
Subpart (a):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The supply depends upon the
The
The equilibrium is a condition where the aggregate demand curve of the economy intersects with the aggregate supply curve of the economy. Then there will be an equilibrium point derived where the economy will be in its equilibrium without any excess demand or supply. The quantity on the X axis will represent the
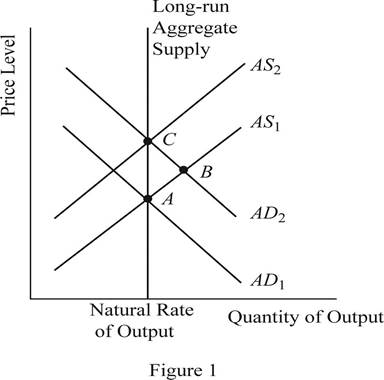
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or
Subpart (b):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
When the money supply of the economy increases with the intervention of the Central Bank of the economy, the money with the public will increase. When the money with the public increases, they will feel wealthier and as a result they will demand more consumer goods and services. As a result, the aggregate demand of the economy increases and it will shift the AD curve towards the right. This can be identified as the change to the equilibrium point B as shown in Figure 1. Thus, in short, the increase in the money supply leads to the increase in the output and price level of the economy.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (c):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
When the AD curve shifts towards the right and increases the output and the price level in the short run, over time, the nominal wages, prices as well as the perceptions and expectations of the economy would adjust to the new equilibrium level. As a result of this gradual adjustment, the cost of production will increase and the result will be a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve of the economy. Then the economy will return to its natural level of output at a higher price level of the economy. This can be identified as the movement from point B to point C in the graph shown above.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (d):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
The sticky wages theory suggests that when there is inflation in the economy, the wage rate will adjust very slowly to the inflation. More or less the wage rates will be sticky and the main reason will be the long term contracts between the employer and the employees. Thus, in the short run equilibriums such as point A and point B, the wages of the economy would be more or less equal to each other. Whereas the point C represents the long run equilibrium and thus, the wages at the point C will be higher than that in point A and B.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (e):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (e):
Explanation of Solution
The sticky wages theory suggests that when there is inflation in the economy, the wage rate will adjust very slowly to the inflation. More or less, the wage rates will be sticky and the main reason will be the long term contracts between the employer and the employees. So, the nominal wages at equilibrium point A and B will be same. But the increase in the general price level in the economy would reduce the real wages of the workers because, the real wage is the nominal wage divided by the price level. When the denominator increases, it will reduce the value of the real wages in the economy.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (f):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
When the increase in the money supply happens in the economy, it will lead to the increase in the nominal wages as well as the price level in the economy in the long run. As a result of the increase in the nominal wage rate along with the price level in the economy, the real wage rate of the economy would remain unchanged. Thus, the neutrality of money applies in the long run equilibrium.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
- Please draw the Federal Reserve System’s Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main components.arrow_forward19. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. How does the Federal Reserve currently get the federal funds rate where they want it to be?arrow_forward18. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Carefully compare and contrast fiscal policy and monetary policy.arrow_forward
- 15. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What are the common arguments for and against high levels of federal debt?arrow_forward17. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Explain the difference between present value and future value. Be sure to use and explain the mathematical formulas for both. How does one interpret these formulas?arrow_forward12. Give the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Show and carefully explain the Taylor rule and all of its components, used as a monetary policy guide.arrow_forward
- 20. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What is meant by the Federal Reserve’s new term “ample reserves”? What may be hidden in this new formulation by the Fed?arrow_forward14. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What is the Keynesian view of fiscal policy and why are some economists skeptical?arrow_forward16. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Describe a bond or Treasury security. What are its components and what do they mean?arrow_forward
- 13. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Where does the government get its funds that it spends? What is the difference between federal debt and federal deficit?arrow_forward11. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Why is determining the precise interest rate target so difficult for the Fed?arrow_forwardProblem 1 Regression Discontinuity In the beginning of covid, the US government distributed covid stimulus payments. Suppose you are interested in the effect of receiving the full amount of the first stimulus payment on the total spending in dollars by single individuals in the month after receiving the payment. Single individuals with annual income below $75,00 received the full amount of the stimulus payment. You decide to use Regression Discontinuity to answer this question. The graph below shows the RD model. 3150 3100 3050 Total Spending in the month after receiving the stimulus payment 2950 3000 74000 74500 75000 75500 76000 Annual income a. What is the outcome? (5 points) b. What is the treatment? (5 points) C. What is the running variable? (5 points) d. What is the cutoff? (5 points) e. Who is in the treatment group and who is in the control group? (10 points) f. What is the discontinuity in the graph and how do you interpret it? (10 points) g. Explain a scenario which can…arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





