
Activity-Based Absorption Costing and Pricing LO3—5
Java Source, Inc., (JSI) buys coffee beans from around the world and roasts, blends, and packages them for resale. Some of JSI’s coffees are very popular and sell in large volumes, while a few of the newer blends sell in very low volumes. JSI prices its coffees at
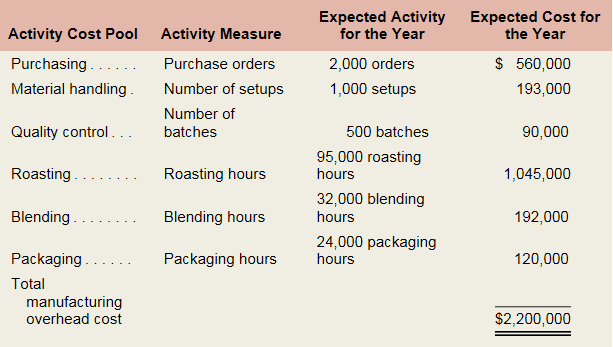
For the coming year, JSI’s budget includes estimated manufacturing
The expected costs for direct materials and direct labor for one-pound bags of two of the company’ s coffee products appear below.

JSI’s controller believes that the company s traditional costing system may be providing misleading cost information. To determine whether or not this is correct, the controller has prepared an analysis of the year’s expected manufacturing overhead costs, as shown in the following table:
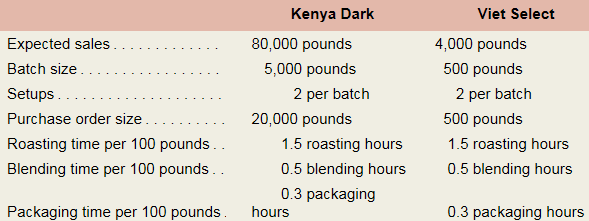
Data regarding the expected production of Kenya Dark and Viet Select coffee are presented below.
Required:
- Using direct labor-hours as the manufacturing overhead cost allocation base, do the following:
- Determine the plantwide predetermined overhead rate that will be used during the year.
- Determine the unit product cost of one pound of Kenya Dark coffee and one pound of Viet Select coffee.
- Using the activity-based absorption costing approach, do the following:
- Determine the total amount of manufacturing overhead cost assigned to Kenya Dark coffee and to Viet Select coffee for the year.
- Using the data developed in (2a) above, compute the amount of manufacturing overhead cost per pound of Kenya Dark coffee and Viet Select coffee.
- Determine the unit product cost of one pound of Kenya Dark coffee and one pound of Viet Select coffee.
- Write a brief memo to the president of ISI that explains what you found in (1) and (2) above and that discusses the implications of using direct labor-hours as the only manufacturing overhead cost allocation base.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
- accounting question?arrow_forwardThree individuals form JEY Corporation with the following contributions: Joe, cash of $50,000 for 50 shares; Ethan, land worth $20,000 (basis of $11,000) for 20 shares; and Young, cattle worth $9,000 (basis of $6,000) for 9 shares and services worth $21,000 for 21 shares. a. These transfers are fully taxable and not subject to § 351. b. Young’s basis in her stock is $27,000. c. Young’s basis in her stock is $6,000. d. Ethan’s basis in his stock is $20,000. e. None of the above.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

