
Test your knowledge of the five major classes of plant hormones (auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid, ethylene) by matching one hormone to each lettered box. (Note that some hormones will match up to more than one box.)
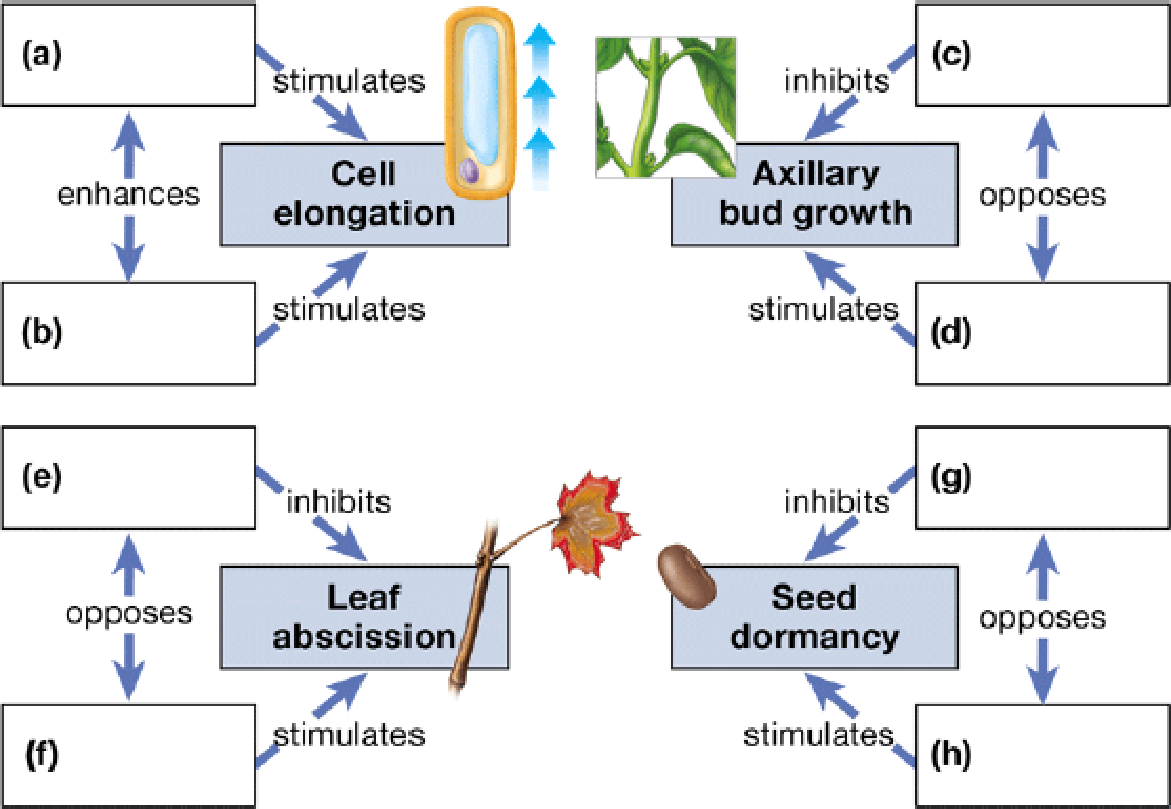
To complete: The given map of the five major classes of plant hormones.
Concept introduction:
Plant hormones are chemical messengers that are produced in trace amounts, but profoundly affect the growth and development of a plant. These include auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid and ethylene.
The plant hormones perform various functions such as promoting growth, breaking dormancy, mediating fruit ripening and providing tolerance to stress.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the completed map representing the five major classes of plant hormones.
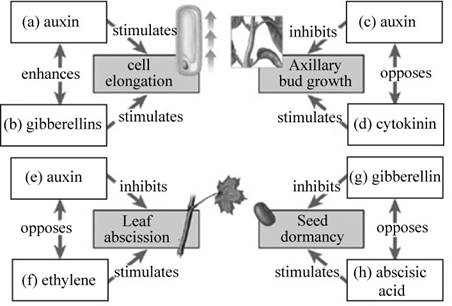
Fig.1: The five major classes of plant hormones.
(a)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: Auxins are a group of plant hormones that promotes cell elongation. They are produced by the apical meristems of shoot and root. They promote the growth of root and shoot of the plant. Hence the correct answer is auxin.
(b)
Correct answer: Gibberellins.
Explanation: The gibberellins are a group of plant hormones that stimulate the elongation of stem by promoting cell elongation. Hence the correct answer is gibberellins.
(c)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: Auxin is produced by the apical bud of the shoot and functions to inhibit the growth of axillary buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Hence, the correct answer is auxin.
(d)
Correct answer: cytokinin.
Explanation: The cytokinins are a group of plant hormones that stimulate rapid cell division in roots and shoots of the plant. It also promotes the growth of lateral buds, thereby nullifying the effects of auxin. Hence, the correct answer is cytokinin.
(e)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: In addition to cell elongation, the auxins also function to retard the abscission of leaves. It also plays a crucial role in nullifying the effects of ethylene. Hence, the correct answer is auxin.
(f)
Correct answer: Ethylene.
Explanation: Ethylene is a gaseous hormone that promotes ripening of fruit and abscission of leaves from trees. Hence, the correct answer is ethylene.
(g)
Correct answer: Gibberellin.
Explanation: The gibberellin is a plant hormone that promotes the germination of seed. It inhibits seed dormancy by nullifying the effects of abscisic acid. Hence the correct answer is gibberellin.
(h)
Correct answer: Abscisic acid.
Explanation: The abscisic acid is a plant hormone that is involved in the stress responses. It inhibits growth, promotes seed dormancy during winter or periods of drought. Hence, the correct answer is abscisic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- Amino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forwardWhat is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forward
- please fill in the empty sports, thank you!arrow_forwardIn one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forward
- The Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





