
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780134296074
Author: GIANCOLI
Publisher: VST
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 32, Problem 57P
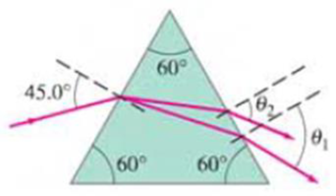
(II) A parallel beam of light containing two wavelengths, λ1 = 465 nm and λ2 = 652 nm, enters the silicate flint glass of an equilateral prism as shown in Fig. 32–54. At what angle does each beam leave the prism (give angle with normal to the face)? See Fig. 32–28.
FIGURE 32–54
Problem 54.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Imagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.
Deduce what overvoltage is like in reversible electrodes.
pls help on these
Chapter 32 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS & ENGINEERS
Ch. 32 - What would be the appearance of the Moon if it had...Ch. 32 - Archimedes is said to have burned the whole Roman...Ch. 32 - What is the focal length of a plane mirror? What...Ch. 32 - An object is placed along the principal axis of a...Ch. 32 - Using the rules for the three rays discussed with...Ch. 32 - Prob. 6QCh. 32 - If a concave mirror produces a real image, is the...Ch. 32 - Prob. 8QCh. 32 - When you look at the Moons reflection from a...Ch. 32 - How can a spherical mirror have a negative object...
Ch. 32 - Prob. 11QCh. 32 - When you look down into a swimming pool or a lake,...Ch. 32 - Draw a ray diagram to show why a stick looks bent...Ch. 32 - (I) When you look at yourself in a 60-cm-tall...Ch. 32 - (II) Show that if two plane mirrors meet at an...Ch. 32 - (II) The block of glass (n = 1.5) shown in cross...Ch. 32 - (II) Show in general that for a light beam...Ch. 32 - (III) A light ray is incident on a flat piece of...Ch. 32 - (I) By what percent is the speed of blue light...Ch. 32 - (I) A light beam strikes a piece of glass at a...Ch. 32 - (II) A parallel beam of light containing two...Ch. 32 - Two identical concave mirrors are set facing each...Ch. 32 - A kaleidoscope makes symmetric patterns with two...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
What type of unconformity separates layer G from layer F?
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
WHAT IF? What would the human life cycle be like if we had alternation of generations? Assume that the multice...
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Choose the best answer to each of the following. Explain your reasoning. Which describes our understanding of f...
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Using the pKa values listed in Table 15.1, predict the products of the following reactions:
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
5. When the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes, this patt...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
- 6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
An Introduction to Physical SciencePhysicsISBN:9781305079137Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

An Introduction to Physical Science
Physics
ISBN:9781305079137
Author:James Shipman, Jerry D. Wilson, Charles A. Higgins, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY