
Concept explainers
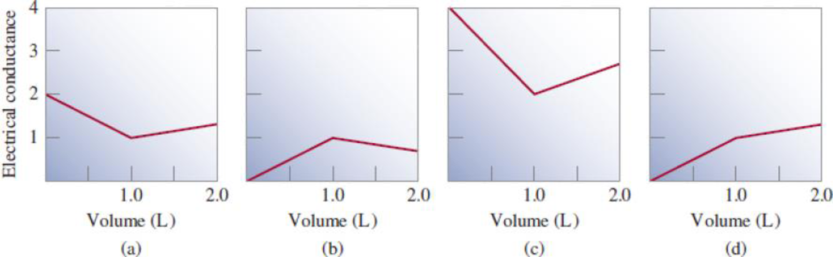
Because acid-base and precipitation reactions discussed in this chapter all involve ionic species, their progress can be monitored by measuring the electrical conductance of the solution. Match the following reactions with diagrams (a)-(d). The electrical conductance is shown in arbitrary units.
(1) A 1.0 M KOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M CH3COOH.
(2) A 1.0 M NaOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M HCl.
(3) A 1.0 M BaCl2 solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M K2SO4.
(4) A 1.0 M NaCl solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M AgNO3.
(5) A 1.0 M CH3COOH solution is added to 1.0 L of 1.0 M NH3.
(a)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 4.174QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
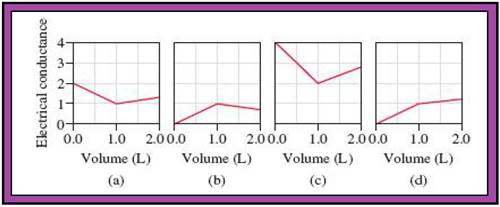
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
If Conductance unit of
(b)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
Answer to Problem 4.174QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
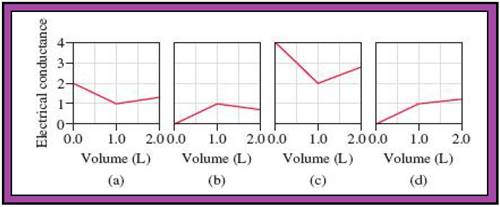
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(c)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance when,
Answer to Problem 4.174QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
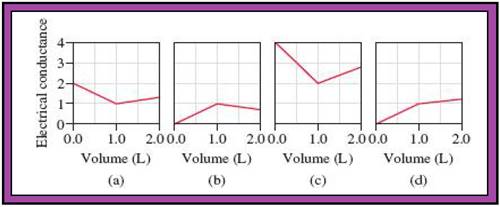
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(d)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 4.174QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data
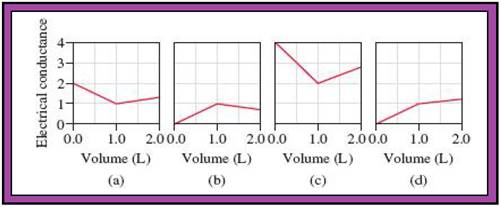
Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
(e)
Interpretation:
The given each reaction are should be matched with given each diagram and significance of slope change points in the given diagrams should be explained.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction:
- If precipitate is formed, when two solutions are mixed together is called precipitation reaction.
- The amount of precipitate formed is related to the amount of reactants taken in to the reaction.
Neutralization reaction:
- The reaction between acid and base to gives a salt is the known as neutralization reaction.
Strong and weak electrolytes:
- The compound dissolved in water and completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
- The compound dissolved in water but not completely dissociates to produces the ions is known as strong electrolytes.
Electrical conductivity of electrolytes:
- The strong electrolytes are having high electrical conductivity than weak electrolytes.
- The number of ion in solution is directly proportional to the electrical conductivity of electrolytes.
Conductivity titration:
- The measurement of electrical conductivity of titration mixture to gives a end point if the reaction.
- The sudden change in the slope is a equivalent point of the titration and it is the end point.
To find the electrical conductance, when
Answer to Problem 4.174QP
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Record the given data

Fig.1
Explanation of Solution
If the conductance unit will be twice its concentration (molarity), when compound is completely dissociates into equal number of ions in solution.
Reaction of
Volume of
If
If
Match the calculated conductance unit of each reaction in given diagrams in Fig.1.
- The reactions (2) and (4) are matched with diagram (a).
- The reaction (5) is matched with diagram (b).
- The reaction (3) is matched with diagram (c).
- The reaction (1) is matched with diagram (d).
The slope change points in the given diagrams are end or equivalent points of the tractions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
CHEMISTRY (LL) W/CNCT >BI<
- Explain why the S-F bond strength is 367 kJ/mol in SF2 and 329 kJ/mol in SF6.arrow_forwardWould Si(CH3)3F react with AgCl? If so, write out the balanced chemical equation. If not,explain why no reaction would take place.arrow_forwardNH3 reacts with boron halides (BX3 where X = F, Cl, Br, or I) to form H3N-BX3 complexes.Which of these complexes will have the strongest N-B bond? Justify your answerarrow_forward
- Synthesize the following:arrow_forwardDid you report your data to the correct number of significant figures? Temperature of cold water (°C) 4.0 Temperature of hot water ("C) 87.0 Volume of cold water (mL) 94.0 Volume of hot water (mL) 78.0 Final temperature after mixing ("C) 41.0 Mass of cold water (g) 94.0 Mass of hot water (g) 78.0 Calorimeter constant (J/°C) 12.44 How to calculate the calorimeter constantarrow_forwardplease draw the arrowsarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





