
Implementation of linked list deletion operation:
Linked List:
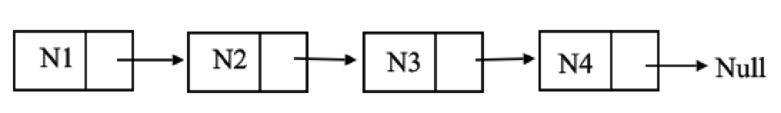
A linear data structure where each element denotes a separate object is known as linked list.
- Each element of a list contains two items, the data and a pointer to next node.
- The last node would point to null.
- The “head” denotes point of entry into a linked list.
- If list is empty then the head is a null pointer.
- The structure of linked list is given below:
/*************************************************************
* This program demonstrates deletion of linked list *
* nodes corresponding to positions obtained from *
* two linked lists *
*************************************************************/
Explanation of Solution
Program:
//Include header files
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//Declare an array "la[]"
int la[100], i=0;
//Define a linked list node
struct lnode
{
//Define data of node
int ldata;
//Define pointer to next node
lnode *lnext;
}*start;
/*Function Prototypes */
lnode *lcreate_node(int lvalue);
void lsortedInsert(struct lnode** head_ref, struct lnode* lnew_node);
void ldisplay(struct lnode* head);
void ldeleteKey(struct lnode **head_ref, int lkey);
void merge(struct lnode *p, struct lnode **q);
struct lnode* lSortedMerge(struct lnode* la, struct lnode* lb);
void lFBS(struct lnode* lsource, struct lnode** frontRef, struct lnode** backRef);
/* Function "lcreate_node()" creates la new node, allocates the memory space and puts the data in it */
struct lnode *lcreate_node(int lnew_data)
{
//Allocate lnode
struct lnode* lnew_node = (struct lnode*) malloc(sizeof(struct lnode));
// Put in the ldata
lnew_node->ldata = lnew_data;
//Make the next of new node to NULL
lnew_node->lnext = NULL;
//Return the new node
return lnew_node;
}
//Define "merge()" that merges two linked lists
void merge(struct lnode *p, struct lnode **q)
{
//Declare nodes of type "lnode*"
struct lnode *lp_curr = p, *lq_curr = *q;
struct lnode *lp_next, *lq_next;
// Loop until positions are available
while (lp_curr != NULL && lq_curr != NULL)
{
// Save the next pointers
lp_next = lp_curr->lnext;
lq_next = lq_curr->lnext;
// Make lq_curr as next of lp_curr
lq_curr->lnext = lp_next;
lp_curr->lnext = lq_curr;
// Update the pointers
lp_curr = lp_next;
lq_curr = lq_next;
}
// Update second list's head pointer
*q = lq_curr;
}
//Define a function "MergeSort()" that sorts linked list by changing next pointers
void MergeSort(struct lnode** headRef)
{
//Declare nodes of type "lnode*"
struct lnode* head = *headRef;
struct lnode* la;
struct lnode* lb;
//If linked list is empty or has single element
if ((head == NULL) || (head->lnext == NULL))
{
return;
}
// Split head into sublists
lFBS(head, &la, &lb);
// Sort sublists
MergeSort(&la);
MergeSort(&lb);
// Merge lists that are sorted
*headRef = lSortedMerge(la, lb);
}
/*Define a function "lFBS()" that divides the list into two halves and returns refernce parameters of result*/
void lFBS(struct lnode* lsource, struct lnode** frontRef, struct lnode** backRef)
{
//Declare nodes "fast" and "slow" of type "lnode*"
struct lnode* fast;
struct lnode* slow;
//If list is empty or contains single element
if (lsource==NULL || lsource->lnext==NULL)
{
//If length < 2
*frontRef = lsource;
*backRef = NULL;
}
else
{
//If list contains more than one element
slow = lsource;
fast = lsource->lnext;
/* Traverse "fast" two nodes, and traverse "slow" one node */
while (fast != NULL)
{
//Traverse the "fast"
fast = fast->lnext;
/* Traverse the list until "fast" reaches null */
if (fast != NULL)
{
//Move to next element
slow = slow->lnext;
fast = fast->lnext;
}
}
/* "slow" is before list's midpoint, split it in two at that point. */
*frontRef = lsource;
*backRef = slow->lnext;
slow->lnext = NULL;
}
}
/* Define a function "lSortedMerge()" that merges the lists that are sorted, it takes header pointers of two lists as arguments */
struct lnode* lSortedMerge(struct lnode* la, struct lnode* lb)
{
//Declare node to store result
struct lnode* result = NULL;
//If either of list is empty
if (la == NULL)
return(lb);
else if (lb==NULL)
return(la);
//Chose either la or lb, and recur
if (la->ldata <= lb->ldata)
{
//Place "la" first
result = la;
//Continue with next element of "la" and "lb"
result->lnext = lSortedMerge(la->lnext, lb);
}
else
{
//place "lb" first
result = lb;
//Continue with next element of "lb" and "la"
result->lnext = lSortedMerge(la, lb->lnext);
}
//Return result
return(result);
}
//Define a main function
int main()
{
//Initialize variables
start = NULL;
//Make the head reference of new node to NULL
struct lnode* head = NULL;
//Insert first node into linked list
struct lnode *lnew_node = lcreate_node(5);
/*Call the function "lsortedInsert()" with "head" and "lnew_node" as arguments and inserts the node into it.*/
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(10);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(20);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(30);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(40);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(50);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(60);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(70);
lsortedInsert(&head, lnew_node);
lnew_node = lcreate_node(80);
//Display the elements of list
cout<<"Elements of first list are: "<<endl;
//Call the function "ldisplay()" to display elements.
ldisplay(head);
//Make the head reference of new node to NULL
struct lnode* head1 = NULL;
//Insert the first node into linked list
struct lnode *new_node1 = lcreate_node(3);
lsortedInsert(&head1, new_node1);
/*Call the function "lsortedInsert()" with "head1" and "new_node1" as arguments and inserts the node into it.*/
new_node1 = lcreate_node(1);
lsortedInsert(&head1, new_node1);
new_node1 = lcreate_node(2);
lsortedInsert(&head1, new_node1);
//Display elements of linked list
cout<<"Elements of second list are: "<<endl;
ldisplay(head1);
//Make the head reference of new node to NULL
struct lnode* head2 = NULL;
//Insert the first node into linked list
struct lnode *new_node2 = lcreate_node(6);
lsortedInsert(&head2, new_node2);
/*Call the function "lsortedInsert()" with "head1" and "new_node1" as arguments and inserts the node into it.*/
new_node2 = lcreate_node(5);
lsortedInsert(&head2, new_node2);
new_node2 = lcreate_node(4);
lsortedInsert(&head2, new_node2);
//Display elements of linked list
cout<<"Elements of third list are: "<<endl;
ldisplay(head2);
//Call "merge()" to merge two linked lists
merge( head1, &head2);
printf("Linked List after merging second and third list: \n");
MergeSort(&head1);
ldisplay(head1);
//Store the values of second list into an array
while( head1!=NULL )
{
//Copy the data at the node into variable "c"
int c = head1->ldata;
//copy value in "c" into the array "la[]"
la[i] = c;
//Increment value of "i"
i++;
// Traverse each element
head1 = head1->lnext;
}
//Declare the variables
int lIndex = 0;
/*Search the element in first list with the position in second list */
for(int k=0;k<i;k++)
{
/*Declare la node "ltemp" and assign "head "into it */
struct lnode* ltemp = head;
//Declare the variables
lIndex=0;
/*Match the values in first array with index in second array */
while(lIndex !=la[k] && ltemp!=NULL)
{
//Traverse the list
ltemp = ltemp->lnext;
//Increment the index value
lIndex++;
}
/*Assign the value 0 to data that are at positions in second list */
ltemp->ldata = 0;
}
/*Call the function "ldeleteKey()" with "head" and value 0 as arguments */
ldeleteKey(&head,0);
//Display the result after deletion
cout<<"Elements of first list after deletion : "<<endl;
//Call "ldisplay()" to display list
ldisplay(head);
cout<<endl;
//Pause the console window
system("pause");
return 0;
}
/*Declare the function "lsortedInsert()" that takes head reference and new node as arguments and inserts the node into list in sorted order */
void lsortedInsert(struct lnode** head_ref, struct lnode* lnew_node)
{
//Declare la node "current"
struct lnode* current;
/*If list is empty or data of new node is less than or equal to present data of list */
if (*head_ref == NULL || (*head_ref)->ldata >= lnew_node->ldata)
{
//Make head reference to "lnew_node->lnext"
lnew_node->lnext = *head_ref;
//Assign new node to head reference
*head_ref = lnew_node;
}
else
{
//Locate node before insertion point
current = *head_ref;
//Place the node in sorted order
while (current->lnext!=NULL && current->lnext->
ldata < lnew_node->ldata)
{
//Traverse the list pointer
current = current->lnext;
}
//Make "current->lnext" to "lnew_node->lnext"
lnew_node->lnext = current->lnext;
//Assign new node to "current->lnext"
current->lnext = lnew_node;
}
}
/*The function "ldisplay()" takes the header pointer of list as arguments and elements of list are displayed */
void ldisplay(struct lnode* head)
{
//Declare a node "ltemp"
struct lnode *ltemp;
//If head is NULL
if (head == NULL)
{
//Display the message
cout<<"The List is Empty"<<endl;
return;
}
//Set "ltemp" as head node
ltemp = head;
/*Display the data in linked list until it reaches null */
while (ltemp != NULL)
{
//Display the data
cout<<ltemp->ldata<<"->";
//Move to next element
ltemp = ltemp->lnext;
}
//Display the end of list
cout<<"NULL"<<endl;
}
/*The function ldeletekey()" takes the header pointer and the deletion element as arguments and deletes the particular element from the list */
void ldeleteKey(struct lnode **head_ref, int lkey)
{
// Store head node
struct lnode* ltemp = *head_ref, *prev;
/*Check for all occurrences of the deletion element in the list */
while (ltemp != NULL && ltemp->ldata == lkey)
{
//Change header pointer
*head_ref = ltemp->lnext;
//Free old head
free(ltemp);
//change "ltemp"
ltemp = *head_ref;
}
//Delete all occurrences of element other than "head"
while (ltemp != NULL)
{
/*Search for key to be deleted, track previous node as 'prev->lnext' is to be changed*/
while (ltemp != NULL && ltemp->ldata != lkey)
{
prev = ltemp;
ltemp = ltemp->lnext;
}
//If key is not in list
if (ltemp == NULL) return;
//Unlink the node from list
prev->lnext = ltemp->lnext;
//Free memory
free(ltemp);
//Update "ltemp" for next loop iteration
ltemp = prev->lnext;
}
}
Explanation:
- The above program declares two linked list and deletes elements of first linked list at positions corresponding to elements in second linked list.
- The function “lcreate_node()” takes an integer value as parameter and creates a node of the linked list.
- The function “lsortedInsert()” takes header pointers of list and new node created as the parameters of the function and inserts the node in the list in sorted order.
- The function “ldisplay()” takes header pointers of linked list as arguments and displays the linked list contents.
- The function “ldeleteKey()” takes header reference pointer of linked list and element to delete as the function arguments and it deletes all element occurrences from list.
- The function “merge()” takes header reference pointer of two linked list as arguments and merges two lists.
- The function “lSortedMerge()”that merges the list that are sorted, it takes header pointers of two list as arguments.
- The function “lFBS()”that divides the list into two halves and returns reference parameters of result.
- In the main function three linked list are defined, elements of second list and third list are merged and then sorted which denotes deletion position index of first list.
- The data values in first list corresponding to positions in merged list are replaced with value 0.
- Delete function is called with header pointer of list and value 0 as function arguments so as to delete all occurrences of 0 from list.
- The final linked after the deletion process is displayed as result.
Output:
Elements of first list are:
5->10->20->30->40->50->60->70->NULL
Elements of second list are:
1->2->3->NULL
Elements of third list are:
4->5->6->NULL
Linked List after merging second and third list:
1->2->3->4->5->6->NULL
Elements of first list after deletion:
5->70->NULL
Press any key to continue . . .
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
EBK DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C
- Briefly describe the issues involved in using ATM technology in Local Area Networksarrow_forwardFor this question you will perform two levels of quicksort on an array containing these numbers: 59 41 61 73 43 57 50 13 96 88 42 77 27 95 32 89 In the first blank, enter the array contents after the top level partition. In the second blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the left-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. In the third blank, enter the array contents after one more partition of the right-hand subarray resulting from the first partition. Print the numbers with a single space between them. Use the algorithm we covered in class, in which the first element of the subarray is the partition value. Question 1 options: Blank # 1 Blank # 2 Blank # 3arrow_forward1. Transform the E-R diagram into a set of relations. Country_of Agent ID Agent H Holds Is_Reponsible_for Consignment Number $ Value May Contain Consignment Transports Container Destination Ф R Goes Off Container Number Size Vessel Voyage Registry Vessel ID Voyage_ID Tonnagearrow_forward
- I want to solve 13.2 using matlab please helparrow_forwarda) Show a possible trace of the OSPF algorithm for computing the routing table in Router 2 forthis network.b) Show the messages used by RIP to compute routing tables.arrow_forwardusing r language to answer question 4 Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.arrow_forward
- using r language Obtain a bootstrap t confidence interval estimate for the correlation statistic in Example 8.2 (law data in bootstrap).arrow_forwardusing r language Compute a jackknife estimate of the bias and the standard error of the correlation statistic in Example 8.2.arrow_forwardusing r languagearrow_forward
 New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L
EBK JAVA PROGRAMMINGComputer ScienceISBN:9781337671385Author:FARRELLPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENTCOMPREHENSIVE MICROSOFT OFFICE 365 EXCEComputer ScienceISBN:9780357392676Author:FREUND, StevenPublisher:CENGAGE L





