
1.
Set up general ledger accounts by entering the balances as of November 1.
1.
Explanation of Solution
General ledger:
General ledger is a record of all accounts of assets, liabilities, and
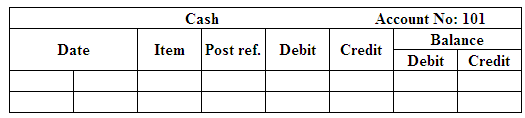
(Figure 1)
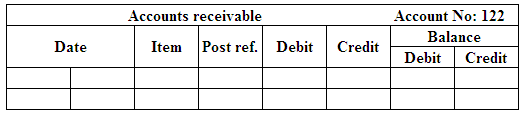
(Figure 2)
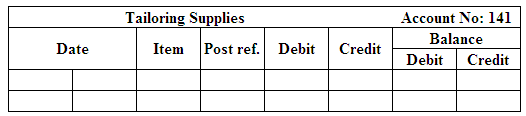
(Figure 3)
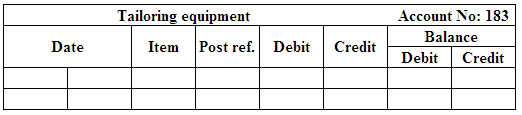
(Figure 4)
(Figure 5)
(Figure 6)
(Figure 7)
(Figure 8)
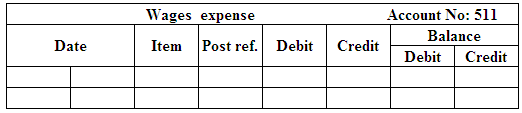
(Figure 9)
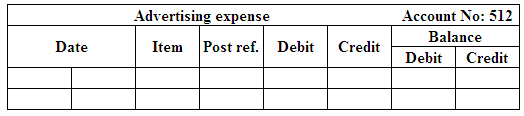
(Figure 10)
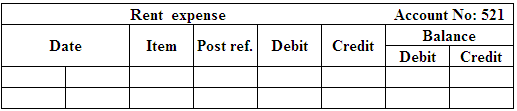
(Figure 11)
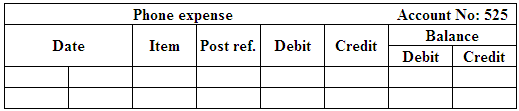
(Figure 12)
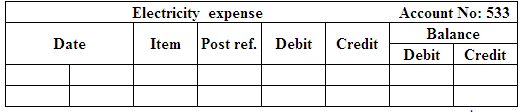
(Figure 13)
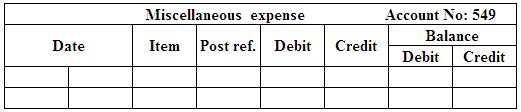
(Figure 14)
2.
Prepare
2.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Post. Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| November 1 | Rent Expense | 521 | 300 | |
| Cash | 101 | 300 | ||
| (To record the payment on November ) | ||||
| November 2 | Tailoring supplies | 141 | 150 | |
| Accounts payable | 202 | 150 | ||
| (To record the purchase of tailoring supplies on account) | ||||
| November 3 | Tailoring Equipment | 183 | 300 | |
| Accounts payable | 202 | 300 | ||
| (To record the purchase machine on account) | ||||
| November 5 | Cash | 101 | 100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 122 | 300 | ||
| Tailoring fees | 401 | 400 | ||
| (To record the amount earned on tailoring fees) | ||||
| November 8 | Advertising expense | 512 | 13 | |
| Cash | 101 | 13 | ||
| (To record the payment made on the newspaper ad) | ||||
| November 9 | Phone Expense | 525 | 28 | |
| Cash | 101 | 28 | ||
| (To record the payment of phone bill) | ||||
| November 10 | Electricity Expense | 533 | 21 | |
| Cash | 101 | 21 | ||
| (To record the payment of electricity bill) | ||||
| November 11 | Cash | 101 | 200 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 122 | 200 | ||
| (To record the cash to be received on account) | ||||
| November 12 | Cash | 101 | 200 | |
| Accounts receivable | 122 | 250 | ||
| Tailoring Fees | 401 | 450 | ||
| (To record the cash on tailoring fees) | ||||
| November 15 | Wages Expense | 511 | 400 | |
| Cash | 101 | 400 | ||
| (To record the payment made to the employee) | ||||
| November 16 | Accounts Payable | 202 | 100 | |
| Cash | 101 | 100 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash on account) | ||||
| November 17 | Miscellaneous Expense | 549 | 12 | |
| Cash | 101 | 12 | ||
| (To record the payment made for magazine subscription) | ||||
| November 19 | Cash | 101 | 300 | |
| Accounts receivable | 122 | 150 | ||
| Tailoring Fees | 401 | 450 | ||
| (To record the cash on tailoring fees) | ||||
| November 23 | Cash | 101 | 300 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 122 | 300 | ||
| (To record the amount of cash received on account) | ||||
| November 24 | Advertising expense | 512 | 13 | |
| Cash | 101 | 13 | ||
| (To record the payment made on the newspaper ad) | ||||
| November 26 | Miscellaneous Expense | 549 | 12 | |
| Cash | 101 | 12 | ||
| (To record the payment made for magazine subscription) | ||||
| November 27 | Cash | 101 | 200 | |
| Accounts receivable | 122 | 400 | ||
| Tailoring Fees | 401 | 600 | ||
| (To record the cash on tailoring fees) | ||||
| November 30 | Cash | 101 | 400 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 122 | 400 | ||
| (To record the cash received on account) |
(Table 1)
3.
3.
Explanation of Solution
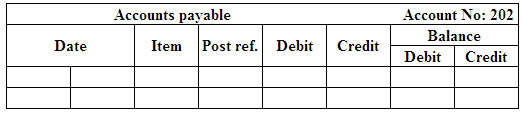
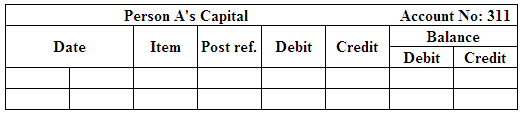
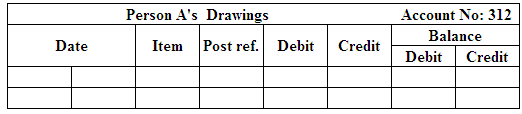
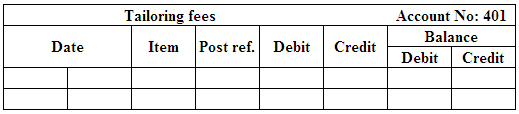
Post the entries to the general ledger.
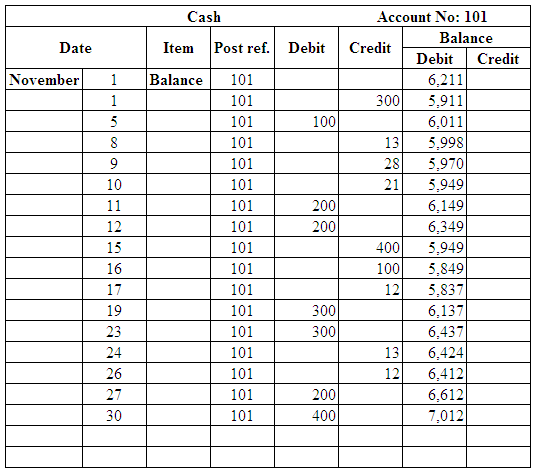
(Figure 18)
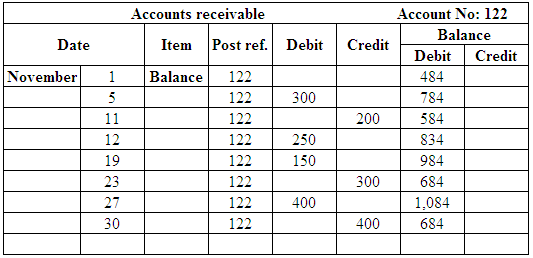
(Figure 19)
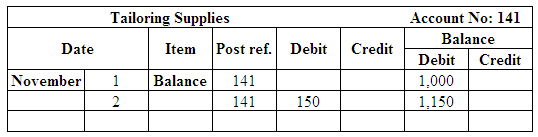
(Figure 20)
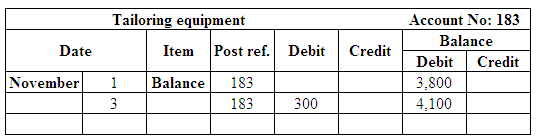
(Figure 21)
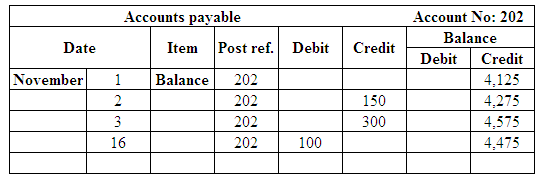
(Figure 22)
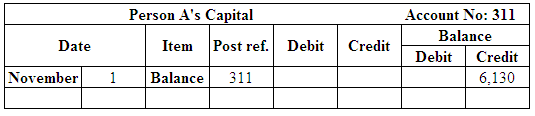
(Figure 23)
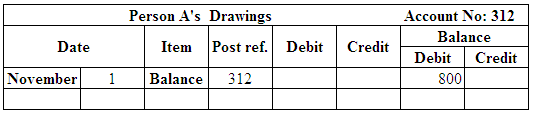
(Figure 24)
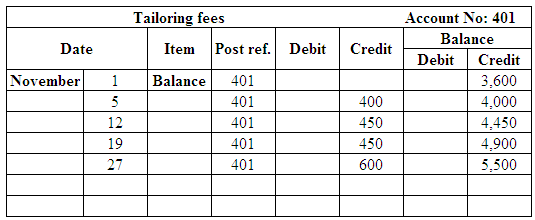
(Figure 25)
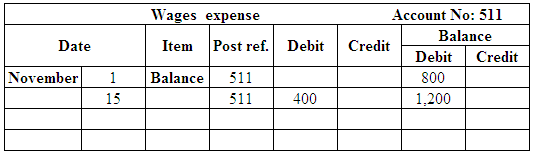
(Figure 26)
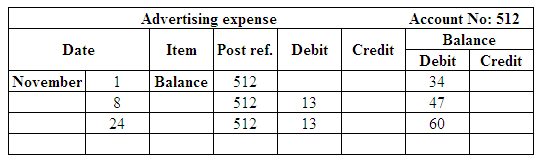
(Figure 27)
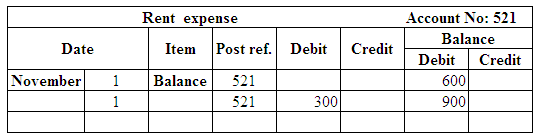
(Figure 28)
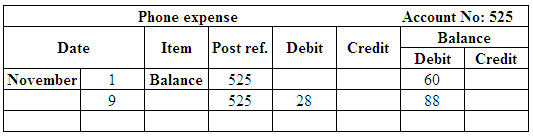
(Figure 29)
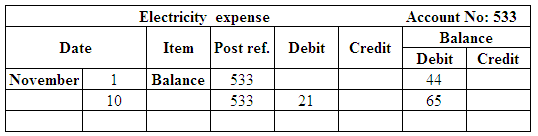
(Figure 30)
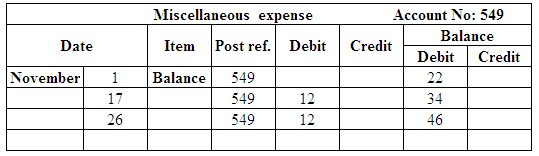
(Figure 31)
4.
Prepare a
4.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a trial balance.
| Company T | |||
| Trial balance | |||
| November 31, 20.. | |||
| Accounts | Account No. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 101 | 7,012 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 122 | 684 | |
| Tailoring Supplies | 141 | 1,150 | |
| Tailoring Equipment | 183 | 4,100 | |
| Accounts Payable | 202 | 4,475 | |
| Person A’s, Capital | 311 | 6,130 | |
| Person A’s, Drawing | 312 | 800 | |
| Tailoring Fees | 401 | 5,500 | |
| Wages Expense | 511 | 1,200 | |
| Advertising Expense | 512 | 60 | |
| Rent Expense | 521 | 900 | |
| Phone Expense | 525 | 88 | |
| Electricity Expense | 533 | 65 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 549 | 46 | |
| Total | 16,105 | 16,105 | |
(Table 2)
Therefore, the total of the debit and credit column of the trial balance reported an amount of $16,105.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: College Accounting, Chapters 1-27, Loose-leaf Version, 23rd + Cengagenowv2, 2 Terms Printed Access Card
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations.arrow_forward
- I need the correct answer to this general accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardYou are employed by an external audit firm that is hired by JBltd, a privately owned incorporated business. Accounting records are maintained on a computer using proprietary software. You have worked on the audit for three years and this year you are in charge of the audit. Your assistant is a newly recruited business graduate who has done an accounting course but has no practical experience. Because of the small size of the company there is limited opportunity for segregation of duties. You decide, as in previous years, that the appropriate audit strategy is to obtain evidence primarily through the performance of substantive procedures. You also plan to perform the audit around the computer as the proprietary software is known to be reliable and details of all transactions and balances can be readily printed out. On arriving at the company's premises in December 2019 to perform the final audit on the 31 October 2019 financial statements, you obtain a copy of the year end bank…arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax CollegeCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,  Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





