
Concept explainers
Fill in the blanks in the table below summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
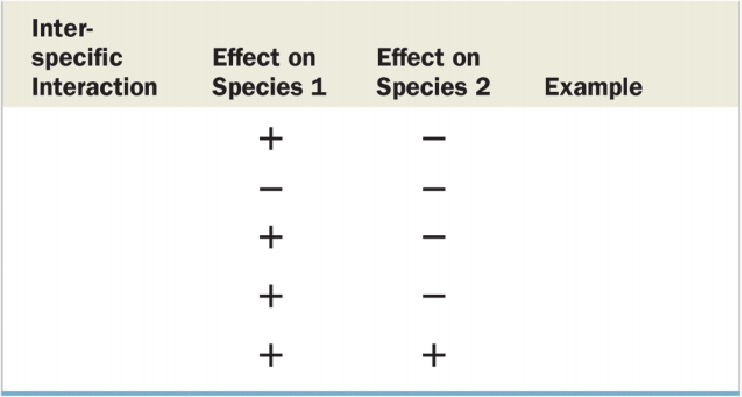
To complete: The blanks summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
Introduction: While surviving in an ecosystem, many species interact with each other. These interactions can be mutually beneficial or harmful for one or the other. There are five main types of interspecific interactions, namely, predation, competition, herbivory, parasitism, and mutualism.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Tabular representation: Table 1 represents the interspecific interactions in a community as follows:
| Interspecific interactions | Effect on species 1 | Effect on species 2 | Examples |
| Predation | + | - | Osprey/fish |
| Competition | - | - | Hyenas/vultures |
| Herbivory | + | - | Deer/shrub |
| Parasitism | + | - | Tapeworm/horse |
| Mutualism | + | + | Clown fish/anemone |
Table 1 Depicts the interspecific interactions in a community.
Explanation of Solution
The five types of interspecific interactions are as follows:
Predation: In predative interspecific interactions, one species preys on the other species for food or territory. It is a type of +/- interaction where one species benefits and the other species does not benefit. For example: interaction between a deer and a lion is predation.
Competition: It is the competitive interspecific interaction where two different types of species are competing for the same resource. Neither of them benefits from this, so it is a type of -/- interaction. For example: the interaction between vulture and hyenas.
Herbivory: It is the interaction between the herbivores and the plants. This interaction is a type of +/- interaction where the deer is benefited while the plant is not. For example: an interaction between deer and grass is herbivory.
Parasitism: It is parasitic form of interspecific interaction that involves one organism using the other for food and shelter. One organism such as the tapeworm inhabits the gut or any other part of the other organism such as the horse. This interaction is a +/- interactions, where only one is benefitted.
Mutualism: In this interaction, the organisms that are interacting are mutually beneficial for each other. One species provides one factor, while the other species provides another factor, for example, in the case of mycorrhiza, the fungus is in mutual interaction with the roots of the gymnosperm tree. The fungal element provides minerals and water from the soil, while the tree provides the nutrients. It is a +/+ form of interaction as both the organisms are benefitted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- Amino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forwardWhat is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forward
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





