
The effect of tax on economic efficiency.
Explanation of Solution
Tax is a unilateral payment made to the government from the public for various purposes. There are many types of taxes, such as income tax, wealth tax, and so forth, which constitute a major portion of the revenue of the government that can be used for making public expenditures. Economic efficiency is a situation where no one can be in a better position without hurting the other. In the case, economic efficiency is the situation where the marginal benefit (of the consumer) from the last unit produced is equal to the marginal cost of the production of the unit. This means that both of them will be the same and neither the consumer nor the producer can be in a better position. The sum of the
Here, the tax imposed on the ride is 20%, which is equal to 6 pounds. This is because the
Thus, the supply vertically shifts by the tax amount of 6 pounds, and as a result, the quantity demanded decreases to 8,500 rides. The owner of the vehicles receives only 27 pounds, which is the reason for the decrease in the supply of the rides in the market. Thus, the consumer has to pay 33 pounds more than the equilibrium price, whereas the owner receives 3 pounds less than the equilibrium price received by him before the tax. Thus, the tax is equally shared among the consumer and the owner (by 3 pounds each). The economic efficiency is reduced by the tax because there will be
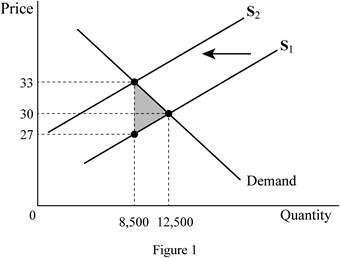
The new quantity demanded after the introduction of the tax is 8,500 rides and the new price after the introduction of the tax is 33 pounds. The price actually received by the owner of the vehicle also reduces to 27 pounds; this means that both the owner and the consumer are paying 3 pounds each as tax. This shows that the tax burden is evenly distributed between the seller and the buyer. There is deadweight loss in the economy because of the tax and it can be denoted by the area shaded in grey colour on the graph.
Concept introduction:
Tax: It is the unilateral payment made by the public towards the government. There are many different types of taxes in the economy, which includes income tax, property tax, professional tax, and so forth.
Economic efficiency: It is the situation where the economy is efficient. This means that the marginal benefit from the last unit produced is equal to the marginal cost of production and the economic surplus will be at is maximum.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Macroeconomics (7th Edition)
- how to solve the attachment?arrow_forwardProblem 3-ABC Challenges: Attrition, Balance and ComplianceCan television inform people about public affairs? Political scientists Bethany Albertson and Adria Lawrence (2009) conducted an experiment in which they randomly assigned people to treatment and control groups to evaluate the effect of watching TV on a person’s information level. Those assigned to the treatment group were told to watch a specific television broadcast and were later asked questions related to what they watched. Those in the controlgroup were not shown the TV broadcast but were asked questions related to the material in the TV broadcast. The dataset contains the following variables: : Dummy variable which =1 if a person reads news and 0 otherwise. : interest in political affairs (not interested=1 to very interested=4) : years of education : female dummy variable (female=1; male=0) : family income in thousands of dollars : information level (low information level=1 to high information level=4) =1 if the…arrow_forwardProblem 2-Experiments/Randomized Control Trial Suppose you are interested in studying the effect of academic counselling on the years it takes for a student to obtain an undergraduate degree. You conduct a randomized control trial to answer the question. You randomly assign 2500 individuals in a university in New York to receive academic counselling and 2500 students to not receive any academic counselling. a. Which people are a part of the treatment group and which people are a part of thecontrol group? b. What regression will you run? Define the variables where required. c. Suppose you estimate = -0.3. Interpret it. d. You test for balance using the variables mentioned in the table below. Based on the results do you think that the treatment and control group are balanced? If your answer is “yes” then explain why. If your answer is “no”, then explain why and mention how will you address the issue of imbalance. e. Suppose that some unmotivated students in the control group decided to…arrow_forward
- How to calculate total cost?arrow_forwardProblem 1-Experiments/Randomized Control TrialSuppose you are interested in studying the effect of being a part of the labor union on anindividual’s hourly wage.You collect data on 1000 people and run the following regression. where is a dummy variable which is equal t to 1 for people who are a part of labor union and0 for others. a. Suppose you estimate . Interpret b. Do you think is biased or unbiased? Explain. Now suppose you conduct a randomized control trial to answer the same question. Yourandomly assign some individuals to be a part of the labor union and others to not be a partof the labor union. The first step you take is to ensure that the randomization was donecorrectly. Then you estimate the following equation: =1 if the student is assigned to be a part of Labor Union=0 if the student is assigned to not be a part of Labor Union c. Why is it important to ensure that the randomization is done correctly? d. Name any two variables that you can use to test if Treatment and…arrow_forwardWhat is kiosk?arrow_forward
- If food is produced in the U.S., sold in the U.S. and consumed in the U.S., a reduction in its price will have which of the following effects ______? Two of the answers are correct. The consumer price index will decrease. None of the answers are correct. The GDP deflator will decrease.arrow_forwardhow to caculate verible cost?arrow_forwardWhat is the deficit?arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





