
Concept explainers
(a)
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and outside air.
(a)
Answer to Problem 35.46P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown below.
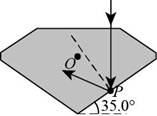
Figure (I)
From Snell’s law of refraction to air-diamond interface to find the critical angle is,
Here,
The value of
Substitute 1 for
Thus, the critical angle of refraction at air-diamond interface is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the critical angle of refraction at air-diamond interface is
(b)
To show: The light travelling towards point
(b)
Answer to Problem 35.46P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and outside air is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the angle of incidence is more than the critical angle all light is reflected from point P.
(c)
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond when the diamond is immersed in the water.
(c)
Answer to Problem 35.46P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
From Snell’s law of refraction to water-diamond interface to find the critical angle is,
Here,
The value of
Substitute 1 for
Thus, the critical angle of incidence at water-diamond interface is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the critical angle of incidence at water-diamond interface is
(d)
The ray incident at point P
(d)
Answer to Problem 35.46P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and water is
Thus, the light undergoes total internal reflection at
Conclusion:
Therefore, the light undergoes total internal reflection at
(e)
The direction in which the diamond is rotated such that the light at a point P
(e)
Answer to Problem 35.46P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
The critical angle for total internal reflection for light in the diamond incident on the interface between the diamond and water is
The light will exit from the diamond only when the incident angle is less than the critical angle. So, to reduce the angle of incidence the diamond should be rotated in clockwise direction on the axis perpendicular to the plane of paper.
Thus, the light will exit at point
Conclusion:
Therefore, the light will exit at point
(f)
The angle of rotation at which the light first exit the diamond at point P
(f)
Answer to Problem 35.46P
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The condition for light ray travelling between air and a diamond is shown in figure (I).
Let the angle is rotated clockwise by
Apply Snell’s law at the water-diamond interface.
The condition of the situation is shown below.
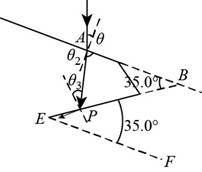
Figure (II)
The angle at the vertex
The requirement is that the angle of incidence
Apply Snell’s law and find angle
Substitute
Thus, the diamond is rotated by
Conclusion:
Therefore, the diamond is rotated by
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 35 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update, 9th Loose-leaf Version + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





