
Concept explainers
a.
Analyze the effects that each of the given transactions will have on the following six components of the company’s financial statements for the month of August.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and
Analyze the effects that each of the given transactions will have on the following six components of the company’s financial statements for the month of August as follows:
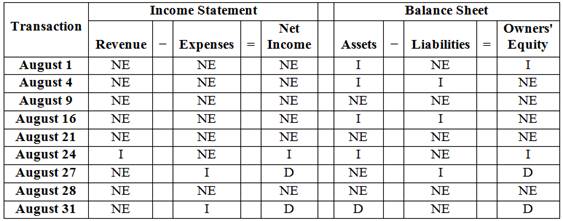
Figure (1)
b.
Prepare journal entries for each transaction.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Prepare journal entries for each transaction as follows:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post ref. |
Debit (in $) | Credit (in $) |
| August 1, 2015 | Cash | 280,000 | ||
| Capital stock | 280,000 | |||
| (To record the issue of the 1,000 shares of capital stock) | ||||
| August 4, 2015 | Land | 60,000 | ||
| Office Building | 340,000 | |||
| Cash | 80,000 | |||
| Notes Payable | 320,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of land and office building) | ||||
| August 9, 2015 | Medical instruments | 75,000 | ||
| Cash | 75,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of computer systems) | ||||
| August 16, 2015 | Office fixtures and equipment | 25,000 | ||
| Cash | 10,000 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 15,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of office fixtures and equipment) | ||||
| August 21, 2015 | Office supplies | 4,200 | ||
| Cash | 4,200 | |||
| (To record the purchase of office supplies purchased on account) | ||||
| August 24, 2015 | Cash | 1,000 | ||
| 12,000 | ||||
| Service revenue | 13,000 | |||
| (To record the service revenue earned) | ||||
| August 27, 2015 | Advertising expense | 450 | ||
| Accounts payable | 450 | |||
| (To record the advertising expense incurred) | ||||
| August 28, 2015 | Cash | 500 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 500 | |||
| (To record the cash collected from accounts receivable) | ||||
| August 31, 2015 | Salary expense | 2,200 | ||
| Cash | 2,200 | |||
| (To record the salary expense paid) |
Table (1)
c.
Post each transaction to the appropriate ledger accounts.
c.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
The condensed form of a ledger is referred to as T-account. The left-hand side of this account is known as debit, and the right hand side is known as credit.
Post each transaction to the appropriate ledger accounts as follows:
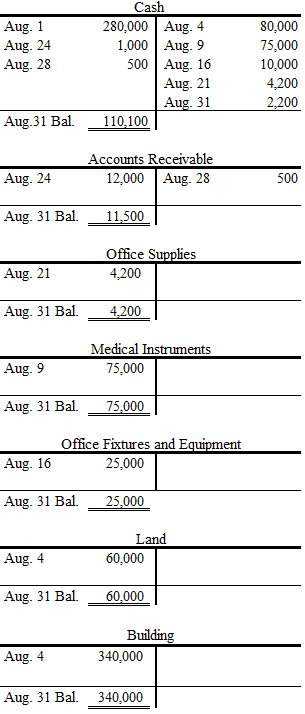
Figure (2)
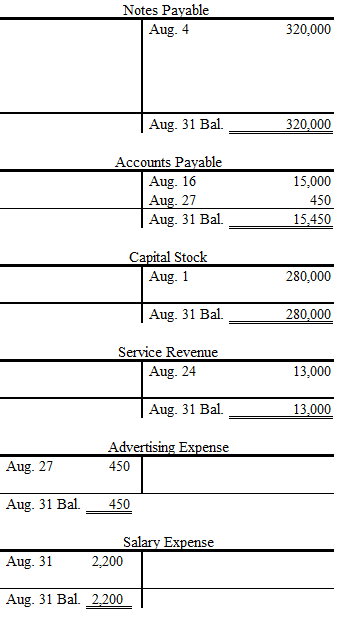
Figure (3)
d.
Prepare a
d.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts balances presented in a tabular form with two column, debit and credit. It checks the mathematical accuracy of the
Prepare a trial balance dated August 31, 2015 as follows:
| Dental Clinic | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| August 31, 2015 | ||
| Cash | $110,100 | |
| Accounts receivable | 11,500 | |
| Office supplies | 4,200 | |
| Medical instruments | 75,000 | |
| Office fixtures and equipment | 25,000 | |
| Land | 60,000 | |
| Building | 340,000 | |
| Notes payable | $320,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 15,450 | |
| Capital stock | 280,000 | |
| | 0 | |
| Veterinary service revenue | 13,000 | |
| Advertising expense | 450 | |
| Salary expense | 2,200 | |
| $628,450 | $628,450 | |
Table (2)
e.
Compute total assets, total liabilities, and owners’ equity and identify whether the month August appeared to be a profitable month.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Assets:
These are the resources owned and controlled by business and used to produce benefits for the company. Assets are classified on the balance sheet as current assets, non-current assets, property, plant, and equipment, and intangible assets.
Liabilities:
The claims creditors have over assets or resources of a company are referred to as liabilities. These are the debt obligations owed by company to creditors. Liabilities are classified on the balance sheet as current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Owners’ equity:
Owner’s equity refers to the right the owner possesses over the resources of the business. Revenues and the expenses are the components of the owner’s equity.
Net income:
The bottom line of income statement which is the result of excess of earnings from operations (revenues) over the costs incurred for earning revenues (expenses) is referred to as net income.
Compute total assets, total liabilities, and owners’ equity as follows:
| Total Assets: | ||
| Cash | $110,100 | |
| Accounts receivable | 11,500 | |
| Office supplies | 4,200 | |
| Medical instruments | 75,000 | |
| Office fixtures and equipment | 25,000 | |
| Land | 60,000 | |
| Building | 340,000 | |
| Total assets | $625,800 | |
| Total Liabilities: | ||
| Notes payable | $320,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 15,450 | |
| Total liabilities | $335,450 | |
| Total Owners' Equity: | ||
| Total assets − Total liabilities | $290,350 |
Table (3)
Identify whether the month August appeared to be a profitable month as follows:
| Amount (In $) | Amount (In $) | |
| Service revenue | 13,000 | |
| Less: Advertising expense | 450 | |
| Salary expense | 2,200 | 2,650 |
| Net income (Profit) | $10,350 |
Table (4)
Hence, the month August appeared to be a profitable month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting With Connect Plus Access Code: The Basis For Business Decisions
- Nicole organized a new corporation. The corporation began business on April 1 of year 1. She made the following expenditures associated with getting the corporation started: Expense Date Amount Attorney fees for articles of incorporation February 10 $ 40,500 Stock issuance costs March 1-March 30 wages March 1-March 30 rent April 1-May 30 wages Note: Leave no answer blank. Enter zero if applicable. March 30 6,550 March 30 2,850 April 1 May 30 24,000 16,375 b. What amount of the start-up costs and organizational expenditures may the corporation immediately expense in year 1 (excluding the portion of the expenditures that are amortized over 180 months)? Start-up costs expensed Organizational expenditures expensedarrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardAfter several profitable years running her business, Ingrid decided to acquire the assets of a small competing business. On May 1 of year 1, Ingrid acquired the competing business for $354,000. Ingrid allocated $59,000 of the purchase price to goodwill. Ingrid's business reports its taxable income on a calendar-year basis. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest whole dollar amount. a. How much amortization expense on the goodwill can Ingrid deduct in year 1, year 2, and year 3? Year 1 Deductible Amortization Expense Year 2 Year 3arrow_forward
- Chapter 19 Homework 15 0.87 points eBook Saved Exercise 19-20 (Algo) Contribution margin ratio by sales territory LO A1 Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work Big Bikes manufactures and sells mountain bikes in two sales territories, West Coast and East Coast. Information for the year follows. The company sold 550 bikes in each territory. Per unit Sales price Variable cost of goods sold West Coast $ 1,500 East Coast $ 1,440 830 70 830 Variable selling and administrative expenses 160 Ask a. Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. b. Compute contribution margin ratio for each sales territory. Which sales territory has the better contribution margin ratio? Print Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. References Required A Required B Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. Sales Variable expenses Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling and administrative expenses Contribution margin West Coast East Coast…arrow_forwardChapter 19 Homework 15 0.87 points eBook Saved Exercise 19-20 (Algo) Contribution margin ratio by sales territory LO A1 Help Save & Exit Submit Check my work Big Bikes manufactures and sells mountain bikes in two sales territories, West Coast and East Coast. Information for the year follows. The company sold 550 bikes in each territory. Per unit Sales price Variable cost of goods sold West Coast $ 1,500 East Coast $ 1,440 830 70 830 Variable selling and administrative expenses 160 Ask a. Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. b. Compute contribution margin ratio for each sales territory. Which sales territory has the better contribution margin ratio? Print Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. References Required A Required B Compute contribution margin (in dollars) for each sales territory. Sales Variable expenses Variable cost of goods sold Variable selling and administrative expenses Contribution margin West Coast East Coast…arrow_forwardDetermine the gross margin of this financial accounting questionarrow_forward
- What are fixed assets projected to be given this information for this accounting question?arrow_forwardSolve this accounting problemarrow_forwardA machine costing $77,500 with a 5-year life and $4,700 residual value was purchased January 2. Compute depreciation for each of the 5 years, using the double-declining-balance method. Year1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





