
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
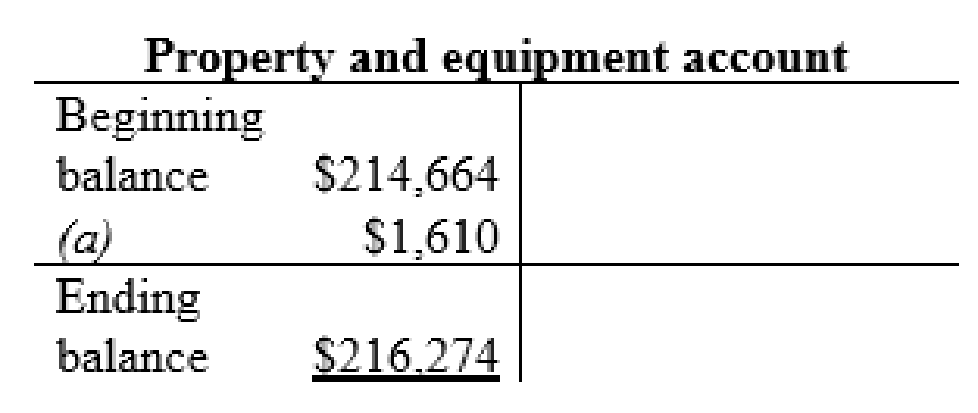
| a | Property and equipment (+A) | $1,610 | |
| Long-term notes payable (+L) | $1,610 | ||
| (To record the long-term notes payable) | |||
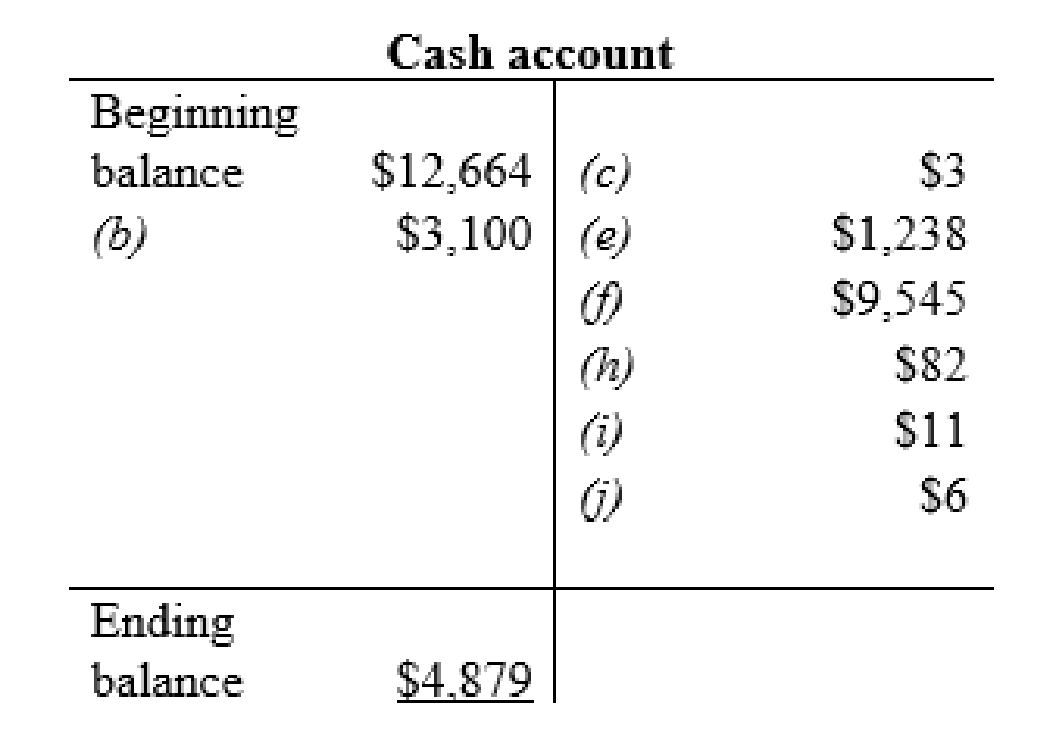
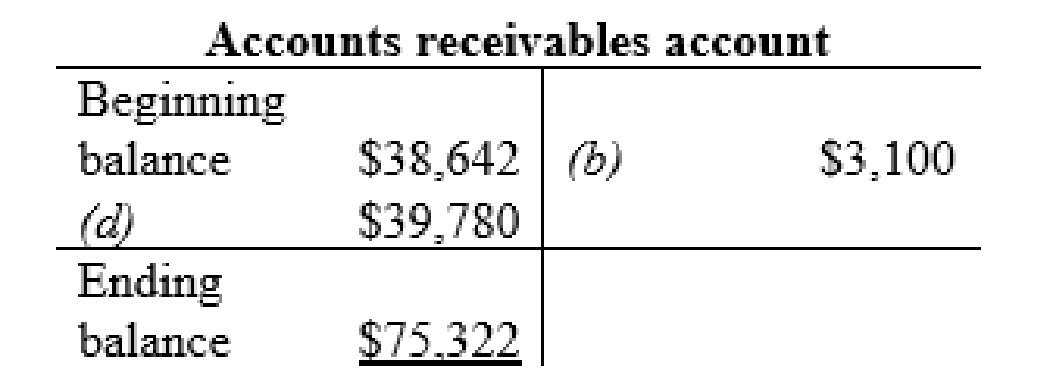
| b | Cash (+A) | $3,100 | |
| Accounts receivable (-A) | $3,100 | ||
| (To record the receivables collected) | |||
| c | Utilities expense (+E) (-SE) | $3 | |
| Cash (-A) | $3 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
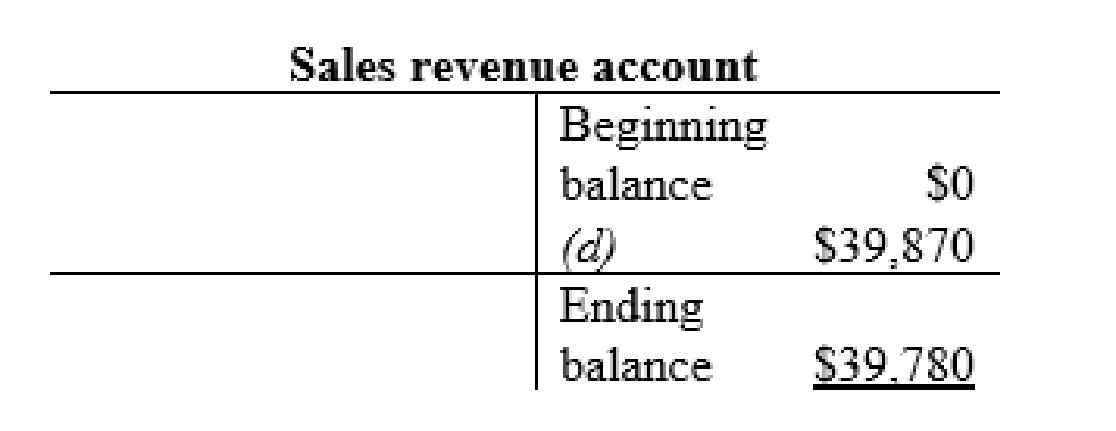
| d | Accounts receivable (+A) | $39,780 | |
| Sales Revenue (+SE, +R) | $39,780 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
| Cost of Sales (+E) (-SE) | $5,984 | ||
| Inventory (-A) | $5,984 | ||
| (To record the cost involved in sales) | |||
| e | Wages (+E) (-SE) | $1,238 | |
| Cash (-A) | $1,238 | ||
| (To record the wages paid) | |||
| f | Income tax payable (-L) | $9,545 | |
| Cash (-A) | $9,545 | ||
| (To record the income taxes paid) | |||
| g | Inventory (+A) | $23 | |
| Accounts payable (+L) | $23 | ||
| (To record the inventory purchased on account) | |||
| h | Prepaid expenses (+A) | $82 | |
| Cash (-A) | $82 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid in advance) | |||
| i | Other long-term debt (-L) | $10 | |
| Interest expense | $1 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $11 | ||
| (To record the debt paid off) | |||
| j | Other assets and intangibles (+A) | $6 | |
| Cash (-A) | $6 | ||
| (To record the purchase of other assets and intangibles) | |||
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
Cash account:
Short-term investments account:
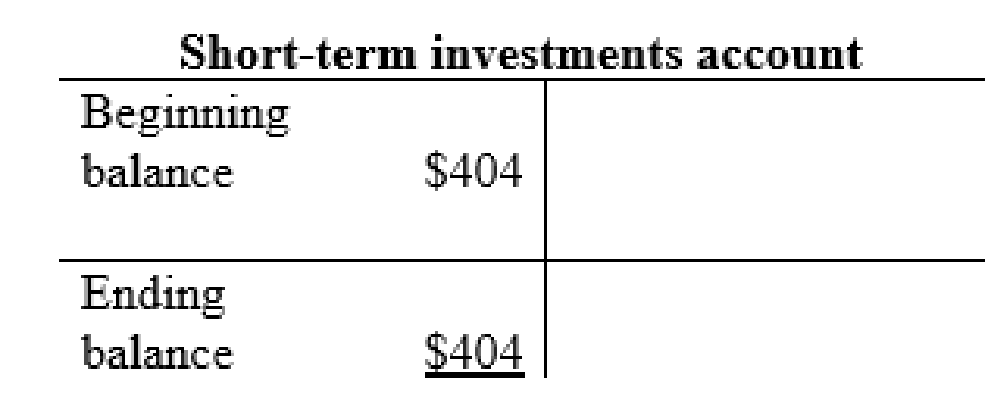
Accounts receivables account:
Inventories account:

Prepaid expenses account:
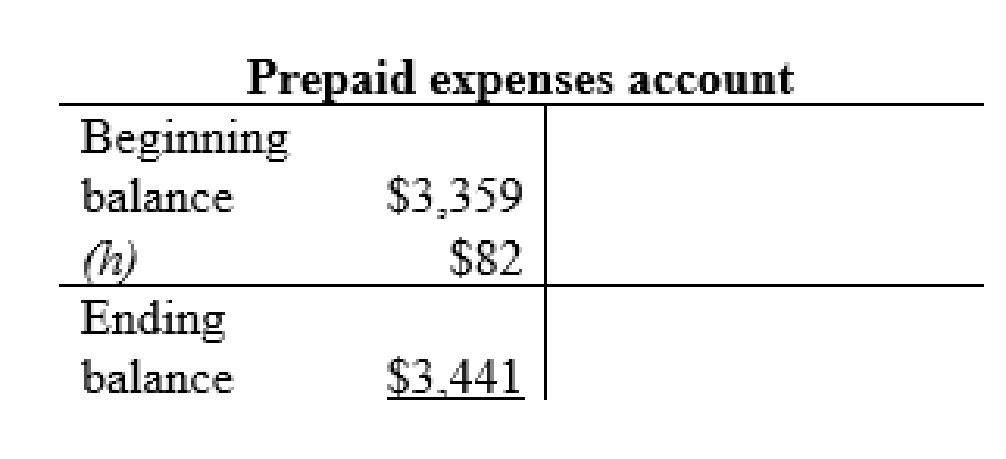
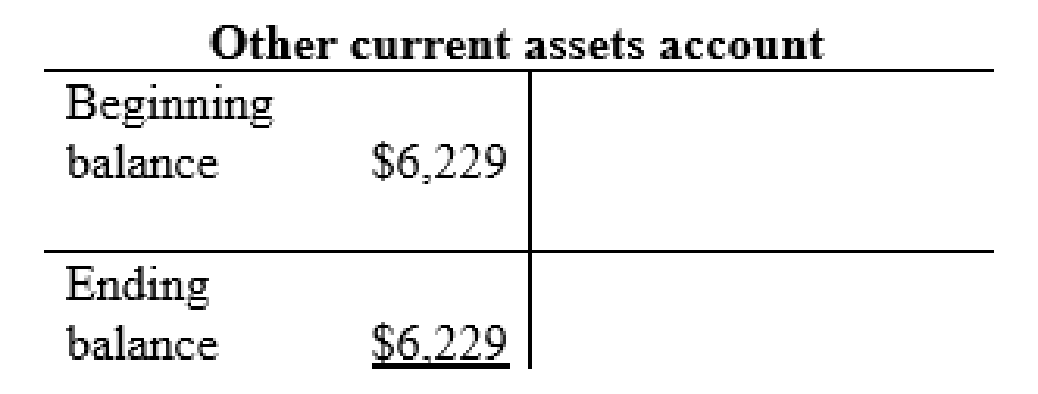
Other current assets account:
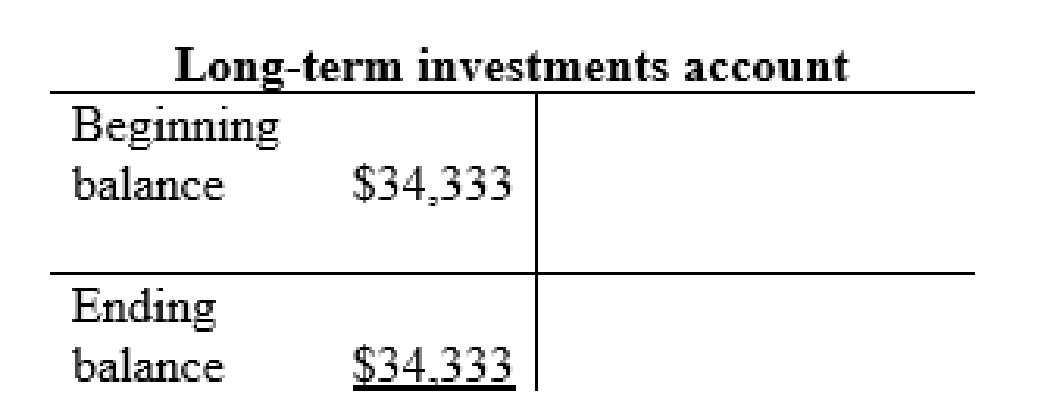
Long-term investments account:
Other assets and intangibles account:
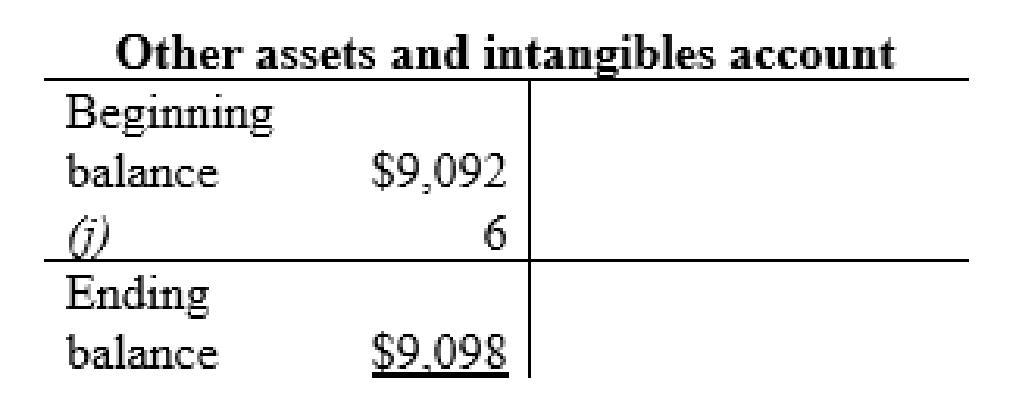
Property and equipment account:
Short-term notes payable account:
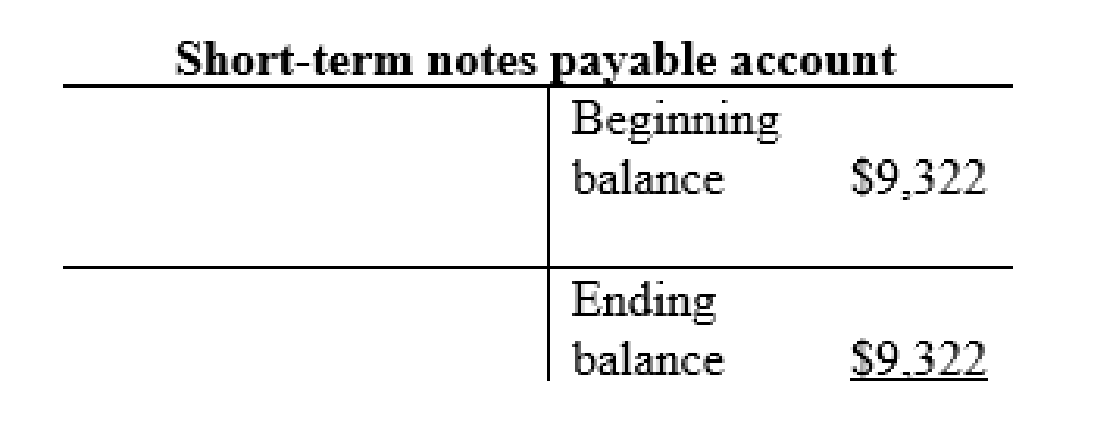
Accounts payable account:
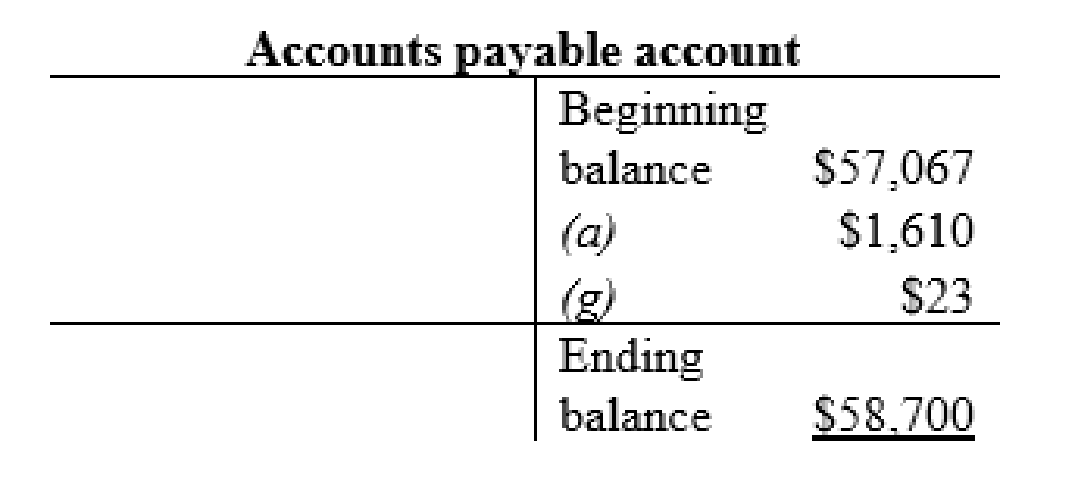
Income taxes payable account:
Long-term note payable account:
Other long-term debt account:
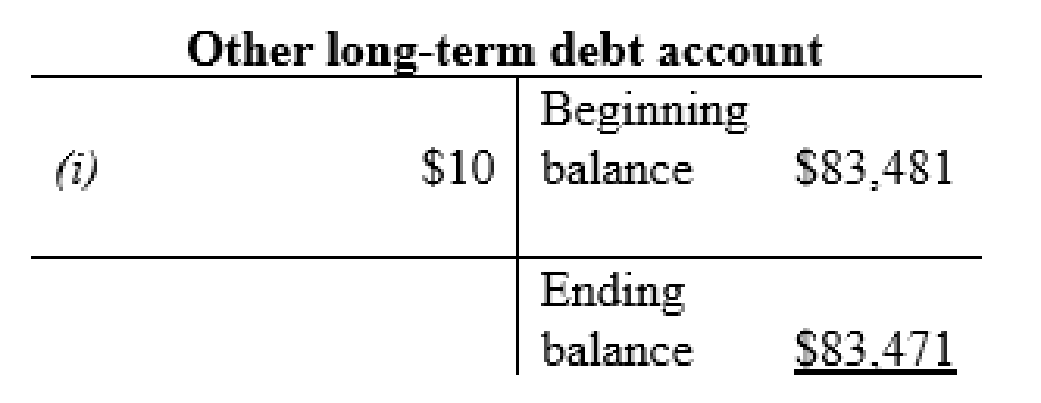
Common stock account:
Sales revenue account:
Cost of sales account:
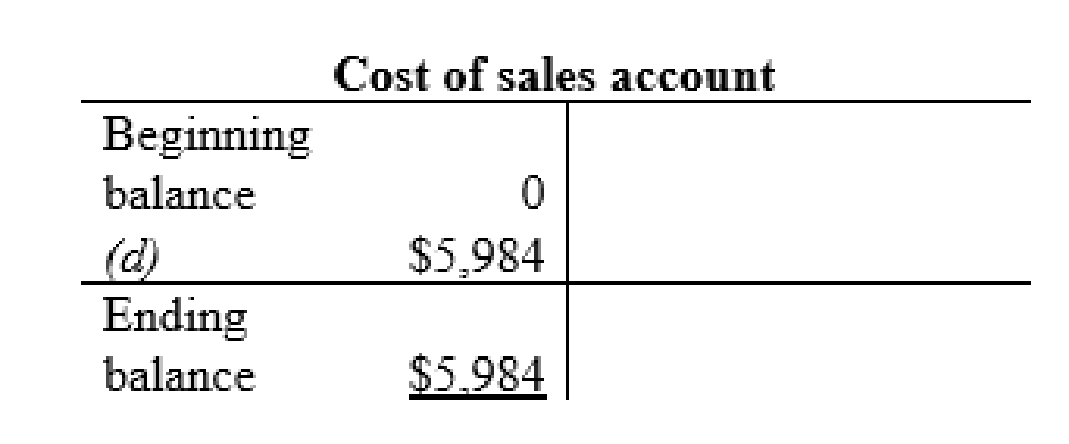
Utilities expense account:
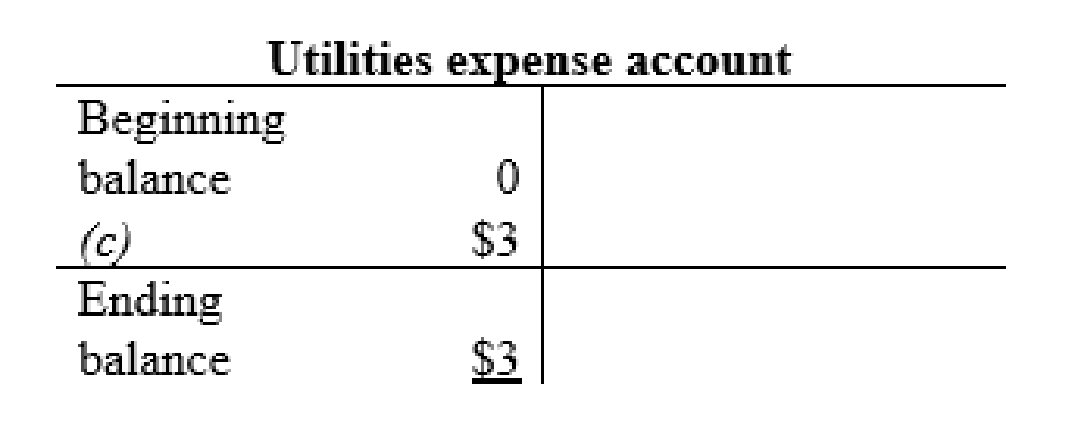
Interest expense account:
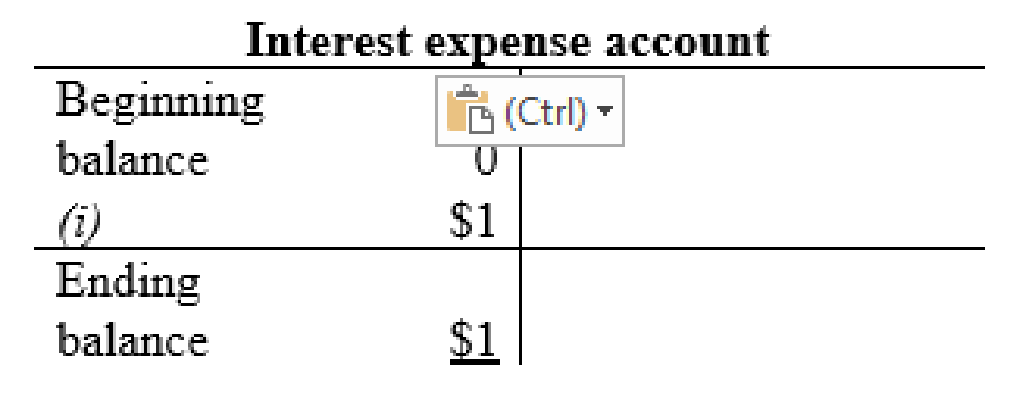
Wage expense account:
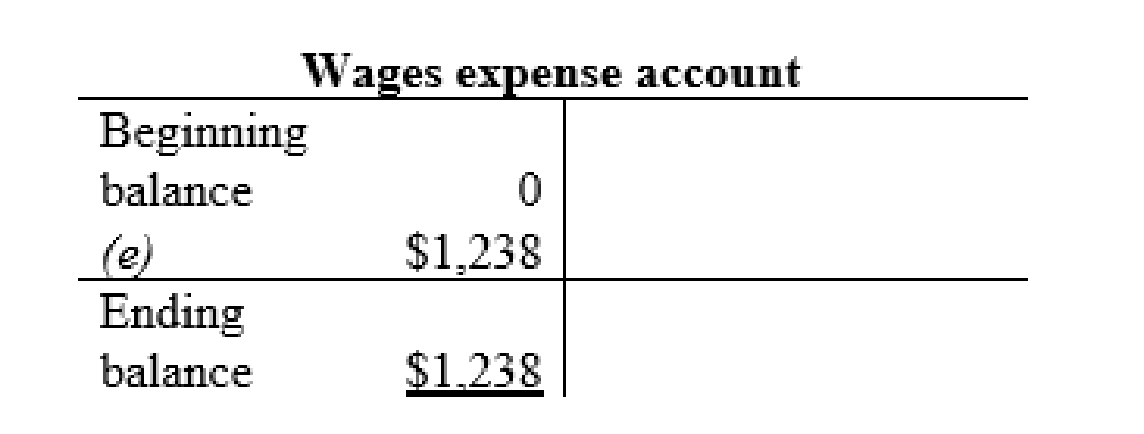
Thus, the t-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Prepare an income statement for the month of January.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement:
| Corporation EM | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the month ended 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Sales revenue | 39,780 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Cost of sales | 5,984 | |
| Wage expense | 1,238 | |
| Utilities expense | 3 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 7,225 | |
| Operating income | 32,555 | |
| Less: Other expense | ||
| Interest expense | 1 | |
| Net Income | $32,554 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company E is $32,554.
4.
Compute the net profit margin ratio and based on the result give suggestion to the company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the net profit margin ratio:
Hence, the net profit margin ratio is 0.82.
- By evaluating the net profit margin ratio, the company has earned $0.82 in net income for every $ 1 in the sales revenue.
- To know the better result about the company, net profit margin ratio should be calculated to identify the way in which the management is generating its revenue and controlling the various expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING ETEXT CARD
- Assets Martinez Company Comparative Balance Sheets December 31 2025 2024 Cash $91,000 $52,000 Accounts receivable 52,000 36,400 Inventory 72,800 52,000 Property, plant, and equipment 156,000 202,800 Accumulated depreciation Total (83,200) [62,400) $288,600 $290,800 Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity Accounts payable $49,400 $ 39,000 Income taxes payable 18,200 20,800 Bonds payable 44,200 85,800 Common stock 46,900 36,400 Retained earnings 130,000 98,800 Total $288,600 $280,800 Martinez Company Income Statement For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Sales revenue $629,200 Cost of goods sold 455,000 Gross profit 174,200 Selling expenses $46,800 Administrative expenses 15,600 62,400 Income from operations 111,800 Interest expense 7,800 Income before income taxes 104,000 Income tax expense 20,800 Net income $83,200 Additional data: 1. Depreciation expense was $45,500. 2. Dividends declared and paid were $52,000. 3. During the year, equipment was sold for $22,100 cash. This equipment…arrow_forwardagree or disagree with post The Stockholders' Equity section of a corporate balance sheet fundamentally differs from that of a single-owner business due to the inherent structure of a corporation versus a sole proprietorship. In a single-owner business, you'll usually see a single "Owner's Equity" account, which reflects the owner's investment, withdrawals, and accumulated profits or losses. Conversely, a corporation's Stockholders' Equity is more intricate, reflecting the contributions of multiple owners (stockholders) and the legal framework governing corporate capital. It's divided into contributed capital, which includes common and preferred stock, and retained earnings, which represents accumulated profits not yet distributed as dividends. Additionally, corporations may have accounts like "Additional Paid-in Capital" to capture amounts received above the par value of stock, and "Treasury Stock" to account for shares repurchased by the company. This detailed breakdown highlights…arrow_forwardEast Georgia Community Hospital enters into a contract to provide $15,000 of elective medical care to a patient. After a review of the patient's ability and intent to pay, the hospital does not expect to collect the full contract price of $15,000. However, the hospital occasionally performs "discounted" procedures to members of the community to enhance its standing in the local area. While the hospital invoiced the customer for the full amount of the services, it only expects to collect $10,000. What amount of revenue should the hospital recognize?arrow_forward
- On January 1, Flint Corporation had 62,900 shares of no-par common stock issued and outstanding. The stock has a stated value of $4 per share. During the year, the following transactions occurred. Apr. 1 Issued 18,000 additional shares of common stock for $13 per share. June 15 Declared a cash dividend of $1.95 per share to stockholders of record on June 30. July 10 Paid the $1.95 cash dividend. Dec. 1 Issued 8,000 additional shares of common stock for $13 per share. Dec. 15 Declared a cash dividend on outstanding shares of $2.25 per share to stockholders of record on December 31. (a) Prepare the entries on each of the three dates that involved dividends. (Record journal entries in the order presented in the problem. Credit account titles are automatically indented when amount is entered. Do not indent manually. If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter O for the amount in the relevant debit OR credit box. Entering zero in ALL boxes will result in the…arrow_forwardFinancial accounting Problemarrow_forwardBlossom Corporation issues 72000 shares of $50 par value preferred stock for cash at $60 per share. The entry to record the transaction will consist of a debit to Cash for $4320000 and a credit or credits to ○ Preferred Stock for $4320000 ○ Preferred Stock for $3600000 and Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par-Preferred Stock for $720000 ○ Preferred Stock for $3600000 and Retained Earnings for $720000 ○ Paid-in Capital from Preferred Stock for $4320000arrow_forward
- The current sections of Kingbird Inc's balance sheets at December 31, 2024 and 2025, are presented here. Kingbird's net income for 2025 was $107,100. Depreciation expense was $18,900. 2025 2024 Current assets Cash $73,500 $69,300 Accounts receivable 56,000 62,300 Inventory 117,600 120,400 Prepaid expenses 18,900 15,400 Total current assets $266,000 $267,400 Current liabilities Accrued expenses payable $10,500 $3,500 Accounts payable 59,500 64,400 Total current liabilities $70,000 $67,900 Prepare the operating activities section of the company's statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2025, using the indirect method. (Show amounts that decrease cash flow with either a-sign eg.-15,000 or in parenthesis e.g. (15,000).) KINGBIRD INC. Statement of Cash Flows (Partial) - Indirect Method For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Cash Flows from Operating Activities Net Income Adjustments to reconcile net income to Depreciation Expense 18900 6300 Decrease In Accounts Receivable…arrow_forwardWrong answer will get unhelpful ratearrow_forwardMetlock Lawn Service Company reported a net loss of $15300 for the year ended December 31, 2025. During the year, accounts receivable decreased $25000, inventory increased $20000, accounts payable increased by $30600, and depreciation expense of $26400 was recorded. During 2025, operating activities provided net cash of $77000 O provided net cash of $46700. O used net cash of $46700. ○ used net cash of $9200.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





