
Balance each of the following equations, and classify them as precipitation, acid-base, gas-forming, or
(a) CuCl2 + H2S →CuS + HCl
(b) H3PO4 + KOH → H2O + K3PO4
(c) Ca +HBr → H2 + CaBr2
(d) MgC12 + NaOH → Mg(OH)2 + NaCl
(a)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of reactant and product are shown below.
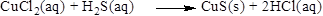
Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below,
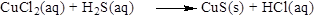
The given compound is copper chloride and hydrogen sulfide which is soluble in water. In this reaction copper chloride reaction with hydrogen sulfide to give copper sulfide and hydrochloric acidater. Most of the salts of
Therefore the given reaction is precipitation reaction
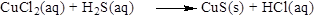
Balance the equation,
Balance the hydrogen atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are two hydrogen atoms in the left side and one hydrogen atoms in the right side. Therefore two molecule of hydrochloric acid is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.
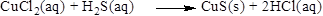
(b)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is acid - base reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is acid - base reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below

The given compound is potassium hydroxide and Phosphoric acid. In this reaction potassium hydroxide reaction with Phosphoric acid to give Tripotassium phosphate and formation of water is also the product.

Balance the equation,
Balance the potassium atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are three potassium atoms in the right side and one potassium atoms in the left side. Therefore three molecule of potassium hydroxide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

Balance the hydrogen atom in the given equation. There are six hydrogen atoms in the left side and two hydrogen atoms in the right side. Therefore three molecule of water is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

(c)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The given reaction is oxidation and reduction reaction and the state of reactant and product is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is oxidation and reduction reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below

The given compound is calcium and hydrogen bromide. In this reaction hydrogen bromide reaction with calcium to give calcium bromide and hydrogen gas. Here the oxidation state of calcium is zero in the reactant and

Balance the equation,
Balance the hydrogen atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are two hydrogen atoms in the right side and one hydrogen atoms in the left side. Therefore two molecule of hydrogen bromide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

(d)
Interpretation:
- The given reaction has to be classified as precipitation or acid-base or gas forming reaction and the reaction has to be balanced.
- State of the product and reactant should be shown.
Concept introduction:
Precipitation reaction: The formation of the product is insoluble when the ions combine in the solution is called precipitation reaction.
Acid - base reaction: Formation of the salt from the cation from the base and anion from the acid and formation of water is also the product.
Gas forming reaction: The reaction of acid and metal carbonates which produce carbonic acid. The carbonic acid decomposes which gives water and carbon dioxide.
Oxidation - reduction reaction: The electrons are transferred to one to other is called oxidation reduction reaction.
Most of the ionic compounds are soluble in water, very few of the ionic compounds are sparingly soluble, and some of the ionic compounds are insoluble in water. When it is soluble in water ions gets separated in the solution.
Soluble compounds in water
Almost all the salts of
Almost all the salts of
Salts of F- are soluble. But some of the fluoride salt of
Salts of
Insoluble compounds in water:
Most of the salts of
Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
Answer to Problem 63PS
The given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below.

Explanation of Solution
The balancing of the reaction and the type of the reaction is shown below, the given reaction is precipitation reaction and the state of the reaction is shown below

The given compound is magnesium chloride and sodium hydroxide. In this reaction magnesium chloride reaction with sodium hydroxide to give magnesium hydroxide and sodiumchloride. Most of the metal hydroxides and oxides are insoluble in water bit some of the alkali metal hydroxides,
the given reaction is precipitation reaction.

Balance the equation,
Balance the chlorine atom in the given equation, when balancing the equation, we should not alter the subscripts and we can change coefficients. There are two chlorine atoms in the left side and one chlorine atoms in the right side. Therefore two molecule of sodium chloride is added to right side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

Balance the oxygen atom in the given equation, there are two oxygen atoms in the right side and one oxygen atoms in the left side. Therefore two molecule of sodium hydroxide is added to left side of reaction. Therefore the balanced equation is given below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Owlv2 With Ebook, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card For Kotz/treichel/townsend/treichel's Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, 10th
- What is surface excess according to the Gibbs model?arrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forward
- a. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forwardGiven the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forwardAt 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning





