Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The name, condensed structural formula and molecular mass of the given molecule should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Name of the compound can be assigned according to below rule:
First, identify the number of carbon atoms present in chain, and then identify the function group if present in the given compound.
Condensed structural formula is defined as the structural formula which shows the spatial arrangement of bonds in an organic compound. In this structural formula, the bonds between the atoms are shown with lines and omit the bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Molecular mass is defined as the sum of mass of each atom present in the compound.
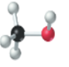
(b)
Interpretation:
The name, condensed structural formula and molecular mass of the given molecule should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Name of the compound can be assigned according to below rule:
First, identify the number of carbon atoms present in chain, and then identify the function group if present in the given compound.
Condensed structural formula is defined as the structural formula which shows the spatial arrangement of bonds in an organic compound. In this structural formula, the bonds between the atoms are shown with lines and omit the bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Molecular mass is defined as the sum of mass of each atom present in the compound.
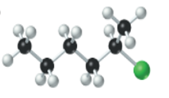
(c)
Interpretation:
The name, condensed structural formula and molecular mass of the given molecule should be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Name of the compound can be assigned according to below rule:
First, identify the number of carbon atoms present in chain, and then identify the function group if present in the given compound.
Condensed structural formula is defined as the structural formula which shows the spatial arrangement of bonds in an organic compound. In this structural formula, the bonds between the atoms are shown with lines and omit the bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Molecular mass is defined as the sum of mass of each atom present in the compound.
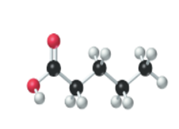
(d)
Interpretation:
The name, condensed structural formula and molecular mass of the given molecule should be drawn.
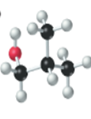
Concept introduction:
Name of the compound can be assigned according to below rule:
First, identify the number of carbon atoms present in chain, and then identify the function group if present in the given compound.
Condensed structural formula is defined as the structural formula which shows the spatial arrangement of bonds in an organic compound. In this structural formula, the bonds between the atoms are shown with lines and omit the bond between carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Molecular mass is defined as the sum of mass of each atom present in the compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
EP GENERAL CHEMISTRY-MOD.MASTERINGCHEM.
- Draw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardI have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning  Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





