
Concept explainers
The
Explanation of Solution
The prices are an expression of consensus on the value of goods, services and factors in the economy. It is a standard measure of value across the globe which is one of the guiding principles of policy decisions. The price system is called the “Invisible Hand” and is the chief connecting mechanism between the two economic agents Consumers and Producers in the laissez faire economy.
The essential features of the price system are:
- It is neutral- The operating principle of the price system is neutrality which implies that neither of the two communicating agents in the economy can determine the prices in isolation and to the exclusion of the other. In other words, in determining the prices of goods and services both producers and consumers interact in the commodity market through the forces of
demand and supply to establish theequilibrium price .Monopoly , however, is an exception where the monopolist fixes the prices swayed by the profit motive. - Prices are market driven- The prices are determined by the economic forces of demand and supply. Prices are determined at the point of interaction of the demand and supply curve. This is shown in the figure below:
- Prices are flexible- The prices in the free market determined by the forces of demand and supply are flexible. They respond to the economic fluctuations and serve as the stabilizing economic mechanism. The prices quickly respond to the economic changes through the bidding process by the consumers and producers.
- Efficiency- The prices ensure efficient allocation of resources until the maximum number of goods and services are sold. The system ensures making the best use of the available resources. This is technical efficiency. Producing the maximum possible output with the available resources is economic efficiency. The price system ensures both technical and economic efficiency.
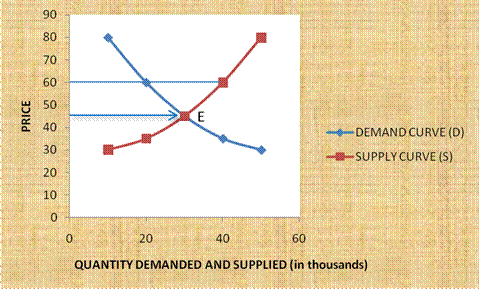
Any deviation between the demand and supply of the commodity activates the forces of demand and supply and the invisible hand of the market forces re-establishes the equilibrium. For example if demand exceeds supply the prices increases. The increase in the prices, reduces the demand and the process of adjustment continues till demand equals supply.
Introduction:
Price System- It is a quintessential foundation of any economic system whereby all goods and services and all factors of production are valued in terms of money. This value is its price and the key factor in the production and consumption decisions in the economy.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Economics Today (19th Edition)
- Answerarrow_forwardM” method Given the following model, solve by the method of “M”. (see image)arrow_forwardAs indicated in the attached image, U.S. earnings for high- and low-skill workers as measured by educational attainment began diverging in the 1980s. The remaining questions in this problem set use the model for the labor market developed in class to walk through potential explanations for this trend. 1. Assume that there are just two types of workers, low- and high-skill. As a result, there are two labor markets: supply and demand for low-skill workers and supply and demand for high-skill workers. Using two carefully drawn labor-market figures, show that an increase in the demand for high skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers. 2. Using the same assumptions as in the previous question, use two carefully drawn labor-market figures to show that an increase in the supply of low-skill workers can explain an increase in the relative wage of high-skill workers.arrow_forward
- Published in 1980, the book Free to Choose discusses how economists Milton Friedman and Rose Friedman proposed a one-sided view of the benefits of a voucher system. However, there are other economists who disagree about the potential effects of a voucher system.arrow_forwardThe following diagram illustrates the demand and marginal revenue curves facing a monopoly in an industry with no economies or diseconomies of scale. In the short and long run, MC = ATC. a. Calculate the values of profit, consumer surplus, and deadweight loss, and illustrate these on the graph. b. Repeat the calculations in part a, but now assume the monopoly is able to practice perfect price discrimination.arrow_forwardThe projects under the 'Build, Build, Build' program: how these projects improve connectivity and ease of doing business in the Philippines?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





