
Test your knowledge of the five major classes of plant hormones (auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid, ethylene) by matching one hormone to each lettered box. (Note that some hormones will match up to more than one box.)
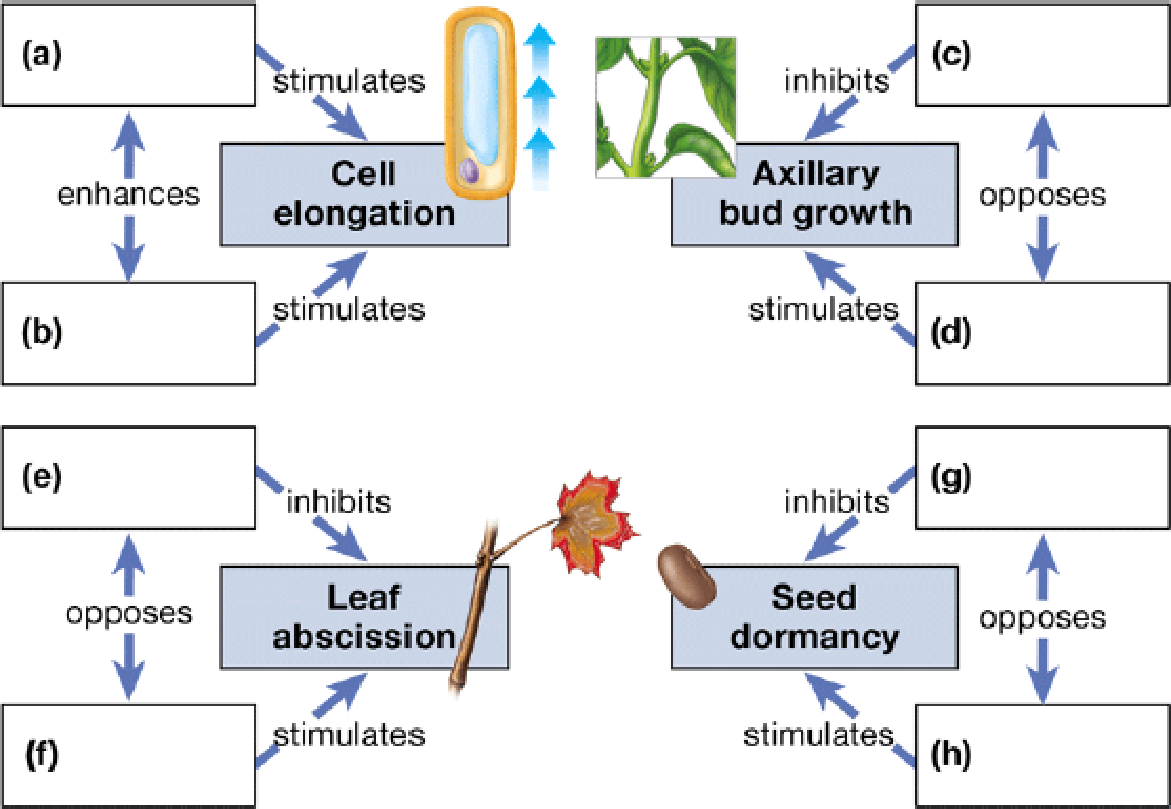
To complete: The given map of the five major classes of plant hormones.
Concept introduction:
Plant hormones are chemical messengers that are produced in trace amounts, but profoundly affect the growth and development of a plant. These include auxins, cytokinins, gibberellins, abscisic acid and ethylene.
The plant hormones perform various functions such as promoting growth, breaking dormancy, mediating fruit ripening and providing tolerance to stress.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the completed map representing the five major classes of plant hormones.
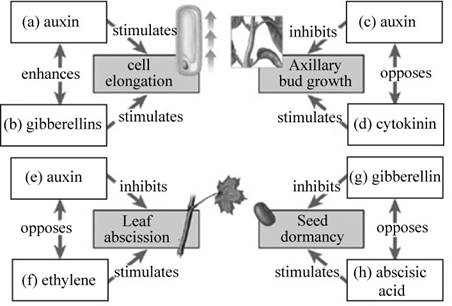
Fig.1: The five major classes of plant hormones.
(a)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: Auxins are a group of plant hormones that promotes cell elongation. They are produced by the apical meristems of shoot and root. They promote the growth of root and shoot of the plant. Hence the correct answer is auxin.
(b)
Correct answer: Gibberellins.
Explanation: The gibberellins are a group of plant hormones that stimulate the elongation of stem by promoting cell elongation. Hence the correct answer is gibberellins.
(c)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: Auxin is produced by the apical bud of the shoot and functions to inhibit the growth of axillary buds, a phenomenon called apical dominance. Hence, the correct answer is auxin.
(d)
Correct answer: cytokinin.
Explanation: The cytokinins are a group of plant hormones that stimulate rapid cell division in roots and shoots of the plant. It also promotes the growth of lateral buds, thereby nullifying the effects of auxin. Hence, the correct answer is cytokinin.
(e)
Correct answer: Auxin.
Explanation: In addition to cell elongation, the auxins also function to retard the abscission of leaves. It also plays a crucial role in nullifying the effects of ethylene. Hence, the correct answer is auxin.
(f)
Correct answer: Ethylene.
Explanation: Ethylene is a gaseous hormone that promotes ripening of fruit and abscission of leaves from trees. Hence, the correct answer is ethylene.
(g)
Correct answer: Gibberellin.
Explanation: The gibberellin is a plant hormone that promotes the germination of seed. It inhibits seed dormancy by nullifying the effects of abscisic acid. Hence the correct answer is gibberellin.
(h)
Correct answer: Abscisic acid.
Explanation: The abscisic acid is a plant hormone that is involved in the stress responses. It inhibits growth, promotes seed dormancy during winter or periods of drought. Hence, the correct answer is abscisic acid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS+CONNECTIONS
- Not part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forwardNoggin mutation: The mouse, one of the phenotypic consequences of Noggin mutationis mispatterning of the spinal cord, in the posterior region of the mouse embryo, suchthat in the hindlimb region the more ventral fates are lost, and the dorsal Pax3 domain isexpanded. (this experiment is not in the lectures).a. Hypothesis for why: What would be your hypothesis for why the ventral fatesare lost and dorsal fates expanded? Include in your answer the words notochord,BMP, SHH and either (or both of) surface ectoderm or lateral plate mesodermarrow_forwardNot part of a graded assignment, from a past midtermarrow_forward
- Explain in a flowcharts organazing the words down below: genetics Chromosomes Inheritance DNA & Genes Mutations Proteinsarrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardWhat does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about water reabsorption in this individual at this time? What does the heavy dark line along collecting duct tell us about ADH secretion in this individual at this time?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning





