
(a)
(b) Consumer surplus when the market price decreases to $19.
(c) Consumer surplus when the market price falls from $29 to $19.
Concept Introduction
Consumer surplus: The difference in amounts that the consumers are ready to pay for a particular good and service and the total amount they actually pay for that good is known as consumer surplus. The amount saved as surplus can be used to buy some other good.
Market Price: The price at which a product is offered in the market is called its market price. It is the current price at which a good or service can be bought or sold.
Explanation of Solution
(a) Consumer surplus when the market price is $29.
- The formula to calculate the consumer surplus is:
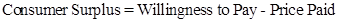
- Following table shows consumer surplus when the market price of a computer game is $29.
| Potential Consumers | Willingness to pay($) | Price paid($) | Individual consumer surplus($) |
| Consumer 1 | 40 | 29 | 11 |
| Consumer 2 | 35 | 29 | 6 |
| Consumer 3 | 30 | 29 | 1 |
| Consumer 4 | 25 | - | - |
| Consumer 5 | 20 | - | - |
| Consumer 6 | 15 | - | - |
| Total Consumer Surplus | 18 |
- The above table shows that consumer 1, consumer 2, consumer 3 will purchase the game as the market price is less than their willingness to pay
producing total surplus of $18.
- As the market price is greater than what consumer 4, consumer 5, and consumer 6 are willing to pay, so they are not willing to purchase.
Conclusion:
Thus, the total consumer surplus is $18.
(b) Consumer surplus when the market price decreases to $19.
- The formula to calculate the consumer surplus is:
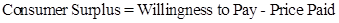
- Following table shows consumer surplus when the market price of the computer game decreases to $19.
| Potential Consumers | Willingness to pay($) | Price paid($) | Individual consumer surplus($) |
| Consumer 1 | 40 | 19 | 21 |
| Consumer 2 | 35 | 19 | 16 |
| Consumer 3 | 30 | 19 | 11 |
| Consumer 4 | 25 | 19 | 6 |
| Consumer 5 | 20 | 19 | 1 |
| Consumer 6 | 15 | - | - |
| Total Consumer Surplus | 55 |
- The above table shows all the other consumers, except consumer 6 will purchase the computer game producing a total consumer surplus of $55.
Conclusion;
Thus, the total consumer surplus is $55.
(c) Consumer surplus when the market price falls from $29 to $19.
- There is a change in the consumer surplus of each consumer when the market price falls from $29 to $19.
- Following table shows change in consumer surplus when the market price falls from $29 to $19.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4=3-2 |
| Potential Consumer | Consumer Surplus when the Market Price is $29($) | Consumer Surplus when the Market Price is $19($) | Change in individual consumer surplus($) |
| Consumer 1 | 6 | 21 | 10 |
| Consumer 2 | 11 | 16 | 10 |
| Consumer 3 | 1 | 11 | 10 |
| Consumer 4 | - | 6 | 6 |
| Consumer 5 | - | 1 | 1 |
| Consumer 6 | - | - | - |
| Total Consumer Surplus | 18 | 55 | 37 |
- The above table shows that there is an increase in consumer surplus of $10 each of consumer 1, consumer 2 and consumer 3.
- As the market price falls from $29 to $19, consumer 4 and consumer 5 are willing to buy the product producing a consumer surplus of $6 and $1.
Conclusion:
Thus, the change in total consumer surplus is $37.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- how commond economies relate to principle Of Economics ?arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forwardCritically analyse the five (5) characteristics of Ubuntu and provide examples of how they apply to the National Health Insurance (NHI) in South Africa.arrow_forward
- Outline the nine (9) consumer rights as specified in the Consumer Rights Act in South Africa.arrow_forwardIn what ways could you show the attractiveness of Philippines in the form of videos/campaigns to foreign investors? Cite 10 examples.arrow_forwardExplain the following terms and provide an example for each term: • Corruption • Fraud • Briberyarrow_forward
- In what ways could you show the attractiveness of a country in the form of videos/campaigns?arrow_forwardWith the VBS scenario in mind, debate with your own words the view that stakeholders are the primary reason why business ethics must be implemented.arrow_forwardThe unethical decisions taken by the VBS management affected the lives of many of their clients who trusted their business and services You are appointed as an ethics officer at Tyme Bank. Advise the management regarding the role of legislation in South Africa in providing the legal framework for business operations.arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





