
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780321973610
Author: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 31.1, Problem 31.1TYU
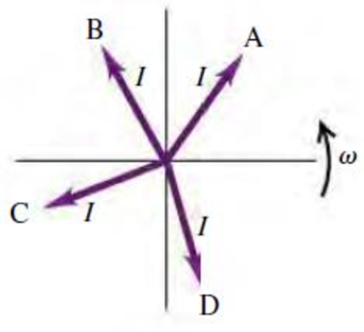
The accompanying figure shows four different current phasors with the same angular frequency ω. At the time shown, which phasor corresponds to (a) a positive current that is becoming more positive; (b) a positive current that is decreasing toward zero; (c) a negative current that is becoming more negative; (d) a negative current that is decreasing in magnitude toward zero?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule02:09
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Chapter 31 Solutions
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
Ch. 31.1 - The accompanying figure shows four different...Ch. 31.2 - An oscillating voltage of fixed amplitude is...Ch. 31.3 - Rank the following ac circuits in order of their...Ch. 31.4 - Prob. 31.4TYUCh. 31.5 - How does the resonance frequency of an L-R-C...Ch. 31.6 - Each of the following four transformers has 1000...Ch. 31 - Household electric power in most of western Europe...Ch. 31 - The current in an ac power line changes direction...Ch. 31 - In an ac circuit, why is the average power for an...Ch. 31 - Equation (31.14) was derived by using the...
Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.5DQCh. 31 - Equation (31.9) says that ab = L di/dt (see Fig....Ch. 31 - Is it possible for the power factor of an L-R-C...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, can the instantaneous...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, what are the phase...Ch. 31 - When an L-R-C series circuit is connected across a...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.11DQCh. 31 - A light bulb and a parallel-plate capacitor with...Ch. 31 - A coil of wire wrapped on a hollow tube and a...Ch. 31 - A circuit consists of a light bulb, a capacitor,...Ch. 31 - A circuit consists of a light bulb, a capacitor,...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.16DQCh. 31 - An ideal transformer has N1, windings in the...Ch. 31 - An inductor, a capacitor, and a resistor are all...Ch. 31 - You want to double the resonance angular frequency...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.1ECh. 31 - A sinusoidal current i = I cos t has an rms value...Ch. 31 - The voltage across the terminals of an ac power...Ch. 31 - A capacitor is connected across an ac source that...Ch. 31 - An inductor with L = 9.50 mH is connected across...Ch. 31 - A capacitance C and an inductance L are operated...Ch. 31 - Kitchen Capacitance. The wiring for a refrigerator...Ch. 31 - (a) Compute the reactance of a 0.450-H inductor at...Ch. 31 - (a) What is the reactance of a 3.00-H inductor at...Ch. 31 - A Radio Inductor. You want the current amplitude...Ch. 31 - A 0.180-H inductor is connected in series with a...Ch. 31 - A 250- resistor is connected in series with a...Ch. 31 - A 150- resistor is connected in series with a...Ch. 31 - You have a 200- resistor, a 0.400-H inductor, and...Ch. 31 - The resistor, inductor, capacitor, and voltage...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.16ECh. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, the rms voltage across...Ch. 31 - A resistor with R = 300 and an inductor are...Ch. 31 - The power of a certain CD player operating at 120...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, the components have...Ch. 31 - (a) Show that for an L-R-C series circuit the...Ch. 31 - (a) Use the results of part (a) of Exercise 31.21...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit with L = 0.120 H, R = 240...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit is connected to a 120-Hz...Ch. 31 - A series ac circuit contains a 250- resistor, a...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit the source is operated...Ch. 31 - Analyzing an L-R-C Circuit. You have a 200-...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit is constructed using a...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, R = 300, L = 0.400 H,...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit consists of a source with...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, R = 150 , L = 0.750 H,...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, R = 400 , L = 0.350 H,...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, L = 0.280 H and C =...Ch. 31 - Section 31.6 Transformers 31.34Off to Europe! You...Ch. 31 - A Step-Down Transformer. A transformer connected...Ch. 31 - A Step-Up Transformer. A transformer connected to...Ch. 31 - A coil has a resistance of 48.0 . At a frequency...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.38PCh. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit has C = 4.80 F, L = 0.520...Ch. 31 - Five infinite-impedance voltmeters, calibrated to...Ch. 31 - CP A parallel-plate capacitor having square plates...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.42PCh. 31 - A series circuit has an impedance of 60.0 and a...Ch. 31 - A large electromagnetic coil is connected to a...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, R = 300 , XC = 300 ,...Ch. 31 - At a frequency 1, the reactance of a certain...Ch. 31 - A High-Pass Filter. One application of L-R-C...Ch. 31 - A Low-Pass Filter. Figure P31.48 shows a low-pass...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit is connected to an ac...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit is connected to an ac...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit the magnitude of the...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, the phase angle is...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit has R = 500 . L = 2.00 H,...Ch. 31 - The L-R-C Parallel Circuit. A resistor, an...Ch. 31 - The impedance of an L-R-C parallel circuit was...Ch. 31 - A 400- resistor and a 6.00-F capacitor are...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit consists of a 2.50-F...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit has R = 60.0 , L = 0.800...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series circuit, the source has a...Ch. 31 - In an L-R-C series ac circuit, the source has a...Ch. 31 - A resistance R, capacitance C, and inductance L...Ch. 31 - The Resonance Width. Consider an L-R-C series...Ch. 31 - An L-R-C series circuit draws 220 W from a 120-V...Ch. 31 - DATA A coworker of yours was making measurements...Ch. 31 - DATA You are analyzing an ac circuit that contains...Ch. 31 - DATA You are given this table of data recorded for...Ch. 31 - CALC In an L-R-C series circuit the current is...Ch. 31 - CALC (a) At what angular frequency is the voltage...Ch. 31 - Prob. 31.69PPCh. 31 - If the electrode oscillates between two points 20...Ch. 31 - The signal from the oscillating electrode is fed...Ch. 31 - If the frequency at which the electrode is...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
When you rub your cold hands together, the friction between them results in heat that warms your hands. Why doe...
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
All of the following processes are involved in the carbon cycle except: a. photosynthesis b. cell respiration c...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
4. How do gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy differ?
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
For parts a, b, and c, draw a diagram illustrating the alleleson homologous chromosomes for the following genot...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Two culture media were inoculated with four different bacteria. After incubation, the following results were ob...
Microbiology: An Introduction
4. Three groups of nonvascular plants are _______, ______, and _______. Three groups of seedless vascular plant...
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are standing a distance x = 1.75 m away from this mirror. The object you are looking at is y = 0.29 m from the mirror. The angle of incidence is θ = 30°. What is the exact distance from you to the image?arrow_forwardFor each of the actions depicted below, a magnet and/or metal loop moves with velocity v→ (v→ is constant and has the same magnitude in all parts). Determine whether a current is induced in the metal loop. If so, indicate the direction of the current in the loop, either clockwise or counterclockwise when seen from the right of the loop. The axis of the magnet is lined up with the center of the loop. For the action depicted in (Figure 5), indicate the direction of the induced current in the loop (clockwise, counterclockwise or zero, when seen from the right of the loop). I know that the current is clockwise, I just dont understand why. Please fully explain why it's clockwise, Thank youarrow_forwardA planar double pendulum consists of two point masses \[m_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}, \qquad m_2 = 1.00~\mathrm{kg}\]connected by massless, rigid rods of lengths \[L_1 = 1.00~\mathrm{m}, \qquad L_2 = 1.20~\mathrm{m}.\]The upper rod is hinged to a fixed pivot; gravity acts vertically downward with\[g = 9.81~\mathrm{m\,s^{-2}}.\]Define the generalized coordinates \(\theta_1,\theta_2\) as the angles each rod makes with thedownward vertical (positive anticlockwise, measured in radians unless stated otherwise).At \(t=0\) the system is released from rest with \[\theta_1(0)=120^{\circ}, \qquad\theta_2(0)=-10^{\circ}, \qquad\dot{\theta}_1(0)=\dot{\theta}_2(0)=0 .\]Using the exact nonlinear equations of motion (no small-angle or planar-pendulumapproximations) and assuming the rods never stretch or slip, determine the angle\(\theta_2\) at the instant\[t = 10.0~\mathrm{s}.\]Give the result in degrees, in the interval \((-180^{\circ},180^{\circ}]\).arrow_forward
- What are the expected readings of the ammeter and voltmeter for the circuit in the figure below? (R = 5.60 Ω, ΔV = 6.30 V) ammeter I =arrow_forwardsimple diagram to illustrate the setup for each law- coulombs law and biot savart lawarrow_forwardA circular coil with 100 turns and a radius of 0.05 m is placed in a magnetic field that changes at auniform rate from 0.2 T to 0.8 T in 0.1 seconds. The plane of the coil is perpendicular to the field.• Calculate the induced electric field in the coil.• Calculate the current density in the coil given its conductivity σ.arrow_forward
- An L-C circuit has an inductance of 0.410 H and a capacitance of 0.250 nF . During the current oscillations, the maximum current in the inductor is 1.80 A . What is the maximum energy Emax stored in the capacitor at any time during the current oscillations? How many times per second does the capacitor contain the amount of energy found in part A? Please show all steps.arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current of 10 A along what we’ll define to the be x-axis. A square loopin the x-y plane with side length 0.1 m is placed near the wire such that its closest side is parallel tothe wire and 0.05 m away.• Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop using Ampere’s law.arrow_forwardDescribe the motion of a charged particle entering a uniform magnetic field at an angle to the fieldlines. Include a diagram showing the velocity vector, magnetic field lines, and the path of the particle.arrow_forward
- Discuss the differences between the Biot-Savart law and Coulomb’s law in terms of their applicationsand the physical quantities they describe.arrow_forwardExplain why Ampere’s law can be used to find the magnetic field inside a solenoid but not outside.arrow_forward3. An Atwood machine consists of two masses, mA and m B, which are connected by an inelastic cord of negligible mass that passes over a pulley. If the pulley has radius RO and moment of inertia I about its axle, determine the acceleration of the masses mA and m B, and compare to the situation where the moment of inertia of the pulley is ignored. Ignore friction at the axle O. Use angular momentum and torque in this solutionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY