
PRIN.OF CORPORATE FINANCE
13th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013900
Author: BREALEY
Publisher: RENT MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 31, Problem 1PS
Summary Introduction
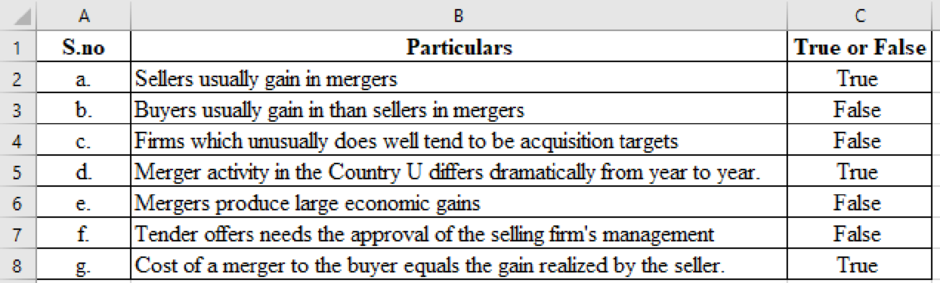
To indicate: Whether the transactions are true or false.
Expert Solution & Answer
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Yellow Ocean Paint is evaluating Project A. In year 3, Yellow Ocean Paint would have revenue of $688,000 and costs of $314,000 if it
pursues Project A, and the firm would have revenue of $579,000 and costs of $219,000 if it does not pursue Project A. Depreciation
taken by the firm in year 3 would be $216,000 if the firm pursues the project and $162,000 if the firm does not pursue the project. The
tax rate is 20 percent. What is the operating cash flow for year 3 that Yellow Ocean Paint should use in its NPV analysis of Project A?
Input instructions: Round your answer to the nearest dollar.
22,000 dollars
The excess of the present value of benefits over the present value of costs of a course of Action is called as:
a.All of these
b.Benefits
c.Wealth
d.Payoff
The decisions relating to the use of profits or income of an entity or organization are known
a.Any of these
b.Dividend decisions
c.Finance decisions
d.Investment Decision
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What are the three interrelated areas of finance? (a) Financial markets, option and forwards (b) Banking, financial institutions and swap currency (c) Investment, Financial management and Financial market & Financial institution (d) All of abovearrow_forwardThe method that converts the amount of present cash into an amount of cash of equivalent value in future is: a.Budgeting b.Both a and b c.Discounting method d.Compounding methodarrow_forwardThe government finance which includes the principles and practices relating to the Procurement and management of funds for Central Government, and Local bodies is known as: a.Public Finance b.All of these c.Private Finance d.Business Financearrow_forward
- what is financial ratios?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is the activity which finance people are involved? (a) Investing decisions (b) Marketing decisions (c) Promotion decisions (d) Non of Abovearrow_forwardYou plan to invest $3,500 per year for 39 years into an IRA. What will the value of the IRA be after 39 years if the interest rate is 9% per year? Your answer may vary due to rounding.arrow_forward
- In finance, we refer to the market where new securities are bought and sold for the first time? (a) Money market (b) Capital market (c) Primary market (d) Secondary marketarrow_forward1: ________ is shown on a multiple-step but not on a single-step income statement. A. Credited to Inventory B. A customer utilizes a prompt payment incentive. C. Debited to the Inventory account D. Gross profitarrow_forwardwhat is corporate finance? explain it.arrow_forward
- A lorenz curve graphs the _________________ received by everyone up to a certain quintile. A. Unequal distribution over time B. Normative shares of income C. Cumulative shares of income D. Total share of incomearrow_forwardNeedhdjxjx ususs shsharrow_forwardCalculate dividends for this question i need help.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
