
Subpart (a):
The production possibility frontier .
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
Figure -1 illustrates production possibility frontier.
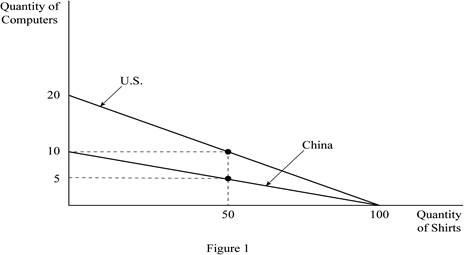
Figure 1 shows the production possibilities frontiers for the two countries; U.S. and China. In Figure 1, the horizontal axis measures the quantity of shirts produced by both the countries and the vertical axis measures the quantity of computers produced. If either worker of the two countries, that is an American or a Chinese worker devotes all his labor hours in producing shirts, each worker can produce 100 shirts in a year. Then, it is the vertical intercept of the PPF for both the American and the Chinese worker. If they devote all of their time to the production of computers, then the U.S. worker can produce 20 computers in a year, while the Chinese worker can produce only 10 computers per year. These are the horizontal intercepts of the PPF for the U.S. and the Chinese worker, respectively. Since the
Concept introduction:
Production possibility frontier (PPF): PPF is a curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs consisting of resources and other factors.
Subpart (b):
Opportunity cost and price of the good.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
To determine the export pattern of shirts, the
Opportunity cost of shirts in the U.S. is calculated as,
Thus, the price of 1 shirt in the U.S. is 0.2 computers.
Opportunity cost of shirts in China is calculated as,
Thus, the price of 1 shirt in China is 0.1 computers.
Since China has a lower opportunity cost of shirts, China has a comparative advantage in its production. So, China will produce and export shirts to the U.S. in exchange for computers from the U.S. since the latter has a comparative advantage in the production of computers (5 shirts
The range of prices of shirts at which trade can occur is between 0.1 and 0.2 computers, per computer.
An example would be a price of 0.15 computers. Suppose China produced only shirts (100 shirts) and exported 50 shirts in exchange for 7.5
The United States is also benefited from this trade. Suppose American workers produced only computers (20 computers) and traded 7.5 of computers to China for 50 shirts. The U.S. would have 12.5 (20-7.5) computers and 50 shirts. Thus, the U.S. would be better off than before trade (10 computers and 50 shirts).
Concept introduction:
Production possibility frontier (PPF): PPF is a curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs consisting of resources and other factors.
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost is the cost of foregone alternative, that is, loss of an alternative when another alternative is chosen.
Comparative advantage: It refers to the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer.
Subpart (c):
Opportunity cost and price of the good.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
For the calculation of price, the calculation of opportunity cost is required.
Opportunity cost of a computer in the U.S. is calculated as,
Thus, the price of 1 computer in the U.S. is 5 shirts.
Opportunity cost of a computer in China is calculated as,
Thus, the price of 1 computer in China is 10 shirts.
The range of prices of computers at which trade can occur is between 5 and 10 shirts per computer. This is because, at a price lower than 5 shirts, the U.S. will choose to produce its own shirts and will be unwilling to export computers, as the opportunity cost of a shirt for the U.S. is 0.2
Concept introduction:
Production possibility frontier (PPF): PPF is a curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs consisting of resources and other factors.
Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost is the cost of foregone alternative, that is, loss of an alternative when another alternative is chosen.
Comparative advantage: It refers to the ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer.
Subpart (d):
Gains from the trade.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
Concept introduction:
Specialization: Specialization refers to allocate the work according to their efficiency. If an individual, company or country has produced a good at lower opportunity cost, then that particular individual, company or country should produce those goods.
Trade: The trade refers to the exchange of capital, goods, and services across different countries.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
- If the US Federal Reserve increases interests on reserves, how will that change the original equilibrium shown in the graph? Euros par US alar 1.10 1.00 0.90- E 0.80- 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40- 0.30 0.20 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 Quantity of US Dollars traded for Euros (trillions/day) It will increase the demand for Dollars and decrease the supply, so the exchange rate decreases, and the quantity traded increases. O It will decrease the demand for Dollars and increase the supply, so the exchange rate decreases and the impact on the quantity traded is unknown. O It will increase the demand for Dollars and decrease the supply, so the exchange rate increases and the impact on the quantity traded is unknown O It will decrease the demand for Dollars and increase the supply, so the exchange rate decreases, and the quantity traded increases. Question 22 5 ptsarrow_forward1. Based on the video, answer the following questions. • What are the 5 key characteristics that differentiate perfect competition from monopoly? Based on the video. • How does the number of sellers in a market influence the type of market structure? Based on the video. • In what ways does product differentiation play a role in monopolistic competition? Based on the video. • How do barriers to entry affect the level of competition in an oligopoly? Based on the video. • Why might firms in an oligopolistic market engage in non-price competition rather than price wars? Based on the video. Reference video: https://youtu.be/Qrr-IGR1kvE?si=h4q2F1JFNoCI36TVarrow_forward1. Answer the following questions based on the reference video below: • What are the 5 key characteristics that differentiate perfect competition from monopoly? • How does the number of sellers in a market influence the type of market structure? • In what ways does product differentiation play a role in monopolistic competition? • How do barriers to entry affect the level of competition in an oligopoly? • Why might firms in an oligopolistic market engage in non-price competition rather than price wars? Discuss. Reference video: https://youtu.be/Qrr-IGR1kvE?si=h4q2F1JFNoCI36TVarrow_forward
- Explain the importance of differential calculus within economics and business analysis. Provide three refernces with your answer. They can be from websites or a journals.arrow_forwardAnalyze the graph below, showing the Gross Federal Debt as a percentage of GDP for the United States (1939-2019). Which of the following is correct? FRED Gross Federal Debt as Percent of Gross Domestic Product Percent of GDP 120 110 100 60 50 40 90 30 1940 1950 1960 1970 Shaded areas indicate US recessions 1980 1990 2000 2010 1000 Sources: OMD, St. Louis Fed myfred/g/U In 2019, the Federal Government of the United States had an accumulated debt/GDP higher than 100%, meaning that the amount of debt accumulated over time is higher than the value of all goods and services produced in that year. The debt/GDP is always positive during this period, so the Federal Government of the United States incurred in budget deficits every year since 1939. From the mid-40s until the mid-70s, the debt/DGP was decreasing, meaning that the Federal Government of the United States was running a budget surplus every year during those three decades. During the second half of the 1970s, the Federal Government…arrow_forwardAn imaginary country estimates that their economy can be approximated by the AD/AS model below. How can this government act to move the equilibrium to potential GDP? LRAS Price Level P Y Real GDP E SRAS AD The AD/AS model shows that a contractionary fiscal policy is suitable, but the choice of increasing taxes, decreasing government expenditure or doing both simultaneously is mostly political The AD/AS model shows that increasing taxes is the best fiscal policy available. The AD/AS model shows that decreasing government expenditure is the best fiscal policy available. The AD/AS model shows that an expansionary fiscal policy capable of shifting the AD curve to the potential GDP level would decrease Real GDP but increase inflationary pressuresarrow_forward
- Question 1 Coursology Consider the four policies bellow. Classify them as either fiscal or monetary policy: I. The United States Government promoting tax cuts for small businesses to prevent a wave of bankruptcies during the COVID-19 pandemic II. The Congress approving a higher budget for the Affordable Health Care Act (also known as Obamacare) III. The Federal Reserve increasing the required reserves for commercial banks aiming to control the rise of inflation IV. President Joe Biden approving a new round of stimulus checks for households I. fiscal, II. fiscal, III. monetary, IV. fiscal I. fiscal, II. monetary, III. monetary, IV. monetary I. monetary, II. fiscal, III. fiscal, IV. fiscal I. monetary, II. monetary, III. fiscal, IV. monetaryarrow_forwardConsider the following supply and demand schedule of wooden tables.a. Draw the corresponding graphs for supply and demand.b. Using the data, obtain the corresponding supply and demand functions. c. Find the market-clearing price and quantity. Price (Thousand s USD Supply Demand 2 96 1104 196 1906 296 2708 396 35010 496 43012 596 51014 696 59016 796 67018 896 75020…arrow_forwardConsider a firm with the following production function Q=5000L-2L2.a. Find the maximum production level.b. How many units of labour are needed at that point. c. Obtain the function of marginal product of labour (MRL) d. Graph the production function and the MRL.arrow_forward
- Exercise 4A firm has the following total cost function TC=100q-5q2+0.5q3. Find the average cost function.arrow_forwardA firm has the following demand function P=200 − 2Q and the average costof AC= 100/Q + 3Q −20.a. Find the profit function. b. Estimate the marginal cost function. c. Obtain the production that maximizes the profit. d. Evaluate the average cost and the marginal cost at the maximising production level.arrow_forwardRubber: Initial investment: $159,000 Annual cost: $36,000 Annual revenue: $101,000 Salvage value: $12,000 Useful life: 10 years Using the cotermination assumptions, a study period of 6 years, and a MARR of 9%, what is the present worth of the rubber alternative? Assume that the rubber alternative's equipment has a market value of $18,000 at the end of Year 6.arrow_forward
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

 Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Economics Today and Tomorrow, Student EditionEconomicsISBN:9780078747663Author:McGraw-HillPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax
Principles of Economics 2eEconomicsISBN:9781947172364Author:Steven A. Greenlaw; David ShapiroPublisher:OpenStax





