
Concept explainers
Explanation of Solution
Graph of functions using logarithmic scale:
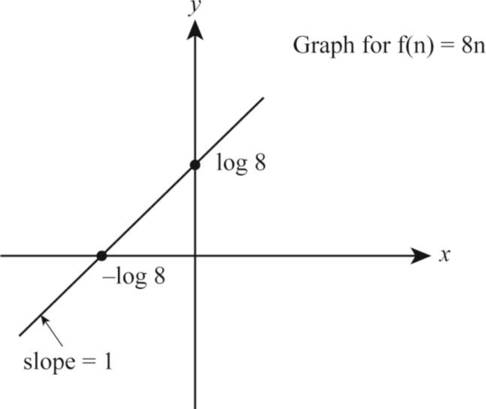
8n:
Let the function be:
Take the logarithm on both the sides of the above function as follows:
According to the given data, let us take
Thus, from the above Equation (2), the value of
The following is the graph representation corresponding to the values
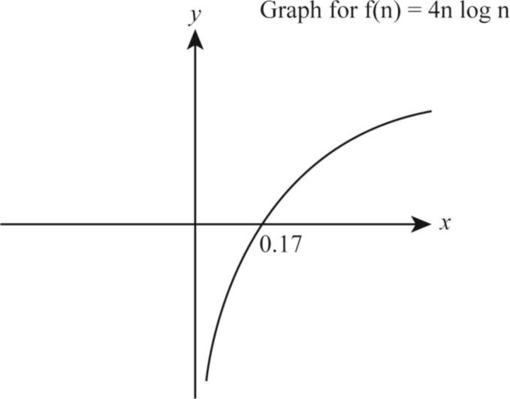
4n logn:
Let the function be:
Take the logarithm on both the sides of the above function as follows:
According to the given data, let us take
The following is the graph representation corresponding for the function
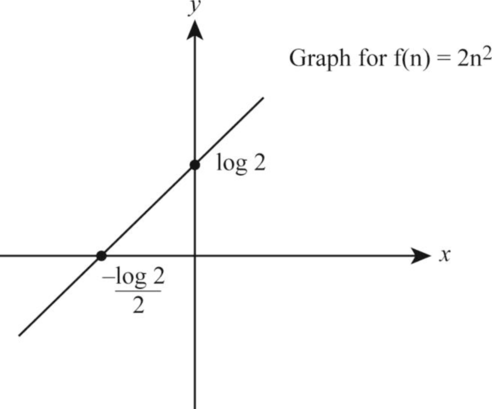
Let the function be:
Take the logarithm on both the sides of the above function as follows:
According to the given data, let us take
Thus, from the above Equation (6), the value of
The following is the graph representation corresponding to the values
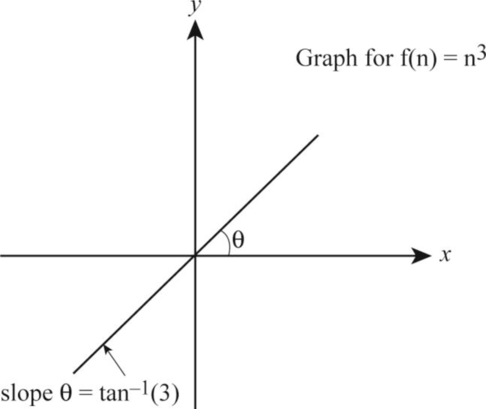
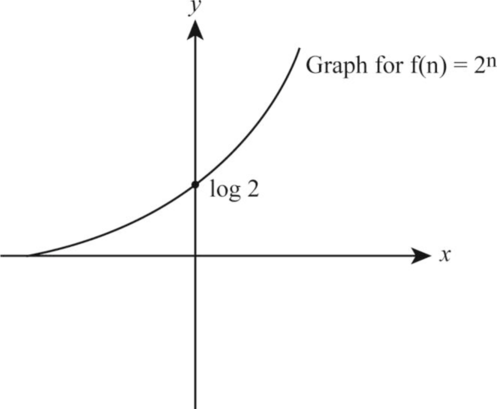
Let the function be:
Take the logarithm on both the sides of the above function as follows:
According to the given data, let us take
The following is the graph representation corresponding to the value on respective x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Let the function be:
Take the logarithm on both the sides of the above function as follows:
According to the given data, let us take
The following is the graph representation corresponding to the value on respective x-axis and y-axis respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Data Structures and Algorithms in Java
 Operations Research : Applications and AlgorithmsComputer ScienceISBN:9780534380588Author:Wayne L. WinstonPublisher:Brooks ColeProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
Operations Research : Applications and AlgorithmsComputer ScienceISBN:9780534380588Author:Wayne L. WinstonPublisher:Brooks ColeProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning- COMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning





