
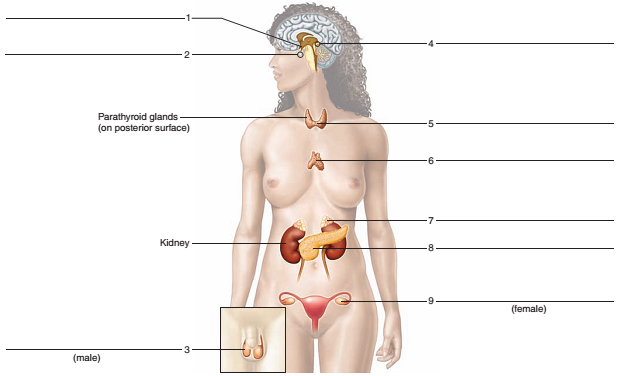
FIGURE 36.1 Label the major endocrine gladds.
To determine:
The endocrine glands in the given figure.
Introduction :
The glands of the endocrine system are termed as the endocrine glands. These glands secrete their secretions (hormones) directly into the blood, without the use of any kind of ducts. The glands included in the endocrine system are the pituitary glands, testes, ovaries, thyroid glands, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pineal glands, and pancreas.
Explanation of Solution
The endocrine glands in the given figure are labeled as follows:
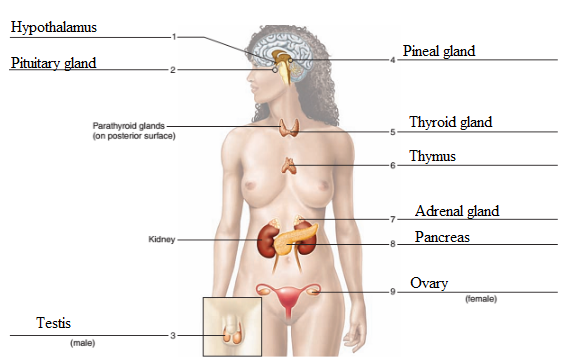
- Hypothalamus − It is small portion of the brain that is located at the brain’s base, near the pituitary gland. Its main function is to regulate body temperature.
- Pituitary gland - Pituitary gland is present in sella turcica of sphenoid bone. This gland is also termed as the master gland as the hormones released by this gland affect the metabolism, growth, sexuality, development, and reproduction of the body.
- Testis - Testes are the paired glands and are the important male reproductive organ that produces spermatozoa and androgens.
- Pineal gland − It is an endocrine gland found in the brain. It secrets melatonin that regulates the sleep-wake cycles in humans.
- Thyroid gland - Thyroid gland is the ductless gland located in the neck region. It produces thyroxine hormone. Thyroid stimulating hormone or thyrotropic hormone is a glycoprotein that stimulates the thyroid gland to secrete thyroxine (T4) hormone and then triiodothyronine hormone (T3).
- Thymus - Thymus is located in mediastinum and thoracic cavity of neck. In adolescent, it helps in the development of immune system.
- Adrenal gland - Adrenal glands are triangular shaped glands that are present at the top of both the kidneys. The adrenal cortex is the outermost portion of this gland. The adrenal medulla is the innermost portion of the adrenal gland that secretes flight and fight hormones, epinephrine and norepinephrine.
- Pancreas - The pancreas is located at the back of the stomach and behind the stomach. It functions as an endocrine gland and as well as an exocrine gland. Many enzymes and juices are secreted by the enzymes during the digestive process. The two important enzymes of this gland are insulin and glucagon.
- Ovary − It is an organ found in the reproductive system of the females to produce ovum.
The endocrine glands in the given figure are labeled as follows:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Holes Human Anatomy & Physiology Fetal Pig Version
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Microbiology Fundamentals: A Clinical Approach
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Normal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO2 level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO2 triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. How might the location and slope of the O₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO₂ line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardforaging/diet type teeth tongue stomach intestines cecum Insectivory numerous, spiky, incisors procumbentExample: moleExample: shrew -- simple short mostly lacking Myrmecophagy absent or reduced in numbers, peg-likeExample: tamandua anteater extremely long simple, often roughened short small or lacking Terrestrial carnivory sharp incisors; long, conical canines; often carnassial cheek teeth; may have crushing molarsExample: dog -- simple short small Aquatic carnivory homodont, spiky, numerousExample: common dolphin -- simple or multichambered (cetaceans only) variable small or absent Sanguinivory very sharp upper incisors; reduced cheek teethExample: vampire bat grooved tubular, highly extensible long small or lacking Herbivory (except nectivores) incisors robust or absent; canines reduced or absent; diastema; cheek teeth enlarged with complex occlusal surfacesExample: beaver -- simple (hindgut fermenters) or multichambered (ruminants) long large Filter feeding none…arrow_forward3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 པར『ན་ cm 30 Species B 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 cm 10 Species C 0/4, 0/0,3/3, 3/3 020arrow_forward
- 3. Shown below is the dental formula and digestive tract anatomy of three mammalian species (A, B, and C). What kind of diet would you expect each species to have? Support your answers with what you can infer from the dental formula and what you can see in the diagram. Broadly speaking, what accounts for the differences? Species A 3/3, 1/1, 4/4, 3/3 cm 30 Species B 0/4, 0/0, 3/3, 3/3 cm 10 Species C 4/3, 1/1, 2/2, 4/4 E 0 cm 20 AILarrow_forwardNormal dive (for diving humans) normal breathing dive normal breathing Oz level CO₂ level urgent need to breathe Oz blackout zone high CO₂ triggers breathing 6. This diagram shows rates of oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide accumulation in the blood in relation to the levels needed to maintain consciousness and trigger the urgent need to breathe in diving humans. • How might the location and slope of the O2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • How might the location and slope of the CO2 line differ for diving marine mammals such as whales and dolphins? • • Draw in predicted lines for O2 and CO2, based on your reasoning above. How might the location of the Urgent Need to Breathe line and the O2 Blackout Zone line differ for diving marine mammals? What physiological mechanisms account for each of these differences, resulting in the ability of marine mammals to stay submerged for long periods of time?arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- If a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade one small protein molecule into 8 molecules of pyruvic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume there is no other carbon source. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in molecules of ATP.arrow_forwardIf a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade a 30 mM solution of citric acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume no other carbon source is available. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- When beta-lactamase was isolated from Staphylcoccus aureus and treated with a phosphorylating agent, only the active site, serine was phosphorylated. Additionally, the serine was found to constitute 0.35% (by weight) of this beta-lactamase enzyme. Using this, calculate the molecular weight of this enzyme and estimate the number of amino acids present in the polypeptide.arrow_forwardBased on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?arrow_forwardhelp tutor pleasearrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





