
a.
The definition of rafter.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Rafter is defined as the building component that extended from hip to the wall. It is generally made of wood. It supports the load of roof deck. There are many types of rafter used in the building depending upon the size and location. The figure is shown below:
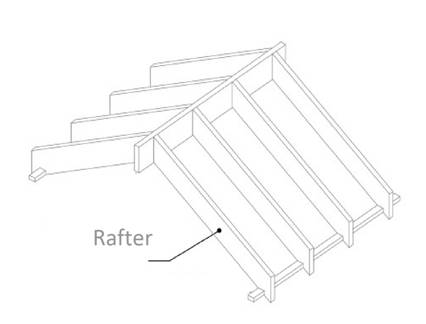
b.
The definition of truss.
b.
Explanation of Solution
It is defined as the collection of structural members that have only two force members. The whole structure acts as a single structure. The top member in the truss are generally in compression and the bottom member in the truss are generally in tension. Truss is used in railway bridges, stadium and electrical transmission towers. The figure is shown below:
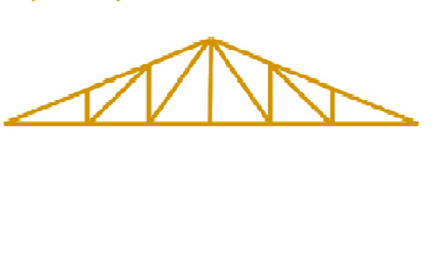
c.
The definition of the ceiling joist.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Ceiling joist is defined as the horizontal member that transfers the load from rooftop to vertical member. It lies between the beams in the building. It is placed on the top of the wall frame. if there are no ceiling joists are present in the house all the rooftop load will directly transfer to the wall. The figure is shown below:
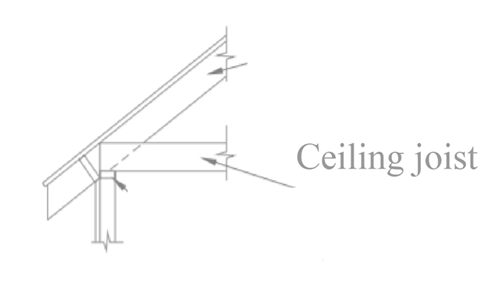
d.
The definition of collar tie.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Collar tie is defined as the horizontal member that runs in between rafters. Collar ties are always in tension. It helps in keeping the rafter beam with the ridge beam. It is always required in the upper third portion of rafter length. The main reason to provide the collar ties that it prevents the uplift force in case of winds. The figure is shown below:
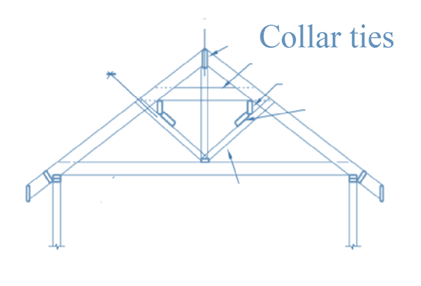
e.
The definition of jack studs.
e.
Explanation of Solution
A jack stud is a block of wood that is usually attached to the underside of the main stud to strengthen it. The jack stud is usually cut a shorter little than the other studs to five allowances for the opening. The figure is shown below:
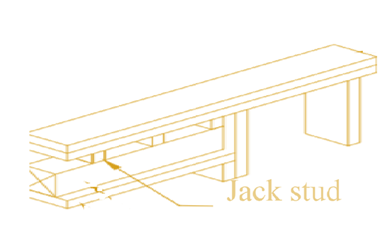
f.
The definition of rim joist.
f.
Explanation of Solution
It is defined as the structural member that withstand the lateral support for the joist to help in keeping all the joists together. It is generally made of the same material as the joists are made. It is attached perpendicular to the joist. The figure is shown below:
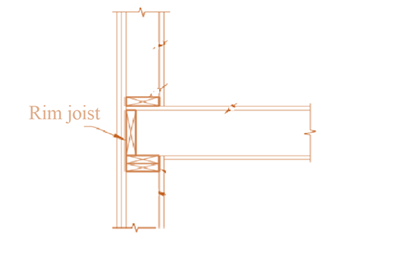
g.
The definition of chord.
g.
Explanation of Solution
It is defined as the outer member of the truss. The chord is subjected to compressive and bending stresses. It is part of the structural member of the truss. Chords define the envelope or shape.
The figure is shown below:
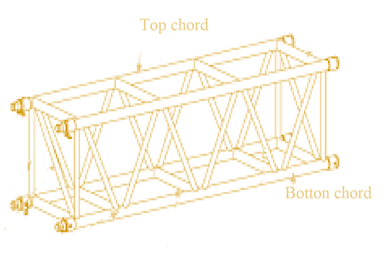
(h)
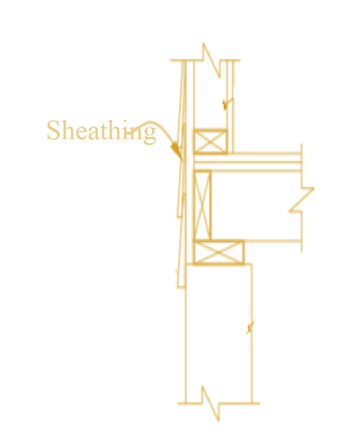
The definition of sheathing.
(h)
Explanation of Solution
It is defined as the material that is used in the wall or floor to provide the surface for other materials. There are many types of sheathing are used in building construction. It is a protective shield that is used in rooftop, walls and floor. It protects the house from rainwater, sunlight and wind. It can be made of wood or fiber. The figure is shown below:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course List)
- Calculate ALL nodal displacements and ALL the member forces in the truss. Please use the ID's noted in the truss diagramarrow_forwardQ3. In a water flood operation in reservoir A, water is being distributed to severalinjection wells from a common injection system; that is, water is supplied to all thewells at approximately the same well head pressure. Routine measurement of theindividual well injection rates by the team of field operators showed that one well wasreceiving approximately 45% more than its neighbours. The sum of the kh productsfor all of the injection wells were approximately the same depth. As a member of theteam, explain:What are the possible causes of the abnormally high injection rate in this well, andwhat production logs or other tests might be run to further diagnose the problem andplan remedial action?arrow_forwardQuestion 1 20 pts Test data on the bending strength of construction wood poles of various diameter are presented below assuming the same length. Kip- 1000 lbf. Using the following data with 2nd order Newton polynomial interpolation, we want to determine the strength of the material for x=4.5 in. Which data point will be used as x? After you found x0, enter the value of x-xo in the solution. Answer shall be in one decimal place. Distance (in) 2.6 1.5 8.3 2.8 5.7 Strength (kips) 100 200 300 400 500arrow_forward
- Solve pleasearrow_forwardsolve all of the last names from A-K to please for example use k=100k/in , m =1000lb/g . use el centro (2nd picture ) to solve the questions. Thank you for your help! for the following questions ignore that last name and just solve it pleae: Verify the modes that are orthogonal Normalize the first mode uisng electro with 2%damping, Determine Sa&Sd only for the first modearrow_forwardFor question 2 do 2% please. Use El centro spectrum to answer the secon question please. Thank you for your help!arrow_forward
- solve pleasearrow_forwardA mechanism for pushing small boxes from an assembly line onto a conveyor belt is shown with arm OD and crank CB in their vertical positions. For the configuration shown, crank CB has a constant clockwise angular velocity of 0.6π rad/s. Determine the acceleration QE of E (positive if to the right, negative if down). 450 mm 215 mm 565 mm A 185 mm 105 mm 110185. mm mm Answer: a = i B 40 mm E m/s²arrow_forwardPlease answer the following questions in the picture, use the second picture to answer some of the questions. I appreciate your help! Explain step by step, thank you!arrow_forward
- Question 5. Three pipes A, B, and C are interconnected as in Fig. 2. The pipe characteristics are given below. Find the rate at which water will flow in each pipe. Find also the pressure at point P. (Neglect minor losses) Pipe D (in) L (ft) f A 6 2000 0.020 B 4 1600 0.032 C 8 3000 0.02 -El. 200 ft P -El. 120 ft B Fig. 2 -El. 50 ft.arrow_forwardcalculate all nodal displacementts and all the member forces of the trussarrow_forwardNOTE: Use areal methods only for V,M,N diagrams(Do NOT use the equations) (also draw the N diagram(s) for the entire structure)arrow_forward
 Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Architectural Drafting and Design (MindTap Course...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781285165738Author:Alan Jefferis, David A. Madsen, David P. MadsenPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning

