
To find:
a) Draw Lewis structure for possible arrangement of
b) Assign formal charges of each structure.
c) Give reason why structure is not stable.
Answer to Problem 4.113QA
Solution:
a) i) ii)
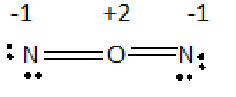
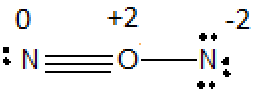
b) i) Formal charge on each N is -1 and on O is +2.
ii) Formal charge on one of N is -2 and on O is +2.
c) In both structure the formal charge on oxygen is +2. Since oxygen is more electronegative than Nitrogen none of these structure is stable.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Each molecule contains two Nitrogen and one oxygen has an overall charge zero. Nitrogen and oxygen are in group 15 and 16 and have bonding capacity three and two. Nitrogen can show hypervalency.
2) Calculations:
The number of valence electrons are,
| Elements | Valence electrons | ||
| Symbol | Number of atom | In one atom | Total |
| N | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| O | 1 | 6 | 6 |
| Valence electrons in molecule | 16 | ||
First possible arrangement of
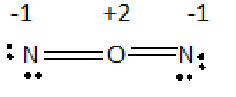
Second possible arrangement of
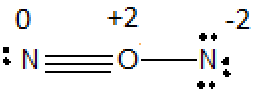
Formula:
To find formal charge we need to use following equation,
Calculation:
Step 1) Calculations of formal charge on atoms in first structure,
Step 2) Calculations of formal charge on atoms in second structure,
Oxygen has electronegativity 3.5 and nitrogen has electronegativity 3.0. Thus, structures with formal negative charges on nitrogen and formal positive charges on oxygen are not preferred. Therefore none of these structures is stable.
Conclusion:
a) Lewis structure for possible arrangement of
i) ii)
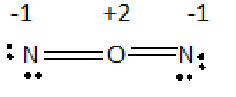
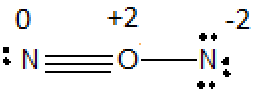
b) i) Formal charge on each N is -1 and on O is +2.
ii) Formal charge on one of N is -2 and on O is 2+
c) Oxygen is more electronegative than Nitrogen and each of structure contains +2 charge on oxygen so none of these structure is likely to be stable.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Chemistry: An Atoms-Focused Approach (Second Edition)
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure name × HO OH ☐ OH CI CI O CI OH OHarrow_forwardく Check the box under each a amino acid. If there are no a amino acids at all, check the "none of them" box under the table. Note for advanced students: don't assume every amino acid shown must be found in nature. COO H3N-C-H CH2 HO CH3 NH3 O CH3-CH CH2 OH Onone of them Explanation Check + H3N O 0. O OH + NH3 CH2 CH3-CH H2N C-COOH H O HIC + C=O H3N-C-O CH3- - CH CH2 OH Х 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center Accesarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forward
- theres 2 productsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Organic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forwardDifferentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forwardAn aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forward
- Draw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the first photoarrow_forwardGgggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





