables
(c)
Introduction: A consolidated worksheet is used to prepare the consolidated financial statements of the parent company and its subsidiary. It reflects the individual values of the parent and the subsidiary and then one consolidated figure for both the entities.
Three part consolidation worksheet for 20X5
(c)
Answer to Problem 4.36P
The consolidated net income is $157,000
The consolidated retained earnings as on December 31, 20X5 is $397,000
The total consolidated assets are $1,269,000
The total consolidated liabilities and equity are $1,269,000
Explanation of Solution
| Consolidated Work paper as on December 31, 20X5 | |||||
| Particulars | P | S | Eliminations | Consolidated | |
| Income statement | Debit | Credit | |||
| Sales | $ 700,000 | $ 400,000 | $ 1,100,000 | ||
| Less: | |||||
| Cost of goods sold | $(500,000) | $(250,000) | $ (750,000) | ||
| Depreciation expense | $ (25,000) | $ (15,000) | $ 3,000 | $ (43,000) | |
| Other expenses | $ (75,000) | $ (75,000) | $ (150,000) | ||
| Income from S' | $ 57,000 | $57,000 | |||
| Net income | $ 157,000 | $ 60,000 | $ 157,000 | ||
| Statement of Retained Earnings | |||||
| Beginning balance | $ 290,000 | $ 100,000 | $100,000 | $ 290,000 | |
| Income, from above | $ 157,000 | $ 60,000 | $ 60,000 | $ 157,000 | |
| Dividends declared | $ (50,000) | $ (20,000) | $(20,000) | $ (50,000) | |
| Ending balance | $ 397,000 | $ 140,000 | $160,000 | $(20,000) | $ 397,000 |
| Assets | |||||
| Cash | $ 82,000 | $ 25,000 | $ 107,000 | ||
| Accounts Receivables | $ 50,000 | $ 55,000 | $ 16,000 | $ 89,000 | |
| Inventory | $ 170,000 | $ 100,000 | $ 270,000 | ||
| Land | $ 80,000 | $ 20,000 | $ 100,000 | ||
| Buildings and equipment | $ 500,000 | $ 150,000 | $ 33,000 | $ 683,000 | |
| Investment in S's stock | $ 240,000 | $ 37,000 | |||
| $203,000 | |||||
| Differential | $ 53,000 | $ 53,000 | |||
| Goodwill | $ 20,000 | $ 20,000 | |||
| Total assets | $1,122,000 | $ 350,000 | $ 1,269,000 | ||
| Liabilities | |||||
| Accumulated Depreciation | $ 155,000 | $ 75,000 | $ 3,000 | $ 233,000 | |
| Accounts payable | $ 70,000 | $ 35,000 | $ 16,000 | $ 89,000 | |
| Mortgages payable | $ 200,000 | $ 50,000 | $ 250,000 | ||
| Common stock: | $ 300,000 | 50,000 | $ 50,000 | $ 300,000 | |
| Retained earnings from above | $ 397,000 | $ 140,000 | $140,000 | $ 397,000 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $1,122,000 | $ 350,000 | $ 1,269,000 | ||
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ADVANCED FIN. ACCT. LL W/ACCESS>CUSTOM<
- I am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forward
- Calculate the division return on assetsarrow_forwardPlease give me true answer this financial accounting questionarrow_forwardRaptors Inc. creates aluminum alloy parts for commercial aircraft. In a recent transaction Raptors leased a high precision lathe machine from Grizzlies Corp. on January 1, 2024. The following information pertains to the leased asset and the lease agreement: Cost of lathe to lessor $140,000 Grizzlies normal selling price for lathe 178,268 Useful life 7 years Estimated value at end of useful life 8,000 Lease provisions Lease term 5 years Payment frequency Annual Start date of lease January 1 Payment timing December 31 Estimated residual value at end of lease (unguaranteed) 20,000 Interest rate implicit in the lease (readily determinable by lessee) 7% Lessee's incremental borrowing rate 8% The lathe machine will revert back to the lessor at end of lease term, title does not transfer to lessee at any time, and there is not a bargain purchase option. Required…arrow_forward
- Financial Accountingarrow_forwardCan you please solve this financial accounting problem without use Ai?arrow_forwardHobbiton Tours Ltd. has the following details related to its defined benefit pension plan as at December 31, 2024: Pension fund assets of $1,900,000 and actuarial obligation of $1,806,317. The actuarial obligation represents the present value of a single benefit payment of $3,200,000 that is due on December 31, 2030, discounted at an interest rate of 10%; i.e. $3,200,000 / 1.106 = $1,806,317. Funding during 2025 was $55,000. The actual value of pension fund assets at the end of 2025 was $2,171,000. As a result of the current services received from employees, the single payment due on December 31, 2030, had increased from $3,200,000 to $3,380,000. Required Compute the current service cost for 2025 and the amount of the accrued benefit obligation at December 31, 2025. Perform this computation for an interest rate of 8%. Derive the pension expense for 2025 under various assumptions about the expected return and discount rate. Complete the following table: Case…arrow_forward
- Calculate Debt Ratios and Debt to Equity Ratio for 2016arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forwardIn 2026, Maple Leafs Co. sells its single machine, which cost $100,000 and has an undepreciated capital cost (UCC) of $25,000 for tax purposes. For financial reporting, the machine has carrying amount of $40,000. The sale price of the machine is $30,000. Aside from the sale of the machine, the company has other income (before taxes) of $600,000, which includes non-taxable dividends of $120,000 dollars received during the year. There are no other permanent or temporary differences. The company faces an income tax rate of 35%. Required Provide the journal entries for the company for 2026.arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
