
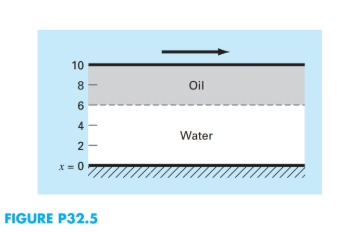
Two plates are 10cmapart, as shownin Fig.P32.5. Initially, both plates and the fluid are still. At
and the following relationships hold true at the oil-water interface:
What is the velocity of the two fluid layers at
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 32 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
- A straight-line H is tangent to the function g(x)=-6x-3+ 8 and passes through the point (- 4,7). Determine, the gradient of the straight-line Choose.... y-intercept of the straight-line Choose... + which of the following is the answers -1.125 -6.72 1.125 7.28 0.07 - 7.28 6.72arrow_forwardYou are required to match the correct response to each statement provided. Another term/word that can be used synonymously to Choose... gradient. A term/phrase that is associated with Arithmetic Progression. Common difference → An identity matrix can be referred to as a Choose... ÷ What is the inequality sign that represents "at most"? VIarrow_forwardAffect of sports on students linked with physical problemsarrow_forward
- 26.1. Locate and determine the order of zeros of the following functions: (a). e2z – e*, (b). z2sinhz, (c). z*cos2z, (d). z3 cosz2.arrow_forwardQ/ show that: The function feal = Se²²²+d+ is analyticarrow_forwardComplex Analysis 2 First exam Q1: Evaluate f the Figure. 23+3 z(z-i)² 2024-2025 dz, where C is the figure-eight contour shown in C₂arrow_forward
- Q/ Find the Laurent series of (2-3) cos around z = 1 2-1arrow_forward31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forwardUsing FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative; 1. The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in meters) at an interval of half a second. The data obtained is: t 0 x 0 0.5 3.65 1.0 1.5 2.0 6.80 9.90 12.15 Use CDF to approximate the runner's velocity at times t = 0.5s and t = 1.5s 2. Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative of f(x)=x Inx for an input of 2 assuming a step size of 1. Calculate using Analytical Solution and Absolute Relative Error: = True Value - Approximate Value| x100 True Value 3. Given the data below where f(x) sin (3x), estimate f(1.5) using Langrage Interpolation. x 1 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 f(x) 0.14 -0.69 -0.99 -0.55 0.31 4. The vertical distance covered by a rocket from t=8 to t=30 seconds is given by: 30 x = Loo (2000ln 140000 140000 - 2100 9.8t) dt Using the Trapezoidal Rule, n=2, find the distance covered. 5. Use Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 Rule to approximate for sin x dx. Compare the results for n=4 and n=8arrow_forward
- 1. A Blue Whale's resting heart rate has period that happens to be approximately equal to 2π. A typical ECG of a whale's heartbeat over one period may be approximated by the function, f(x) = 0.005x4 2 0.005x³-0.364x² + 1.27x on the interval [0, 27]. Find an nth-order Fourier approximation to the Blue Whale's heartbeat, where n ≥ 3 is different from that used in any other posts on this topic, to generate a periodic function that can be used to model its heartbeat, and graph your result. Be sure to include your chosen value of n in your Subject Heading.arrow_forward7. The demand for a product, in dollars, is p = D(x) = 1000 -0.5 -0.0002x² 1 Find the consumer surplus when the sales level is 200. [Hints: Let pm be the market price when xm units of product are sold. Then the consumer surplus can be calculated by foam (D(x) — pm) dx]arrow_forward4. Find the general solution and the definite solution for the following differential equations: (a) +10y=15, y(0) = 0; (b) 2 + 4y = 6, y(0) =arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
