
Concept explainers
Calculate the missing amounts and prepare the T-accounts.
Explanation of Solution
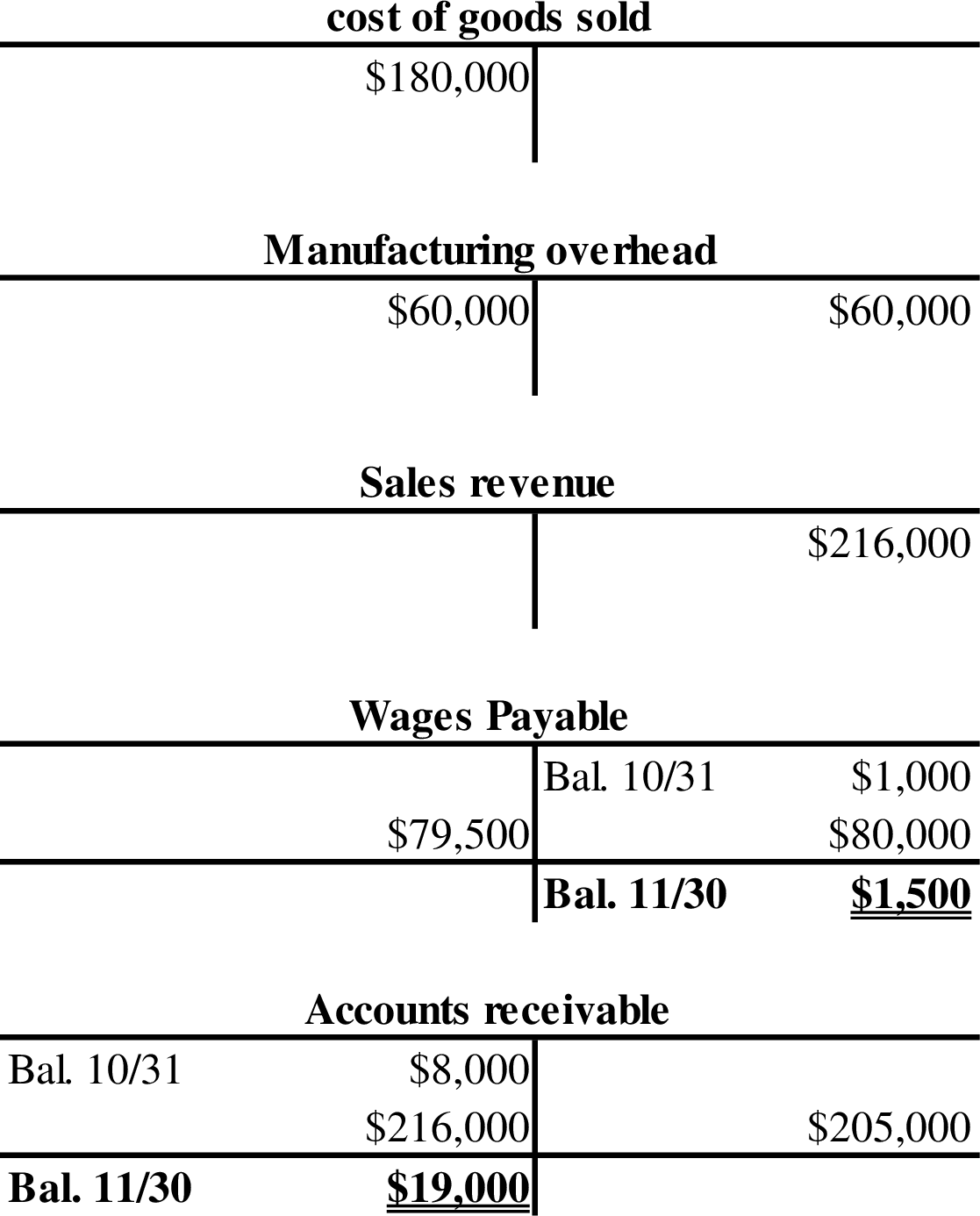
- 1. Calculate the sales revenue for November.
Thus, the sales revenue for November is $216,000.
- 2. Calculate the ending balance of
accounts receivable .
Thus, the ending balance in accounts receivable is $19,000.
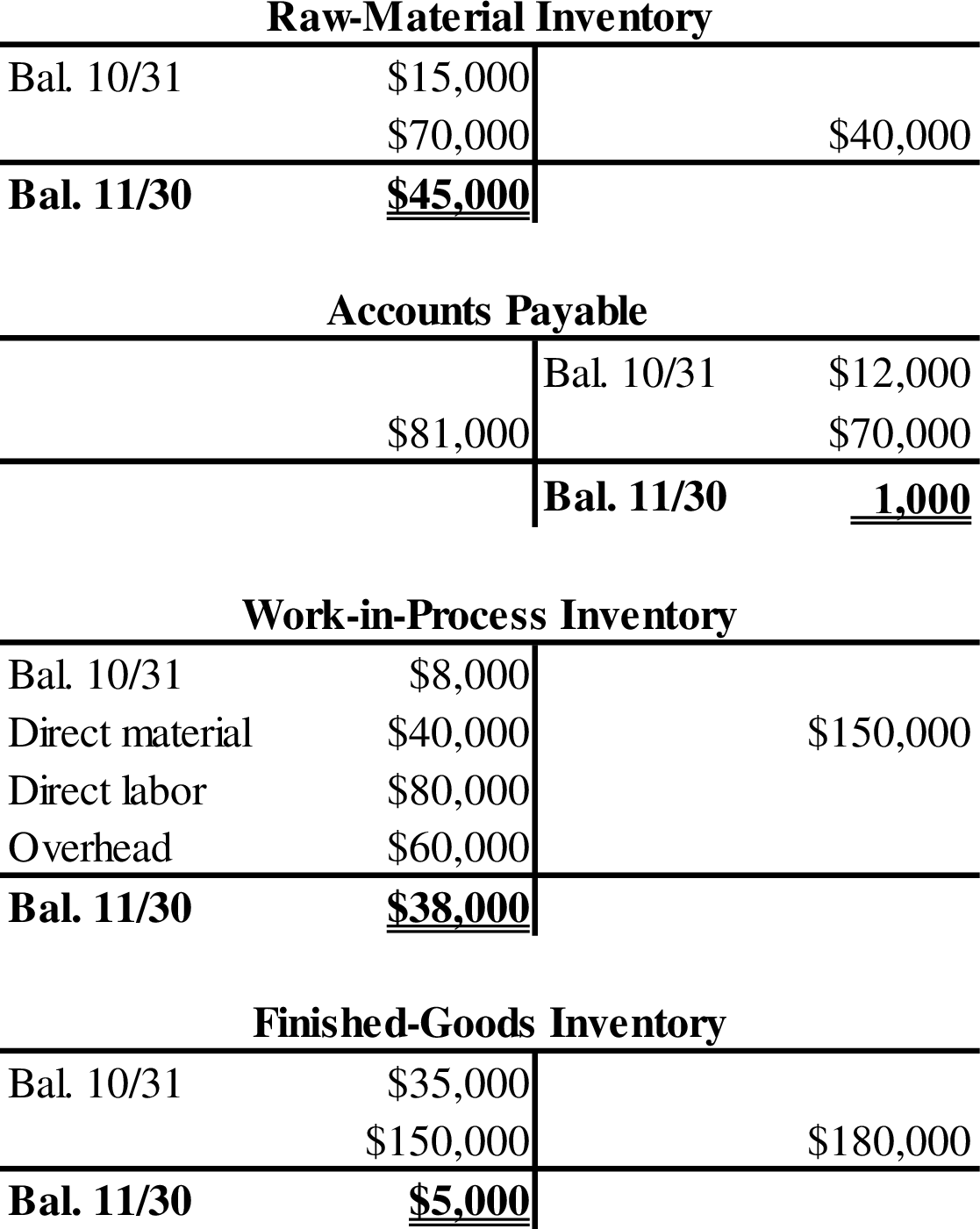
- 3. Calculate the cost of raw materials purchased during November.
Thus, the cost of raw materials purchased during November is $70,000.
- 4. Calculate the ending balance in the work-in-process inventory.
Step 1: Calculate the budgeted direct-labor hours.
Step 2: Calculate the predetermined
Step 3: Calculate the ending balance in the work-in-process inventory.
Thus, the ending balance in the work-in-process inventory is $38,000.
- 5. Calculate the amount of direct labor added to work in process during November.
Thus, the amount of direct labor added to work in process during November is $80,000.
- 6. Calculate the amount of applied overhead for November.
Step 1: Calculate the direct-labor hours.
Step 2: Calculate the amount of applied overhead for November.
Thus, the applied overhead for November is $60,000.
- 7. Calculate the cost of goods completed during November.
Thus, the cost of goods completed during November is $150,000.
- 8. Calculate the amount of raw materials used during November.
Thus, the amount of raw materials used during November is $40,000.
- 9. Calculate the amount of October 31 balance in raw-material inventory.
Thus, the amount of October 31 balances in raw-material inventory is $15,000.
- 10. Calculate the amount of overapplied or underapplied for November.
Thus, there is no underapplied or overapplied overhead for the month November.
Prepare the T-accounts.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Access Card for Managerial Accounting: Creating Value in a Dynamic Business Environment (NEW!!)
- general accountingarrow_forwardBright Electronics has a Computer Division with the following financial details: • Sales: $250,000 • Cost of Goods Sold: $120,000 Operating Expenses: $50,000 Average Invested Assets: $1,200,000 ⚫ Hurdle Rate: 12%arrow_forwardA business has a dividend payout ratio of 0.6, an expected growth rate of 4% per year, and investors require a 9% return on their investment. What should be the price-earnings ratio? a. 10x b. 12x c. 15x d. 6xarrow_forward
- Sunland Enterprises uses a computer to handle its sales invoices. Lately, business has been so good that it takes an extra 3 hours per night, plus every third Saturday, to keep up with the volume of sales invoices. Management is considering updating its computer with a faster model that would eliminate all of the overtime processing. Current Machine New Machine Original purchase cost $15,200 $24,800 Accumulated depreciation $6,700 Estimated annual operating costs $24,700 $19,600 Remaining useful life 5 years 5 years If sold now, the current machine would have a salvage value of $10,100. If operated for the remainder of its useful life, the current machine would have zero salvage value. The new machine is expected to have zero salvage value after 5 years. Prepare an incremental analysis to determine whether the current machine should be replaced. (In the first two columns, enter costs and expenses as positive amounts, and any amounts received as negative amounts. In the third column,…arrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forwardTamarisk Motor Company manufactures automobiles. During September 2025, the company purchased 6,000 head lamps at a cost of $10 per lamp. 40 of these lamps were used to replace the head lamps in autos used by traveling sales staff, and 5,540 lamps were put in autos manufactured during the month. Of the autos put into production during September 2025, 85% were completed and transferred to the company's storage lot. Of the cars completed during the month, 70% were sold by September 30. (a) Determine the cost of head lamps that would appear in each of the following accounts at September 30, 2025. Raw Materials Work in Process Finished Goods A 4200 $ 8310 Cost of Goods Sold +A A Selling Expenses $ 400arrow_forward
- Determine the predetermined factory overhead rate for these general accounting questionarrow_forwardIvanhoe, Inc. has recently started the manufacture of Tri-Robo, a three-wheeled robot that can scan a home for fires and gas leaks and then transmit this information to a smartphone. The cost structure to manufacture 20,400 Tri-Robos is as follows. Cost Direct materials ($51 per robot) $1,040,400 Direct labor ($39 per robot) 795,600 Variable overhead ($7 per robot) 142,800 Allocated fixed overhead ($29 per robot) 591,600 $2,570,400 Total Ivanhoe is approached by Tienh Inc., which offers to make Tri-Robo for $116 per unit or $2,366,400. Following are independent assumptions. Assume that $405,000 of the fixed overhead cost can be avoided. (Enter negative amounts using either a negative sign preceding the number e.g. -45 or parentheses e.g. (45).) Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Purchase price +A Total annual cost $ Make +A $ Buy +A Using incremental analysis, determine whether Ivanhoe should accept this offer. The offer Net Income Increase (Decrease)arrow_forwardPlease need answer the general accounting questionarrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
