
Concept explainers
PROBLEM 3A-5 Transaction Analysis LO3-5
Star Videos, Inc., produces short musical videos for sale to retail outlets. The company's
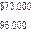
Because the videos differ in length and in complexity7 of production, the company uses a job-order costing system to determine the cost of each video produced. Studio (manufacturing)
Required:
- Using Exhibit 3A-1 as your guide, prepare a transaction analysis that records all of the above transactions. Calculate the ending balances at December 31 for all balance sheet accounts.
- Using Exhibit 3A-3 as your guide, prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the year. If done correctly', your cost of goods manufactured should equal what amount mentioned in the transactions above9
- Using Exhibit 3A-4 as your guide, prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold for the year. If done correctly', your unadjusted cost of goods sold should equal what amount mentioned in the transactions above9
- Using Exhibit 3A-5 as your guide, prepare an income statement for the year.
- Film, costumes, and similar raw materials purchased on account SI83,000.
- Film, costumes, and other raw materials issued to production, S210,000 (85% of this material was considered direct to the videos in production, and the other 15% was considered indirect).
- Utility costs incurred (on account) in the production studio, S78,000.
Depreciation recorded on the studio, cameras, and other equipment, S82,000. Three-fourths of this depreciation related to actual production of the videos, and the remainder related to equipment used in marketing and administration
- Advertising expense incurred (on account), S13L000.
- Salaries and wages paid in cash as follows:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING >CUSTOM<W/AC SM21
 Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial & Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337119207Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
