
Concept explainers
Journal is the primary record of business transactions in chronological (date wise) order. Journal entry contains two effects, one is debit and the other is credit, under the double entry book keeping system.
Procedure for debiting and crediting an account:
• Increase in assets account, increase in expenses account, and decrease in liabilities account should be debited.
• Decrease in assets account, increase in revenue account, and increase in liabilities account should be credited.
All transactions affect the
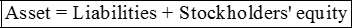
Perpetual inventory system:
It is an inventory system wherein the accounts related to inventory are updated on each purchase and sales that occur. Quantities of inventory are updated on continuous basis.
To prepare: The journal entries.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entries as shown below.
| Date | Particulars | L/F | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aug 1 | Merchandise inventory | 7,500 | ||
| Accounts payable | 7,500 | |||
| (To record merchandise inventory purchased on credit) | ||||
| Aug 5 | Account receivable | 5,200 | ||
| Sales | 5,200 | |||
| (To record sales made on account) | ||||
| Aug 5 | Cost of goods sold | 4,000 | ||
| Merchandise inventory | 4,000 | |||
| (To record cost of goods sold) | ||||
| Aug 8 | Merchandise Inventory | 5,400 | ||
| Account payable | 5,400 | |||
| (To record merchandise inventory purchased on credit) | ||||
| Aug 9 | Merchandise Inventory | 125 | ||
| Cash | 125 | |||
| (To record shipping charges paid by buyer) | ||||
| Aug 10 | Sales return and allowances | 600 | ||
| Account receivable | 600 | |||
| (To record sales return) | ||||
| Aug 10 | Merchandise inventory | 400 | ||
| Cost of goods sold | 400 | |||
| (To record cost of goods sold) | ||||
| Aug 12 | Account payable | 700 | ||
| Merchandise Inventory | 700 | |||
| (To record price reduction worth $400) | ||||
| Aug 14 | Account payable | 200 | ||
| Cash | 200 | |||
| (To record shipping charges paid by buyer) | ||||
| Aug 15 | Cash | 4,508 | ||
| Sales discount | 92 | |||
| Account receivable | 4,600 | |||
| (To record final payment received from Company A) | ||||
| Aug 18 | Account payable | 5,000 | ||
| Merchandise inventory | 50 | |||
| Cash | 4,950 | |||
| (To record cash payment made for merchandise inventory ) | ||||
| Aug 19 | Cost of goods sold | 2,400 | ||
| Merchandise inventory | 2,400 | |||
| (To record cost of goods sold) | ||||
| Aug 19 | Account receivable | 4,800 | ||
| Sales | 4,800 | |||
| (To record sales made on account) | ||||
| Aug 22 | Sales Return and Allowance | 500 | ||
| Account receivable | 500 | |||
| (To record price reduction worth $500) | ||||
| Aug 29 | Cash | 4,300 | ||
| Account receivable | 4,300 | |||
| (To record final payment received from Company A) | ||||
| Aug 30 | Account payable | 7,300 | ||
| Cash | 7,300 | |||
| (To record cash payment made for merchandise inventory ) |
Table (1)
Now prepare the general ledgers as shown below.
| Merchandise Inventory | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 1 | Accounts payable | 7,500 | 7,500 | ||
| Aug 5 | Cost of goods sold | 4,000 | 3,500 | ||
| Aug 8 | Accounts payable | 5,400 | 8,900 | ||
| Aug 9 | Cash | 125 | 9,025 | ||
| Aug 10 | Cost of goods sold | 400 | 9,425 | ||
| Aug 12 | Accounts payable | 400 | 9,025 | ||
| Aug 18 | Accounts payable | 50 | 8,975 | ||
Table (2)
Hence, the ending balance is $8,975.
| Sales Discount | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 15 | 92 | 92 | |||
Table (3)
Hence, the ending balance is $92.
| Sales Return and Allowance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 10 | Accounts receivable | 600 | 600 | ||
| Aug 22 | Accounts receivable | 500 | 1,100 | ||
Table (4)
Hence, the ending balance is $1,100.
| Account Payable | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 1 | Merchandise inventory | 7,500 | 7,500 | ||
| Aug 8 | Merchandise inventory | 5,400 | 12,900 | ||
| Aug 12 | Merchandise inventory | 400 | 12,500 | ||
| Aug 14 | Cash | 200 | 12,300 | ||
| Aug 18 | Merchandise inventory | 50 | 12,250 | ||
| Aug 18 | Cash | 4,950 | 7,300 | ||
| Aug 30 | Cash | 7,300 | 0 | ||
Table (5)
Hence, the ending balance is $ 0.
| Accounts Receivable | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 5 | Sales | 5,200 | 5,200 | ||
| Aug 10 | Sales return | 600 | 4,600 | ||
| Aug 15 | Cash | 4,508 | 92 | ||
| Aug 15 | Sales discount | 92 | 0 | ||
| Aug 19 | Sales | 4,800 | 4,800 | ||
| Aug 22 | Sales return | 500 | 4,300 | ||
| Aug 29 | Cash | 4,300 | 0 | ||
Table (6)
Hence, the ending balance is $0.
| Cash | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 9 | Merchandise inventory | 125 | (125) | ||
| Aug 14 | Accounts payable | 200 | (325) | ||
| Aug 15 | Accounts receivable | 4,508 | 4,183 | ||
| Aug 18 | Accounts payable | 4,950 | (767) | ||
| Aug 29 | Accounts receivable | 4,300 | 3,533 | ||
| Aug 30 | Accounts payable | 7,300 | (3,767) | ||
Table (7)
Hence, the ending balance is $(3,767).
| Cost of goods sold | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 5 | Merchandise inventory | 4,000 | 4,000 | ||
| Aug 10 | Merchandise inventory | 400 | 3,600 | ||
Table (8)
Hence, the ending balance is $3,600.
| Sales | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | Particulars | Post ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
Balance ($) |
| Aug 5 | accounts receivable | 5,200 | 5,200 | ||
| Aug 19 | accounts receivable | 4,800 | 10,000 | ||
Table (9)
Hence, the ending balance is $10,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Financial and Managerial Accounting: Information for Decisions
- I am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





