
a.
Find the
Find the
a.
Answer to Problem 83CE
The mean of the number of items is 9.1.
The median of the number of items is 9.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Step by step procedure to obtain mean, median using MINITAB software is given as,
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display
Descriptive Statistics . - In Variables enter the column Number of Items.
- Choose option statistics, and select Mean and Median.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is given below:
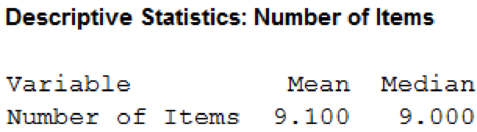
Hence, the mean of the number of items is 9.1, and the median of the number of items is 9.
b.
Find the
Find the standard deviation of the number of items.
b.
Answer to Problem 83CE
The range of the number of items is 14.
The standard deviation of the number of items is 3.566.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Step by step procedure to obtain standard deviation and range using MINITAB software is given as,
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display Descriptive Statistics.
- In Variables enter the column Number of Items.
- Choose option statistics, and select standard deviation and range.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is given below:
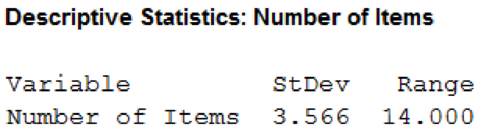
Hence, the range of the number of items is 14 and standard deviation of the number of items is 3.566.
c.
Find the frequency distribution for number of items.
c.
Answer to Problem 83CE
The frequency distribution for number of items is,
| Class | Frequency |
| 3.5-6.5 | 10 |
| 6.5-9.5 | 6 |
| 9.5-12.5 | 9 |
| 12.5-15.5 | 4 |
| 15.5-18.5 | 1 |
| Total | 30 |
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Selection of number of classes:
The “2 to the k rule” suggests that the number of classes is the smallest value of k, where
Formula for class interval:
The formula for the class interval is given as follows:
Frequency distribution:
The frequency table is a collection of mutually exclusive and exhaustive classes that show the number of observations in each class.
Where, i is the class interval and k is the number of classes.
The data set consists of 30 observations. The value of k can be obtained as follows:
Here,
The class interval is,
In practice, the class interval size is usually rounded up to some convenient number. Thus, the reasonable class interval is 3.
Since the minimum value is 4 and the class interval is 3, the first class would be 3.5-6.5.
The frequency distribution for duration in minutes can be constructed as follows:
| Class | Frequency |
| 3.5-6.5 | 10 |
| 6.5-9.5 | 6 |
| 9.5-12.5 | 9 |
| 12.5-15.5 | 4 |
| 15.5-18.5 | 1 |
| Total | 30 |
d.
Find the mean of the data.
Find the standard deviation of the data.
Compare these values with those computed in Part (a).
Explain why the values are different
d.
Answer to Problem 83CE
The mean of the data is 9.
The standard deviation of the data is 3.553.
Explanation of Solution
Arithmetic mean of grouped data:
The mean of the data that is given in frequency distribution (grouped data) is calculated as,
In the formula,
Midpoint:
The midpoint is the average of the lower class limits of two consecutive classes. The formula is,
The frequency distribution table for mean is,
| Class |
Frequency f | M | |
| 3.5-6.5 | 10 | 5 | 50 |
| 6.5-9.5 | 6 | 8 | 48 |
| 9.5-12.5 | 9 | 11 | 99 |
| 12.5-15.5 | 4 | 14 | 56 |
| 15.5-18.5 | 1 | 17 | 17 |
Substitute
Hence, the mean of the data is 9.
Standard deviation of grouped data:
The standard deviation of the data that is given in frequency distribution (grouped data) is calculated as,
In the formula, s denotes the sample standard deviation,
The value of mean is 9. The frequency distribution table for standard deviation is,
| Class |
Frequency f | M | |||
| 3.5-6.5 | 10 | 5 | –4 | 16 | 160 |
| 6.5-9.5 | 6 | 8 | –1 | 1 | 6 |
| 9.5-12.5 | 9 | 11 | 2 | 4 | 36 |
| 12.5-15.5 | 4 | 14 | 5 | 25 | 100 |
| 15.5-18.5 | 1 | 17 | 8 | 64 | 64 |
Substitute
Hence, the standard deviation of the data is 3.553.
The mean value is same for normal method and frequency distribution. But there is a slight change in the value of the standard deviation. This difference is due to using grouped data in frequency distribution. The frequency distribution only gives the estimate of the standard deviation because actual values of the data are not used.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Loose Leaf for Statistical Techniques in Business and Economics
- Name Harvard University California Institute of Technology Massachusetts Institute of Technology Stanford University Princeton University University of Cambridge University of Oxford University of California, Berkeley Imperial College London Yale University University of California, Los Angeles University of Chicago Johns Hopkins University Cornell University ETH Zurich University of Michigan University of Toronto Columbia University University of Pennsylvania Carnegie Mellon University University of Hong Kong University College London University of Washington Duke University Northwestern University University of Tokyo Georgia Institute of Technology Pohang University of Science and Technology University of California, Santa Barbara University of British Columbia University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill University of California, San Diego University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign National University of Singapore…arrow_forwardA company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardFind the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- A retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardShow all workarrow_forwardShow all workarrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL


