
Concept explainers
Problem 3-71B Preparing a Worksheet (Appendix 3A)
Flint Inc. operates a cable television System. At December 31, 2019, the following unadjusted account balances were available:
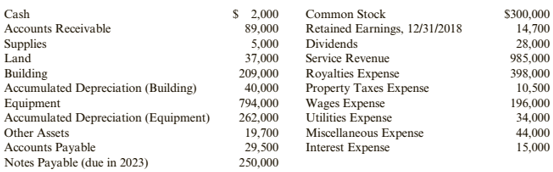
The following data are available for
- At year end, $1,500 Of office supplies remain unused.
- Annual
depreciation on the building is $20,000. - Annual depreciation on the equipment is $150,000
- The interest rate on the note is 8%. Four months' interest is unpaid and unrecorded at December 31, 2019.
- At December 31, 2019, services of $94,000 have performed but are unbilled and unrecorded.
- Utility bills of $2,800 are unpaid and unrecorded at December 31, 2019.
- Income taxes of $49,633 were unpaid and unrecorded at year end.
Â
Required:
- Prepare a worksheet for Flint.
- Prepare an income statement, a
retained earnings statement, and a classifiedbalance sheet for Flint. - Prepare the closing entries.
1.
To prepare: Worksheet of the company A.
Introduction:.Worksheet is a statement that represents the unadjusted balances of ledgers, adjustment entries and the balances after such adjustments. Adjusted balances are the final balances that are presented in the financial statements of a company.
Explanation of Solution
Preparation of worksheet for the period ending 31st December, 2019:
| Account Title | UnadjustedTrial balance | Adjustments | AdjustedTrial balance | |||
| Dr. | Cr. | Dr. | Cr. | Dr. | Cr. | |
| Cash | 2,000 | 2,000 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | 89,000 | 94,000 | 183,000 | |||
| Supplies | 5,000 | 3,500 | 1,500 | |||
| Land | 37,000 | 37,000 | ||||
| Building | 209,000 | 209,000 | ||||
| Accumulated depreciation-building | 40,000 | 20,000 | 60,000 | |||
| Equipment | 794,000 | 794,000 | ||||
| Accumulated depreciation-equipment | 262,000 | 150,000 | 412,000 | |||
| Other assets | 19,700 | 19,700 | ||||
| Accounts payable | 29,500 | 29,500 | ||||
| Interest payable | 6,667 | 6,667 | ||||
| Income tax payable | 49,633 | 49,633 | ||||
| Utilities payable | 2,800 | 2,800 | ||||
| Notes payable | 250,000 | 250,000 | ||||
| Common stock | 300,000 | 300,000 | ||||
| Retained earnings | 14,700 | 14,700 | ||||
| Dividends | 28,000 | 28,000 | ||||
| Service revenue | 985,000 | 94,000 | 1,079,000 | |||
| Royalties expense | 398,000 | 398,000 | ||||
| Property taxes expense | 10,500 | 10,500 | ||||
| Wages expense | 196,000 | 196,000 | ||||
| Utilities expense | 34,000 | 2,800 | 36,800 | |||
| Miscellaneous expense | 44,000 | 44,000 | ||||
| Interest expense | 15,000 | 6,667 | 21,667 | |||
| Income tax expense | 49,633 | 49,633 | ||||
| Supplies expense | 3,500 | 3,500 | ||||
| Depreciation expense-building | 20,000 | 20,000 | ||||
| Depreciation expense-equipment | 150,000 | 150,000 | ||||
| Total | 1,881,200 | 1,881,200 | 326,600 | 326,600 | 2,204,300 | 2,204,300 |
Table (1)
Working Note:
Computation of interest payable:
2.
To prepare: Income statement, statement of retained earnings and balance sheet.
Introduction: Income statement, statement of retained earnings and balance sheet are financial statements. These statements are prepared for reporting purposes.
Explanation of Solution
Preparation of income statement for the Year ending31st December, 2019:
| CompanyA | ||
| Income Statement,For the Year ending on 31stDecember, 2019 | ||
| Amount ($) | Amount ($) | |
| Revenues: | ||
| Service revenue | 1,079,000 | |
| Total Revenue | 1,079,000 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Royalties expense | 398,000 | |
| Property taxes expense | 10,500 | |
| Wages Expense | 196,000 | |
| Utilities Expense | 36,800 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 44,000 | |
| Interest Expense | 21,667 | |
| Supplies expense | 3,500 | |
| Depreciation expense-building | 20,000 | |
| Depreciation expense-equipment | 150,000 | |
| Income tax expense | 49,633 | |
| Total Expenses | 930,100 | |
| Net Income | 148,900 | |
Table (2)
Preparation of balance sheet as on 31stDecember, 2019:
| Company A | ||
| Balance Sheet as on 31stDecember 2019 | ||
| Amount ($) | Amount($) | |
| Liabilities and Owners Equity | ||
| Current Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 29,500 | |
| Interest Payable | 6,667 | |
| Income tax payable | 49,633 | |
| Utilities payable | 2,800 | |
| Total Current Liabilities | 88,600 | |
| Non-Current Liabilities | ||
| Note Payable (due in 2023) | 250,000 | |
| Total Non-Current Liabilities | 250,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | ||
| Common Stock | 300,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 135,600 | 435,600 |
| Total Liabilities and Owner’s Equity | 774,200 | |
| Current Assets | ||
| Cash | 2,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 183,000 | |
| Supplies | 1,500 | |
| Other Assets | 19,700 | |
| Total Current Assets | 206,200 | |
| Property, Plant and Equipment | ||
| Land | 37,000 | |
| Building | 209,000 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation-building | ||
| Equipment | 794,000 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation-equipment | ||
| Total Property, Plant and Equipment | 568,000 | |
| Total Assets | 774,200 | |
Table (3)
Preparation of statement of retained earnings as on 31stDecember, 2019:
| Company A | ||
| Statement of Retained Earning | ||
| Amount($) | Amount($) | |
| Owner’s Equity opening balance | 14,700 | |
| Add: Capital introduced by owner | 0 | |
| Add: Net income | 148,900 | |
| Total: | 163,600 | |
| Less: Withdrawals | 0 | |
| Less: Dividends | ||
| Closing Balance | 135,600 | |
Table (4)
3.
To record: closing journal entries.
Introduction: Closing entries are posted to close all the temporary accounts of the accounting books. Closing entries zeros the balances of income statement items, drawings, and dividends.
Explanation of Solution
Recording closing entry for expense accounts:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Income summary | 930,100 | |||
| Royalties expense | 398.000 | |||
| Property taxes expense | 10,500 | |||
| Wages expense | 196,000 | |||
| Utilities expense | 36,800 | |||
| Miscellaneous expense | 44,000 | |||
| Interest expense | 21,667 | |||
| Income tax expense | 49,633 | |||
| Supplies expense | 3,500 | |||
| Depreciation-building expense | 20,000 | |||
| Depreciation-equipment expense | 150,000 | |||
| (to record closing of expense accounts) |
Table (5)
- Since income summary is a temporary income account and temporary income is decreased. Hence, income summary account is debited.
- Since royalties expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, royalties expense account is credited.
- Since property taxes expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, property taxes expense account is credited.
- Since wages expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, wages expense account is credited.
- Since utilities expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, utilities expense account is credited.
- Since miscellaneous expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, miscellaneous expense account is credited.
- Since interest expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, interest expense account is credited.
- Since income tax expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, income tax expense account is credited.
- Since supplies expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, supplies expense account is credited.
- Since depreceiation expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, depreceiation -building expense account is credited.
- Since depreceiation expense is an expense and expense is decreased. Hence, depreceiation −equipment expense account is credited.
Recording closing entry for revenue accounts:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Service revenue | 1,079,000 | |||
| Income summary | 1,079,000 | |||
| (to record closing of revenue account) |
Table (6)
- Since service revenue is an income and income is decreased. Hence, service revenue account is debited.
- Since income summary is a temporary income account and temporary income is increased. Hence, income summary account is credited.
Recording transfer of income summary account:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Income summary | 148,900 | |||
| Retained earnings | 148,900 | |||
| (to record closing entry) |
Table (7)
- Since income summary is a temporary income account and temporary income is decreased. Hence, income summary account is debited.
- Since retained earnings is a reserve and reserve is increased. Hence, retained earnings account is credited.
Transfering drawings and dividends to retained earnings:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Retained earnings | 28,000 | |||
| Dividend | 28,000 | |||
| (to record closing entry) |
Table (8)
- Since retained earnings is a reserve and reserve is decreased. Hence, retained earnings account is debited.
- Since dividends is expense and expense is decreased. Hence, dividends account is credited.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Cornerstones of Financial Accounting
- Bradford Enterprises sells two products, blue pens and green notebooks. Bradford predicts that it will sell 3,200 blue pens and 900 green notebooks in the next period. The unit contribution margins for blue pens and green notebooks are $2.80 and $4.20, respectively. What is the weighted average unit contribution margin? Provide answerarrow_forwardNeed helparrow_forwardRound your answer to two decimal placesarrow_forward
- What are the proceeds to meridian of this financial accounting question?arrow_forwardcan you help me with this General accounting questionarrow_forwardThe Foundational 15 (Static) [LO6-2, LO6-3, LO6-4, LO6-5, LO6-6) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $120 and $80, respectively. Each product uses only one type of raw material that costs $6 per pound. The company has the capacity to annually produce 100,000 units of each product. Its average cost per unit for each product at this level of activity are given below: Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $120 and $80, respectively. Each product uses only one type of raw material that costs $6 per pound. The company has the capacity to annually produce 100,000 units of each product. Its average cost per unit for each product at this level of activity are given below: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Traceable fixed manufacturing overhead Variable selling expenses Common fixed expenses Total cost per unit $100 The…arrow_forward
- what was the cost of merchandise purchased during the year?arrow_forwardNext year, a business estimates that it will sell 30,000 units at a selling price of $15 per unit. Variable costs per unit are 40% of the selling price, and the business estimates that it will make a profit of $100,000. Calculate the fixed costs of the business for next year.arrow_forwardCalculate the fixed costs of the business for next yeararrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning

