
Concept explainers
(a)
The proof that total deviation of a ray from its original path is
(a)
Answer to Problem 124PQ
The total deviation of a ray from its original path is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for refraction law at left side of the given prism.
Here,
Write the expression for refraction law at right side of the given prism.
Here,
Write the expression angle of deviation of the given prism.
Here,
Write the relation among various angle from the geometry of the prism.
Substitute
Further solve this for
Use general trigonometric relation for conversion.
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, it is proved that the angle of deviation is
(b)
The plot of the angle of deviation versus the angle of incidence for
(b)
Answer to Problem 124PQ
The graph is following.
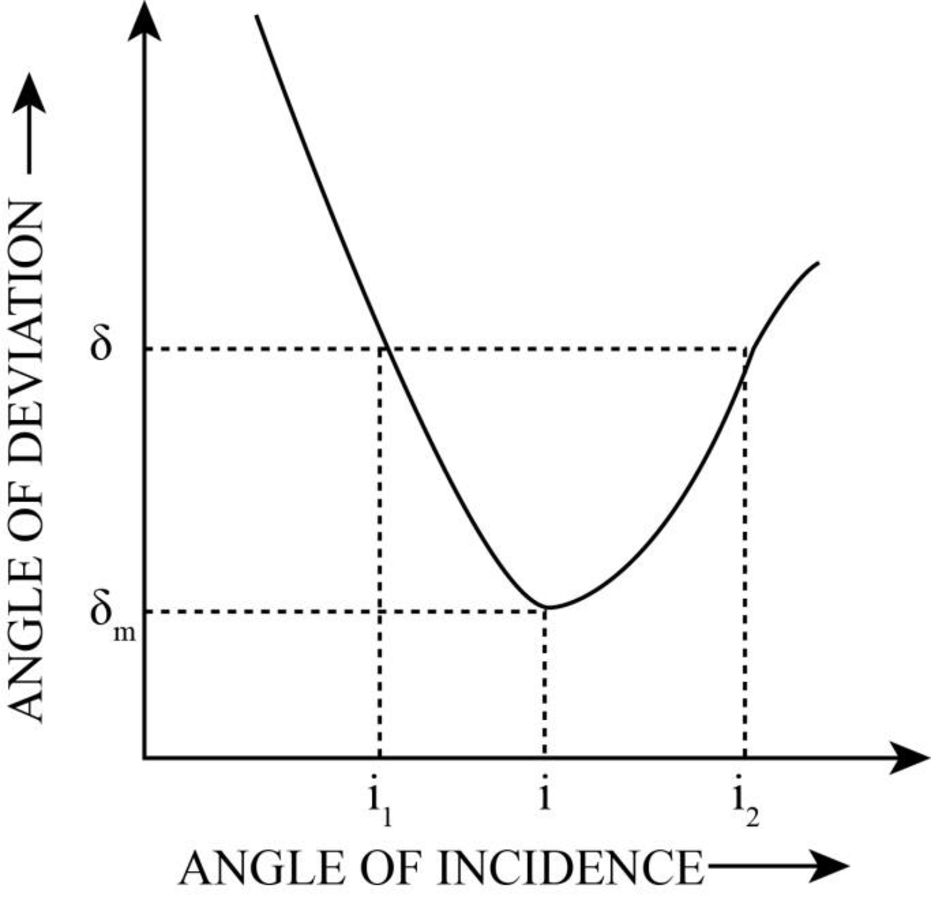
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the angle of deviation of the given prism.
Conclusion:
Substitute
Deviation varies linearly, decreases and then increases approximately with incidence angle
Therefore, the plot of the angle of deviation versus the angle of incidence is as follows.
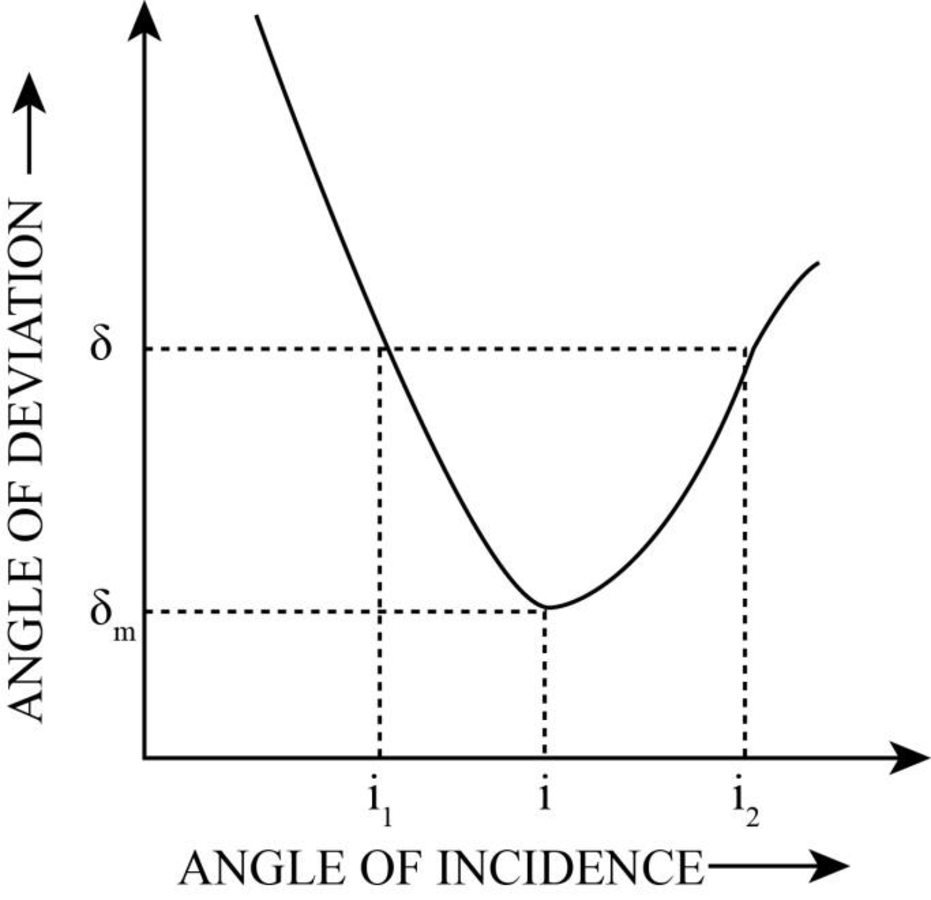
Figure-(1)
(c)
The incidence angle for which the derivation angle is minimum.
(c)
Answer to Problem 124PQ
The incidence angle for which deviation is minimum is
Explanation of Solution
The minimum deviation occurs when the incident and the refracted ray are identical and make equal angles to the normal of the prism.
The angle exhibits a minimum at
Conclusion:
The minimum angle of deviation depends on the refractive index for different wavelength, the refractive index is different.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 38 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
- From your examination of the graph created using the data in Data Table 4 of Period, T vs √L . What would you determine is the relationship between the period of a pendulum and the length of a pendulum?arrow_forwardIn a certain bimetallic strip, the brass strip is 0.100% longer than the steel strip at a temperature of 283°C. At what temperature do the two strips have the same length? Coefficients of linear expansion for steel α = 12.0 × 10−6 K−1 and for brass α = 19.0 × 10−6 K−1 (see Table 13.2).arrow_forwardReview Conceptual Example 2 before attempting this problem. Two slits are 0.158 mm apart. A mixture of red light (wavelength = 693 nm) and yellow-green light (wavelength = 567 nm) falls on the slits. A flat observation screen is located 2.42 m away. What is the distance on the screen between the third-order red fringe and the third-order yellow-green fringe? m = 3 m = 3 m = 0 m = 3 m = 3 Fringes on observation screenarrow_forward
- A film of oil lies on wet pavement. The refractive index of the oil exceeds that of the water. The film has the minimum nonzero thickness such that it appears dark due to destructive interference when viewed in visible light with wavelength 643 nm in vacuum. Assuming that the visible spectrum extends from 380 to 750 nm, what is the longest visible wavelength (in vacuum) for which the film will appear bright due to constructive interference? Number Unitsarrow_forwardA piece of metal is placed on top of a 2.0 - kg wooden block (mass density = 562 kg/m³) piece. UseArchimedes' principle to calculate the mass (in kg) of copper if the top of the wood surface is exactly at thewater's surface?arrow_forwardA filmmaker wants to achieve an interesting visual effect by filming a scene through a converging lens with a focal length of 50.0 m. The lens is placed betwen the camera and a horse, which canters toward the camera at a constant speed of 7.9 m/s. The camera starts rolling when the horse is 36.0 m from the lens. Find the average speed of the image of the horse (a) during the first 2.0 s after the camera starts rolling and (b) during the following 2.0 s.arrow_forward
- What is the direction of the magnetic force on a NEGATIVE CHARGE that moves as shown in each of the six cases?arrow_forwardHi! I need help with these calculations for part i and part k for a physics Diffraction Lab. We used a slit width 0.4 mm to measure our pattern.arrow_forwardExamine the data and % error values in Data Table 3 where the angular displacement of the simple pendulum decreased but the mass of the pendulum bob and the length of the pendulum remained constant. Describe whether or not your data shows that the period of the pendulum depends on the angular displacement of the pendulum bob, to within a reasonable percent error.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





